机器学习 --- 数据集
机器学习 — 数据集
文章目录
- 机器学习 --- 数据集
- 一,sklearn数据集介绍
- 二,sklearn现实世界数据集介绍
- 三,sklearn加载数据集
- 3.1 加载鸢尾花数据集
- 3.2 加载糖尿病数据集
- 3.3 加载葡萄酒数据集
- 四,sklearn获取现实世界数据集
- 五,本地csv数据
- 六,数据集的划分
- 6.1复习不定长参数
- 6.2 数据集划分示例
- 6.2.1列表数据集划分
- 6.2.2 dataframe数据集划分
- 6.2.3 字典数据集划分
- 6.2.4 鸢尾花数据集划分
- 6.2.5 现实世界数据集划分
一,sklearn数据集介绍
数据量小,数据在sklearn库的本地,只要安装了sklearn,不用上网就可以获取

二,sklearn现实世界数据集介绍
数据量大,数据只能通过网络获取

三,sklearn加载数据集
3.1 加载鸢尾花数据集
- 鸢尾花数据
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
iris = load_iris()#加载鸢尾花数据集
# print(iris)
data=iris.data#鸢尾花的特征数据集(x,data,特征)
print(data[:5])
print(type(data))
print(data.shape)
print(data.dtype)
print(iris.feature_names)#特征的名字
target=iris.target#鸢尾花的标签数据集(y,target,标签,labels,目标)
print(target)
print(type(target))
print(target.shape)
print(iris.target_names)#标签名称: 'setosa-山鸢尾' 'versicolor-变色鸢尾' 'virginica-维基利亚鸢尾'print(iris.DESCR)#数据集的描述
print(iris.filename)#数据集的文件名
[[5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2][4.9 3. 1.4 0.2][4.7 3.2 1.3 0.2][4.6 3.1 1.5 0.2][5. 3.6 1.4 0.2]]
<class 'numpy.ndarray'>
(150, 4)
float64
['sepal length (cm)', 'sepal width (cm)', 'petal length (cm)', 'petal width (cm)']
[0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 00 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 11 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 22 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 22 2]
<class 'numpy.ndarray'>
(150,)
['setosa' 'versicolor' 'virginica']
- 使用panda把特征和目标连接起来
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
iris = load_iris()
feature = iris.data
target = iris.target
target.shape=(len(target), 1)
data = np.hstack([feature, target])
cols = iris.feature_names
cols.append("target")
data_frame=pd.DataFrame(data,columns=cols)
data_frame

3.2 加载糖尿病数据集
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import load_diabetes
iris = load_diabetes()
feature = iris.data
target = iris.target
target.shape=(len(target), 1)
data = np.hstack([feature, target])
cols = iris.feature_names
cols.append("target")
data_frame=pd.DataFrame(data,columns=cols)
data_frame

3.3 加载葡萄酒数据集
from sklearn.datasets import load_wine
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
wine = load_wine()
feature = wine.data
target = wine.target
target = target.reshape(-1, 1)
data = np.hstack([feature, target])
cols = wine.feature_names
cols.append("target")
data_frame=pd.DataFrame(data,columns=cols)
data_frame

四,sklearn获取现实世界数据集
所有现实世界数据,通过网络才能下载后,默认保存的目录可以使用下面api获取。实际上就是保存到home目录
from sklearn import datasets
datasets.get_data_home() #查看数据集默认存放的位置
- 示例:获取20分类新闻数据
(1)使用函数: sklearn.datasets.fetch_20newsgroups(data_home,subset)
# 加载联网下载的数据集
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_20newsgroups
from sklearn import datasets
# path=datasets.get_data_home()#查看数据集默认的下载路径
# print(path)#C:\Users\JYL\scikit_learn_datanews=fetch_20newsgroups(data_home="./src",subset="train")#联网加载新闻数据集
print(len(news.data))
print(news.data[0:4])
print(news.target)
print(news.target_names)


五,本地csv数据
- 创建csv文件
方式1:打开计事本,写出如下数据,数据之间使用英文下的逗号, 保存文件后把后缀名改为csv
csv文件可以使用excel打开
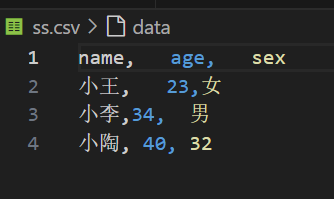
- pandas加载csv
# 加载自己的数据
import pandas as pd
data=pd.read_csv("./src/ss.csv")
data=data.to_numpy()
print(data)
[['小王' 23 '女']['小李' 34 ' 男']['小陶' 40 ' 32']]
六,数据集的划分
6.1复习不定长参数
# 不定长参数
# 一个"*""把多个参数传为元组
# 两个"**"把一个参数传为字典
def test(*args, **kwargs):print(args)print(kwargs)test(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, name="zhangsan", age=18, sex="male")
(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10)
{'name': 'zhangsan', 'age': 18, 'sex': 'male'}
6.2 数据集划分示例
6.2.1列表数据集划分
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split#数据集的划分
x =[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12]
x_train,x_text=train_test_split(x,test_size=0.8,shuffle=True,random_state=42)
# x_train,x_text=train_test_split(x,test_size=10,shuffle=True,random_state=42)
# x_train,x_text=train_test_split(x,train_size=0.2,shuffle=True,random_state=42)
# print(x_train,x_text)# 两个数据容器按照相同的下标进行索引
x =[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
y =[10,20,30,40,50,60,70,80,90,100]
x_train,x_text,y_train,y_text=train_test_split(x,y)
print(x_train,x_text,y_train,y_text)
[5, 2, 4, 9, 8, 1, 10] [6, 7, 3] [50, 20, 40, 90, 80, 10, 100] [60, 70, 30]
6.2.2 dataframe数据集划分
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
data1 = np.arange(1, 16, 1)
data1.shape=(5,3)
data1 = pd.DataFrame(data1, index=[1,2,3,4,5], columns=["one","two","three"])
print(data1)a, b = train_test_split(data1, test_size=0.4, random_state=22)
print("\n", a)
print("\n", b)
one two three
1 1 2 3
2 4 5 6
3 7 8 9
4 10 11 12
5 13 14 15one two three
4 10 11 12
1 1 2 3
5 13 14 15one two three
2 4 5 6
3 7 8 9
6.2.3 字典数据集划分
from sklearn.feature_extraction import DictVectorizer# 修改后的字典数据
data = [{'city': '广州', 'age': 28, 'temperature': 25},{'city': '深圳', 'age': 35, 'temperature': 30},{'city': '杭州', 'age': 40, 'temperature': 28},{'city': '南京', 'age': 25, 'temperature': 22},{'city': '广州', 'age': 32, 'temperature': 27}]# 使用DictVectorizer进行特征提取
transfer = DictVectorizer(sparse=True)
data_new = transfer.fit_transform(data)# 打印稀疏矩阵
print("data_new:\n", data_new)# 转换为密集矩阵并打印
x = data_new.toarray()
print(type(x))
print(x)
data_new:(0, 0) 28.0(0, 2) 1.0(0, 5) 25.0(1, 0) 35.0(1, 4) 1.0(1, 5) 30.0(2, 0) 40.0(2, 3) 1.0(2, 5) 28.0(3, 0) 25.0(3, 1) 1.0(3, 5) 22.0(4, 0) 32.0(4, 2) 1.0(4, 5) 27.0
<class 'numpy.ndarray'>
[[28. 0. 1. 0. 0. 25.][35. 0. 0. 0. 1. 30.][40. 0. 0. 1. 0. 28.][25. 1. 0. 0. 0. 22.][32. 0. 1. 0. 0. 27.]]
6.2.4 鸢尾花数据集划分
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
iris = load_iris()
x = iris.data
y = iris.target
#划分
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.2,shuffle=True,random_state=42)
print(x_train.shape,y_train.shape)
print(x_test.shape,y_test.shape)
print(y_test)
(120, 4) (120,)
(30, 4) (30,)
[1 0 2 1 1 0 1 2 1 1 2 0 0 0 0 1 2 1 1 2 0 2 0 2 2 2 2 2 0 0]
6.2.5 现实世界数据集划分
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_california_housing
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import numpy as np# 加载加利福尼亚住房数据集
housing = fetch_california_housing()# 划分训练集和测试集
list = train_test_split(housing.data, housing.target, test_size=0.2, random_state=22)# 解包返回值
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = list# 打印结果
print("训练集特征数量:", len(x_train))
print("测试集特征数量:", len(x_test))
print("训练集目标形状:", y_train.shape)
print("测试集目标形状:", y_test.shape)
训练集特征数量: 16512
测试集特征数量: 4128
训练集目标形状: (16512,)
测试集目标形状: (4128,)
