SpringBoot后端开发知识点总结(持续更新)
目录
- 1. 常用易混淆注解解释
- 1.1 @Resource和@Autowired注解的区别
- 1.2 @PathVariable和@RequestParam注解的区别
- 2. Mybatis-Plus高级特性
- 2.1 强大的通用CRUD接口
- 2.2 代码生成器
- 3. IDEA实用快捷键
- 4. 前后端联调关键点
- 4.1 代码示例
- 4.2 联调要点
- 4.3 调试技巧
1. 常用易混淆注解解释
1.1 @Resource和@Autowired注解的区别
在Spring框架中,@Resource和@Autowired都是用于依赖注入的注解,但有以下关键区别:
| 特性 | @Autowired | @Resource |
|---|---|---|
| 来源 | Spring框架 | Java标准(JSR-250) |
| 注入方式 | 默认按类型(byType) | 默认按名称(byName) |
| 必需性 | 默认必须(可设required=false) | 非必须 |
| 指定名称 | 需配合@Qualifier | 直接使用name属性 |
| 构造函数注入 | 支持 | 不支持 |
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import javax.annotation.Resource;// 服务接口
interface PaymentService {void pay();
}// 实现类1
@Service("wechatPay")
class WechatPay implements PaymentService {public void pay() {System.out.println("微信支付");}
}// 实现类2
@Service("aliPay")
class AliPay implements PaymentService {public void pay() {System.out.println("支付宝支付");}
}// 客户端类
@Service
class ShoppingCart {/* 最常用场景对比 */// 1. 按类型注入(默认方式)@Autowired // Spring方式:存在多个实现时会报错private PaymentService typeInjectedService;@Resource // Java标准方式:会退化成按名称注入(变量名作为bean名称)private PaymentService resourceInjectedService;// 2. 按名称注入(解决多个实现问题)@Autowired@Qualifier("wechatPay") // Spring方式:需要两个注解private PaymentService qualifiedService;@Resource(name = "aliPay") // Java标准方式:一个注解搞定private PaymentService namedResourceService;// 3. 构造函数注入(推荐方式)private final PaymentService constructorInjected;@Autowired // 唯一支持构造器注入的方式(Spring 4.3+可省略)public ShoppingCart(PaymentService constructorInjected) {this.constructorInjected = constructorInjected;}/* 实际使用示例 */public void checkout(int paymentType) {switch(paymentType) {case 1:qualifiedService.pay(); // 明确使用微信支付break;case 2:namedResourceService.pay(); // 明确使用支付宝break;default:constructorInjected.pay(); // 使用默认注入的实现}}
}
1.2 @PathVariable和@RequestParam注解的区别
这两个注解都用于从HTTP请求中获取参数,但使用场景不同:
| 特性 | @PathVariable | @RequestParam |
|---|---|---|
| 参数位置 | URL路径部分 | URL查询字符串 |
| 示例URL | /user/{id} | /user?id=123 |
| 是否必需 | 默认必需 | 可选(可设required=false) |
| 多值处理 | 不支持 | 支持(数组/集合) |
// @PathVariable 示例
@GetMapping("/users/{userId}")
public User getUser(@PathVariable String userId) {// ...
}// @RequestParam 示例
@GetMapping("/users")
public User getUser(@RequestParam(required = false) String name) {// ...
}
2. Mybatis-Plus高级特性
Mybatis-Plus在Mybatis基础上提供了诸多便利功能:
2.1 强大的通用CRUD接口
内置通用Mapper,无需编写简单SQL
| 分类 | 方法示例 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 插入 | insert(T entity) | 插入一条记录 |
| 删除 | deleteById(Serializable id) | 根据ID删除 |
deleteBatchIds() | 批量删除(根据ID集合) | |
| 更新 | updateById(T entity) | 根据ID更新 |
update(entity, wrapper) | 根据条件更新 | |
| 查询 | selectById() | 根据ID查询 |
selectOne() | 查询一条记录(结果多条会报错) | |
selectList() | 查询列表 | |
selectCount() | 查询总数 | |
| 分页 | selectPage() | 分页查询 |
2.2 代码生成器
一键生成Entity、Mapper、Service等

3. IDEA实用快捷键
| 功能 | Windows快捷键 |
|---|---|
| 全局搜索 | Double Shift |
| 当前文件查找 | Ctrl+F |
| 在所有文件/模块/文件夹查找 | Ctrl+Alt+F |
| 代码格式化 | Ctrl+Alt+L |
| 重写方法 | Ctrl+O |
| 重写/实现方法 | Ctrl+I |
| AI智能补全 | Tab |
| 输入表达式后使用此后缀快速生成变量 | .var |
4. 前后端联调关键点
4.1 代码示例
// 正确示例 - 参数名与后端一致
methods: {deleteInterviewer(interviewerId) {...}).then(() => {var params = {interviewerId: interviewerId}
deleteInterviewer: function(params) {return instance({url: '/interviewer/delete',method: 'delete',params: params})
}
后端接口:
@DeleteMapping("/delete")
public Result delete(@RequestParam String interviewerId) {// 参数名必须与前端一致service.delete(interviewerId);return Result.ok();
}
4.2 联调要点
- 命名一致性:前后端参数名严格一致
- 请求方式匹配:
- GET - 查询
- POST - 创建
- PUT - 更新
- DELETE - 删除
- 数据格式:
- 明确约定JSON字段命名风格(驼峰/下划线)
- 日期格式统一(如yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss)
4.3 调试技巧
使用Postman测试接口
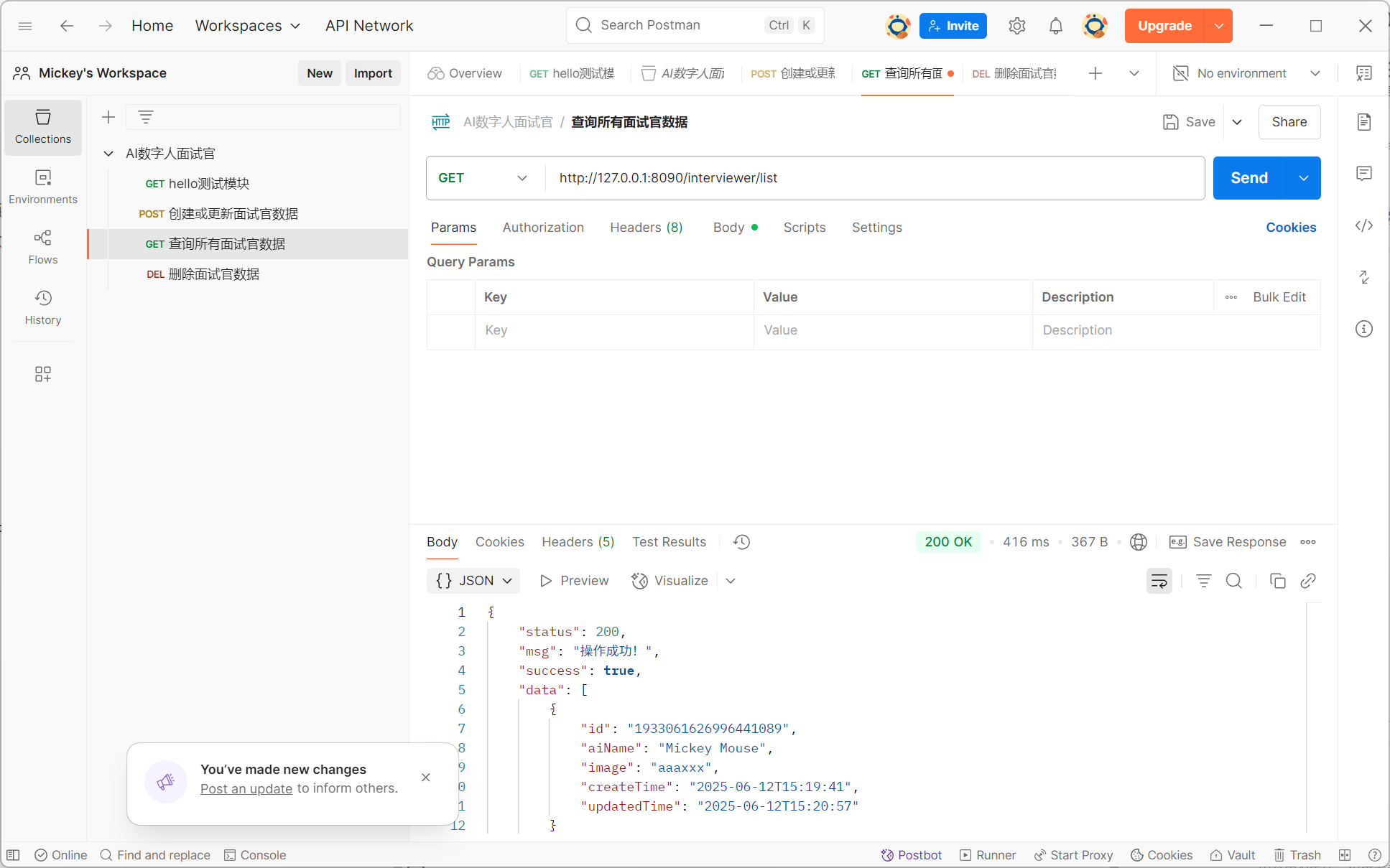
开启SpringBoot的SQL日志:
mybatis-plus:configuration:log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
