【数据结构与算法】数据结构初阶:详解二叉树(二)——堆

🔥个人主页:艾莉丝努力练剑
❄专栏传送门:《C语言》、《数据结构与算法》、C语言刷题12天IO强训、LeetCode代码强化刷题
🍉学习方向:C/C++方向
⭐️人生格言:为天地立心,为生民立命,为往圣继绝学,为万世开太平

重要提醒:为什么我们要学那么多的数据结构?这是因为没有一种数据结构能够去应对所有场景。我们在不同的场景需要选择不同的数据结构,所以数据结构没有谁好谁坏之分,而评估数据结构的好坏要针对场景,如果在一种场景下我们需要频繁地对头部进行插入删除操作,那么这个时候我们用链表;但是如果对尾部进行插入删除操作比较频繁,那我们用顺序表比较好。
因此,不同的场景我们选择不同的数据结构。
前言:本篇文章,我们继续来看二叉树相关的知识点,在初阶的数据结构与算法阶段,我们把知识点分成三部分,复杂度作为第一部分,顺序表和链表、栈和队列、二叉树为第二部分,排序为第二部分,我们之前已经介绍完了第一部分:算法复杂度,本文我们将正式开始学习第二部分中的二叉树部分内容啦。
注意,二叉树的学习需要一定的基础,涉及到【函数栈帧的创建与销毁】,而且二叉树尤其是链式结构二叉树基本上是递归算法的暴力美学。
链接: 【深入详解】函数栈帧的创建与销毁:寄存器、压栈、出栈、调用、回收空间
目录
正文
三、二叉树的顺序结构:堆
(一)堆——顺序结构
1、堆的概念
2、堆的性质
(二)堆结构各种方法的实现
1、各种方法的实现
(1)堆结构的定义
(2)初始化
(3)销毁
(4)打印
(5)交换——Swap方法
(6)向上调整算法
(7)向下调整算法
(8)入堆——数据插入
(9) 判断是否为空
(10)出堆——数据删除
(11)取堆顶元素
(12)循环判断堆为不为空
2、完整代码
(1)Heap.h:
(2)Heap.c:
(3)test.c:
(三)堆的应用——“堆排序”、堆排序和冒泡排序的比较与实现
1、冒泡排序
2、“堆排序”
3、堆排序
(1)降序
(2)升序
结尾
正文
三、二叉树的顺序结构:堆
(一)堆——顺序结构
1、堆的概念

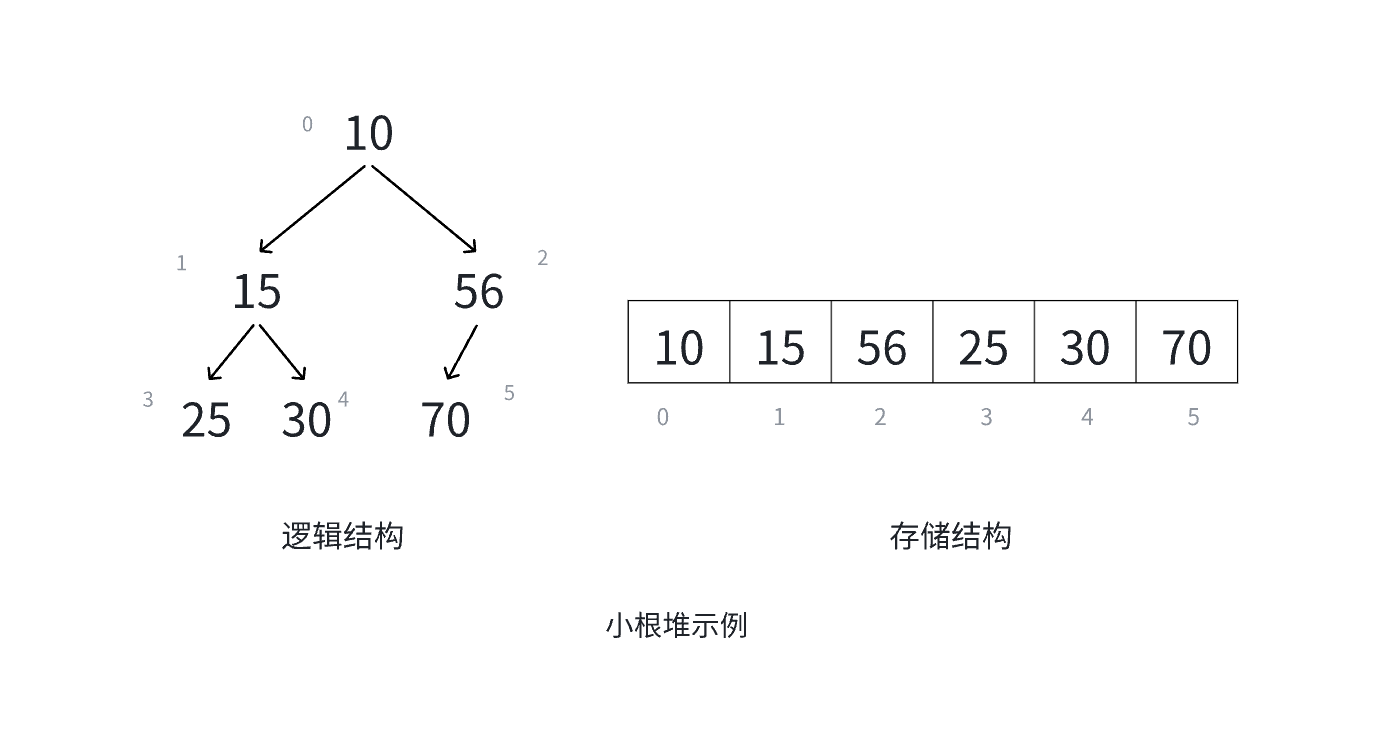
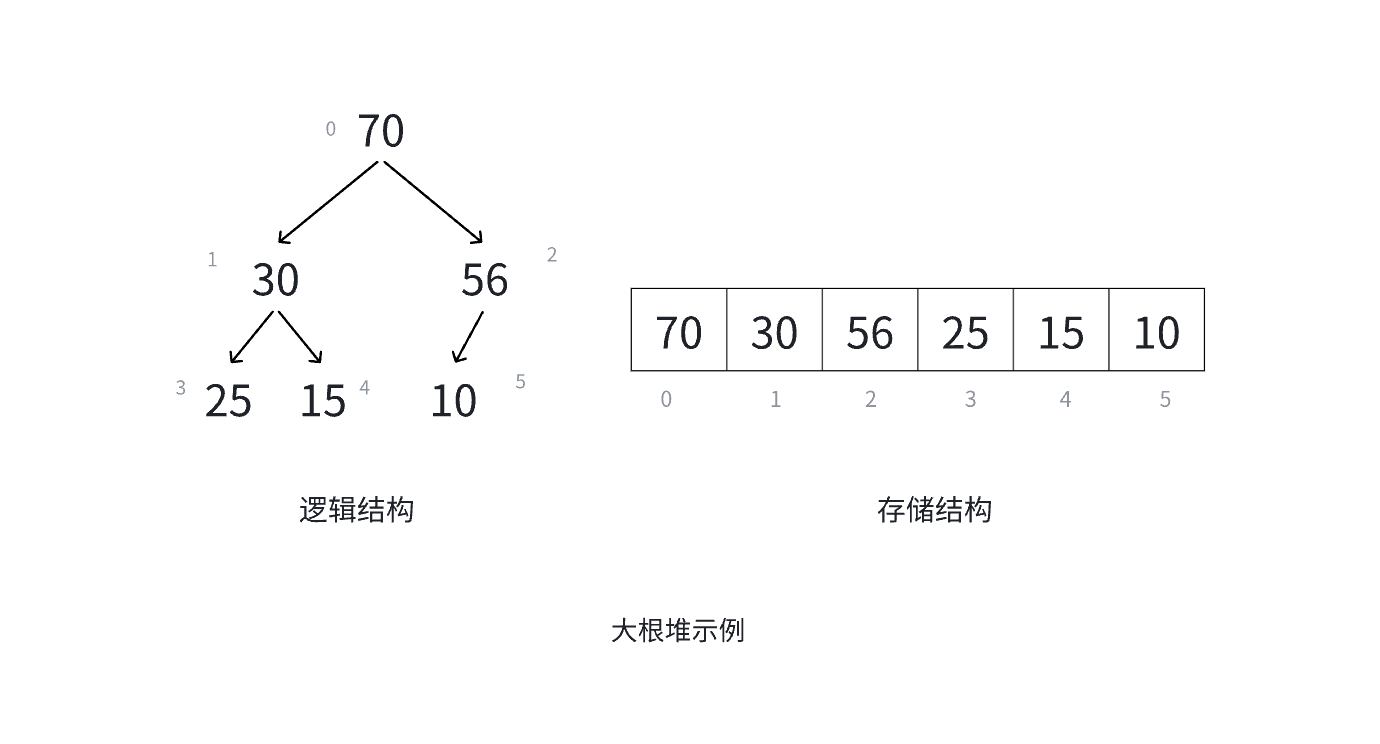
根节点最大的堆就叫最大堆(大根堆),根节点最小的堆就叫最小堆(小根堆)。
下面是小根堆和大根堆的图片示例:
小根堆:
大根堆:
2、堆的性质
性质:
1、堆是一种完全二叉树;
2、堆中某个结点的值总是不大于或不小于其父结点的值。
二叉树性质:
对于具有 n 个结点的完全二叉树,如果按照从上到下、从左到右的数组顺序对所有结点从 0 开始编号,则对于序号为 i 的结点有:
1.若 i > 0,i位置结点的双亲序号: (i - 1)/2 ; i = 0 ,i 为根结点编号,无双亲结点;
2.若2i +1,左孩子序号: 2i + 1,2i + 1 >= n否则没有左孩子;
3.若2i+2,右孩子序号:2i+2,2i + 2 >= n否则没有右孩子。
(二)堆结构各种方法的实现
1、各种方法的实现
(1)堆结构的定义
Heap.h:
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>//定义堆结构
typedef int HPDatatype;
typedef struct Heap {HPDatatype* arr;int size;//有效数据个数int capacity;//空间大小
}HP;(2)初始化
Heap.c:
//初始化
void HPInit(HP* php)
{//断言,不能传NULL,为了提高代码的健壮性assert(php);php->arr = NULL;php->capacity = php->size = 0;
}test.c:
#include"Heap.h"void test01()
{HP hp;HPInit(&hp);
}int main()
{test01();return 0;
}(3)销毁
Heap.c:
//销毁
void HPDestory(HP* php)
{assert(php);if (php)frree(php->arr);php->arr = NULL;//堆的底层就是数组php->size = php->capacity = 0;
}test.c:
#include"Heap.h"void test01()
{HP hp;HPInit(&hp);HPDesTroy(&hp);
}int main()
{test01();return 0;
}
(4)打印
Heap.c:
void HPPrint(HP* php)
{for (int i = 0; i < php->size; i++){printf("%d ", php->arr[i]);}printf("\n");
}(5)交换——Swap方法
Heap.c:
void Swap(int* x, int* y)
{int tmp = *x;*x = *y;*y = tmp;
}(6)向上调整算法
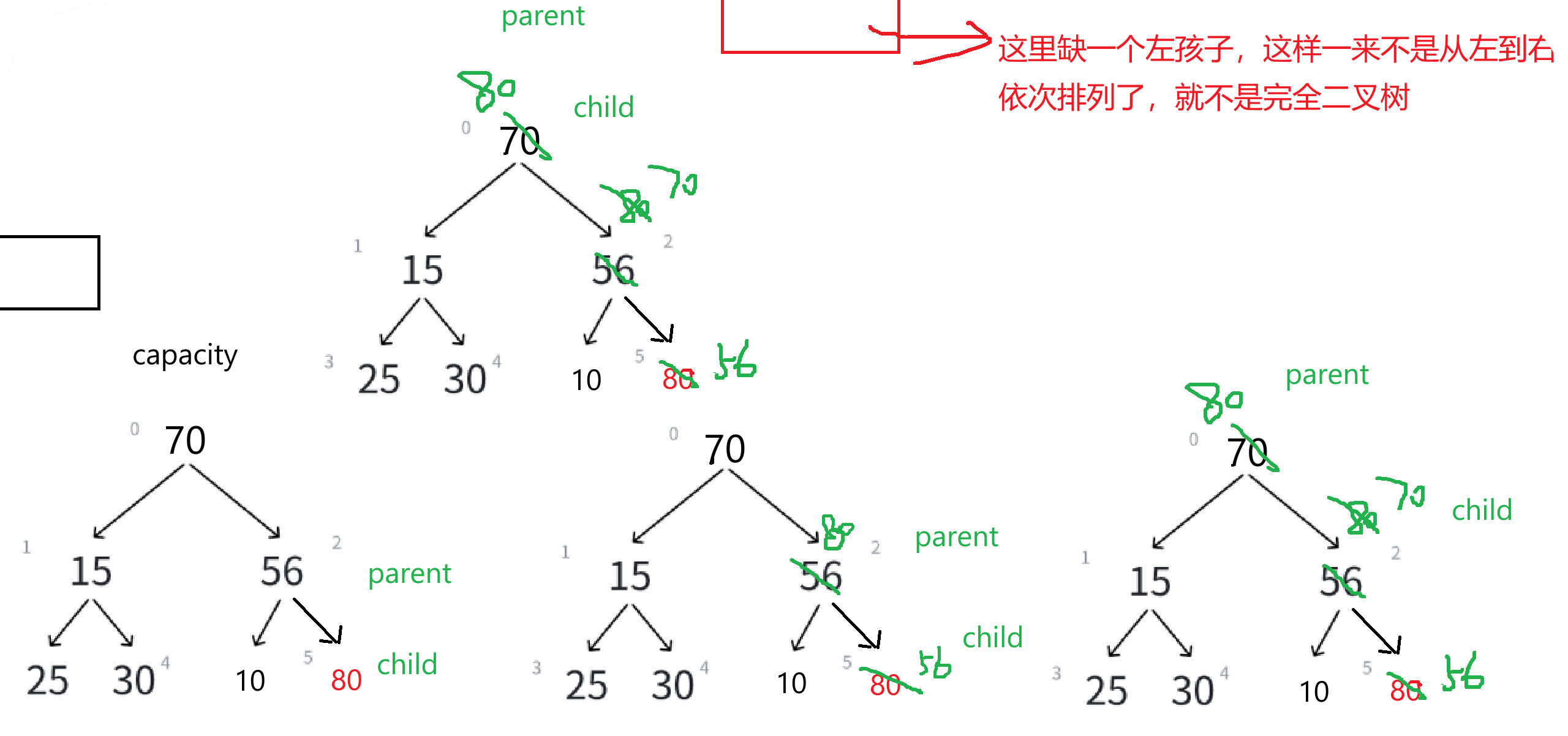
如果存储结构修改一下,改成这样——
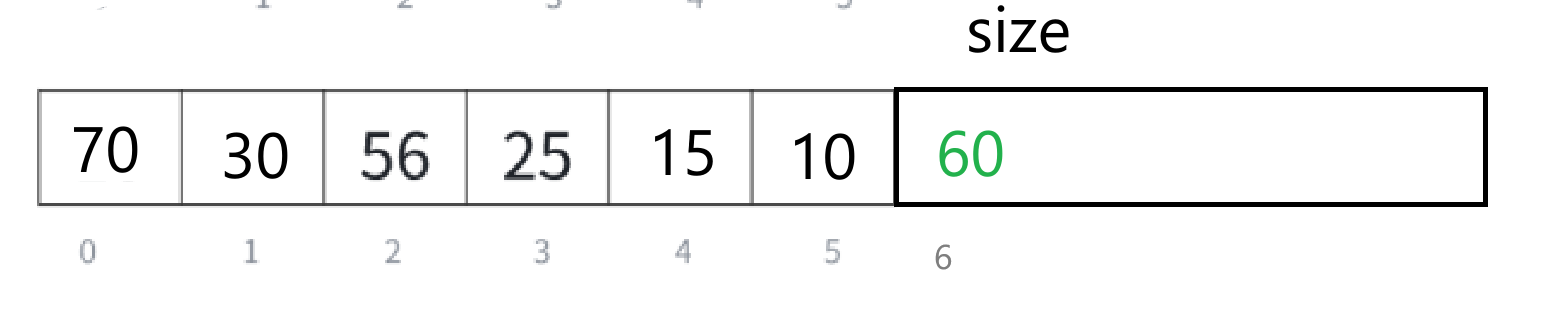
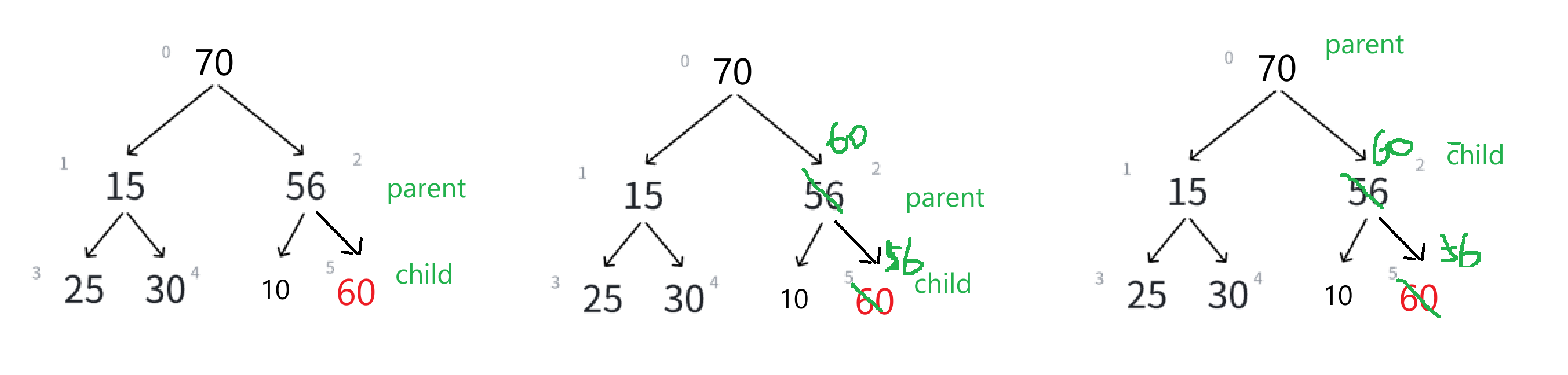
我们理解清楚向上调整之后,就来写一个向上调整算法的代码——
Heap.c:
//向上调整算法
void AdjustUp(HPDataType* arr, int child)
{int parent = (child - 1) / 2;while (child > 0){//建大堆:>//建小堆: <if (arr[child] < arr[parent]){Swap(&arr[child], &arr[parent]);child = parent;parent = (child - 1) / 2;}else {break;}}
}(7)向下调整算法
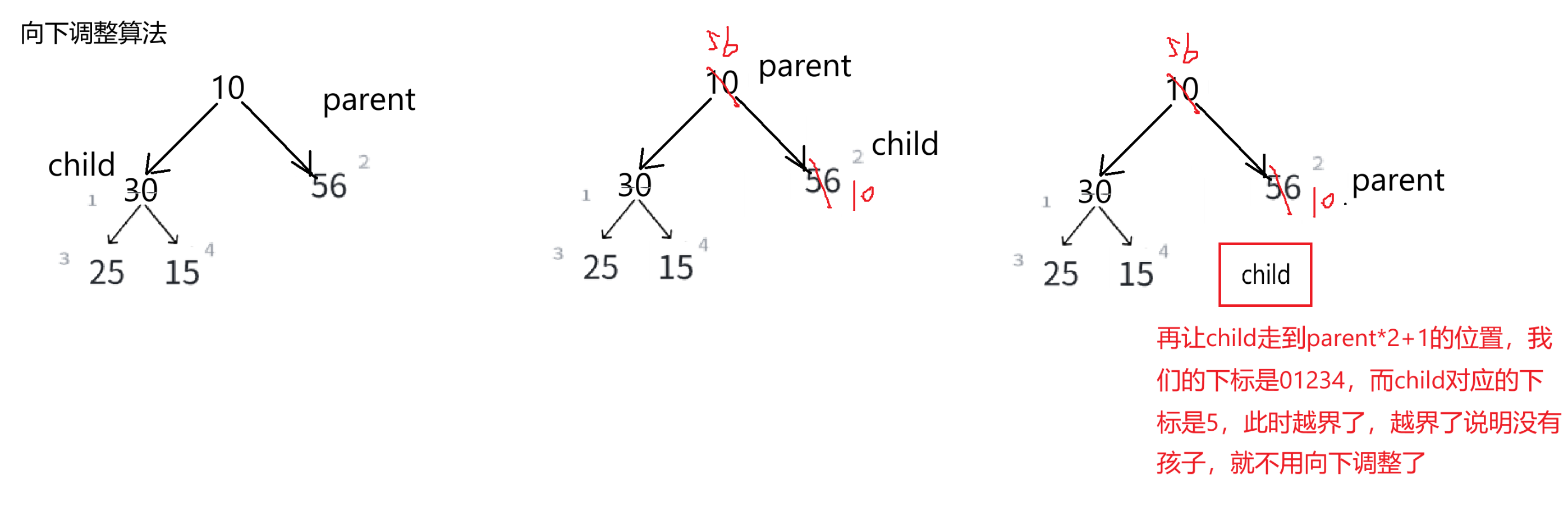
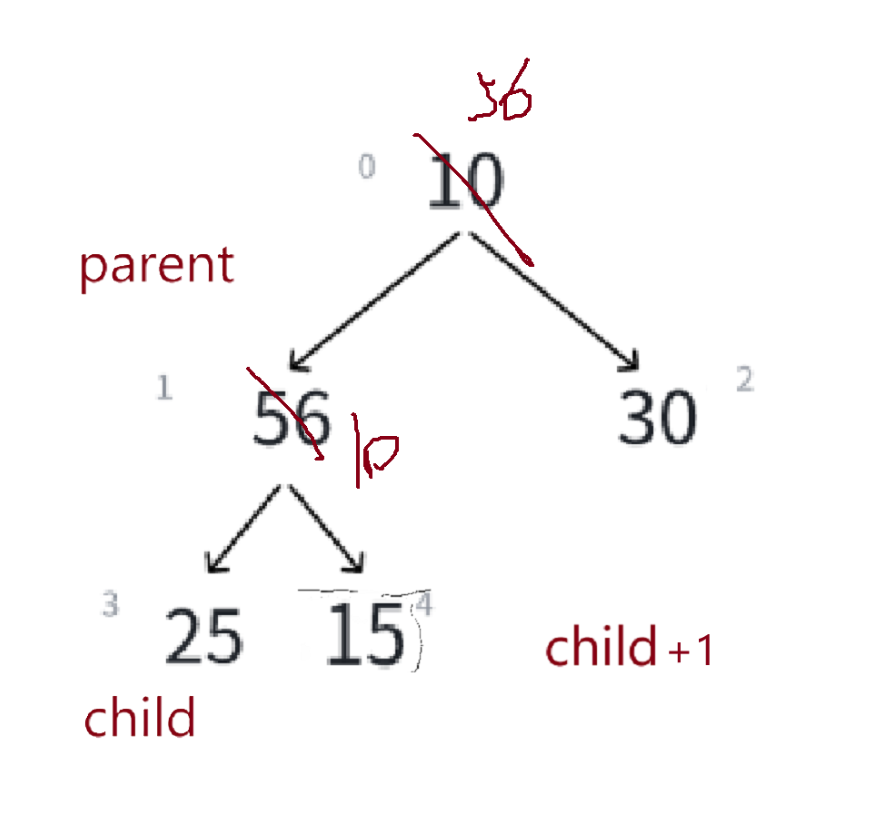
再让child走到parent*2+1的位置,我们的下标是01234,而child对应的下标是5,此时越界了,越界了说明没有孩子,就不用向下调整了
再举一个大根堆的例子——
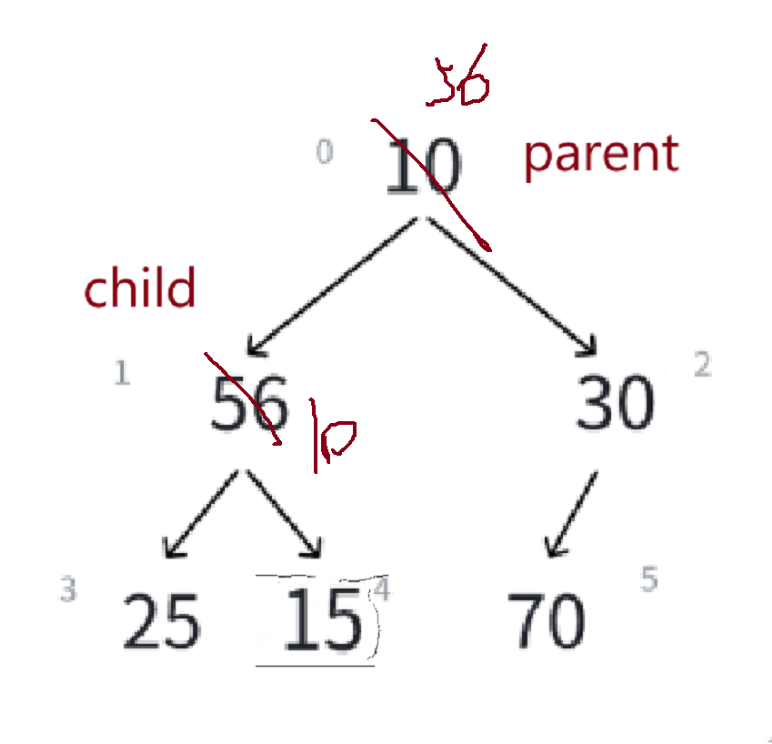
每次交换完,child = parent*2+1,parent挪到child的位置,比较左右孩子,左孩子大,child位置不动,比较子与父大小,大的往上放——
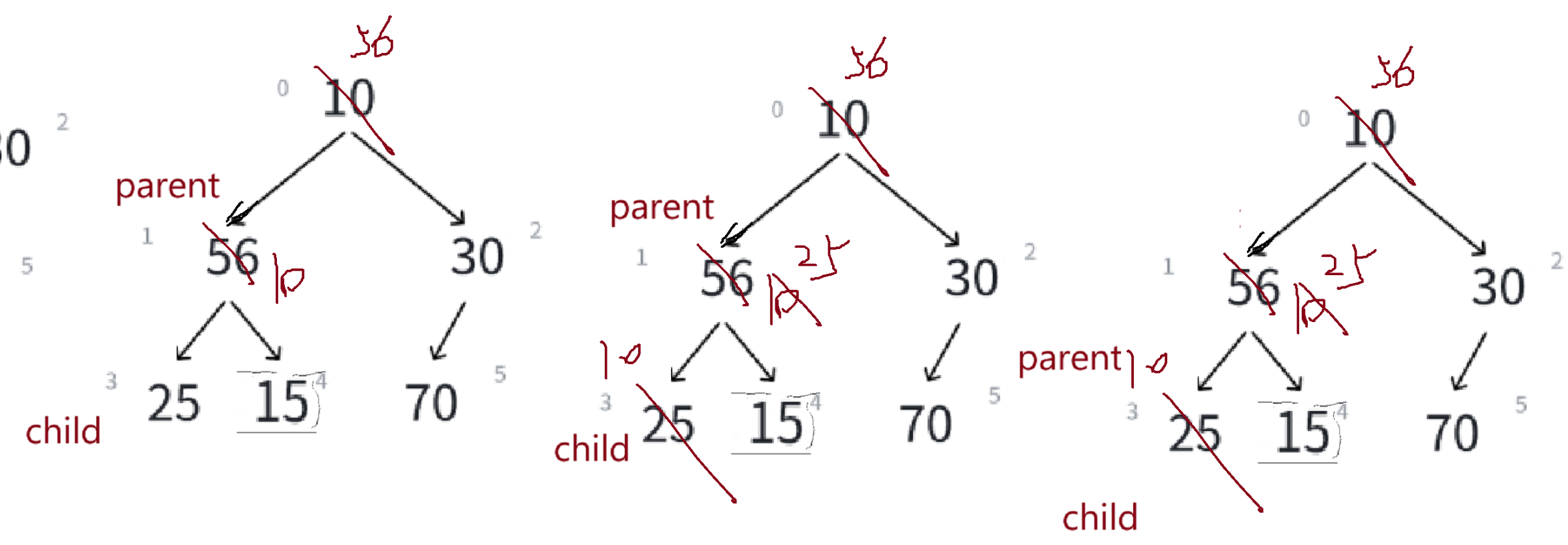
//找最大的孩子if (arr[child] < arr[child + 1]);{child++;}这个代码感觉有问题吗?
child+1可能越界了,我们改一下——
//找最大的孩子if (child + 1 < n && arr[child] < arr[child + 1]);{child++;}这样我们便修复了一个BUG!
Heap.c:
//向下调整算法
void AdjustDown(HPDataType* arr, int parent, int n)
{int child = parent * 2 + 1;while (child < n){//建大堆:<//建小堆: >if (child + 1 < n && arr[child] > arr[child + 1]){child++;}//孩子和父亲比较//建大堆:>//建小堆:<if (arr[child] < arr[parent]){Swap(&arr[child], &arr[parent]);parent = child;child = parent * 2 + 1;}else {break;}}
}(8)入堆——数据插入
Heap.c:
void HPPush(HP* php, HPDataType x)
{assert(php);//空间不够要增容if (php->size == php->capaicty){//增容int newCapacity = php->capaicty == 0 ? 4 : 2 * php->capaicty;HPDataType* tmp = (HPDataType*)realloc(php->arr, newCapacity * sizeof(HPDataType));if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail!");exit(1);}php->arr = tmp;php->capaicty = newCapacity;}//空间足够php->arr[php->size] = x;//向上调整AdjustUp(php->arr, php->size);++php->size;
}test.c:
#include"Heap.h"void test01()
{HP hp;HPInit(&hp);HPPush(&hp, 25);HPPush(&hp, 15);HPPush(&hp, 10);HPPush(&hp, 56);HPPush(&hp, 70);HPPush(&hp, 30);HPPrint(&hp);HPDesTroy(&hp);
}int main()
{test01();return 0;
}
(9) 判断是否为空
Heap.c:
bool HPEmpty(HP* php)
{assert(php);return php->size == 0;
}(10)出堆——数据删除
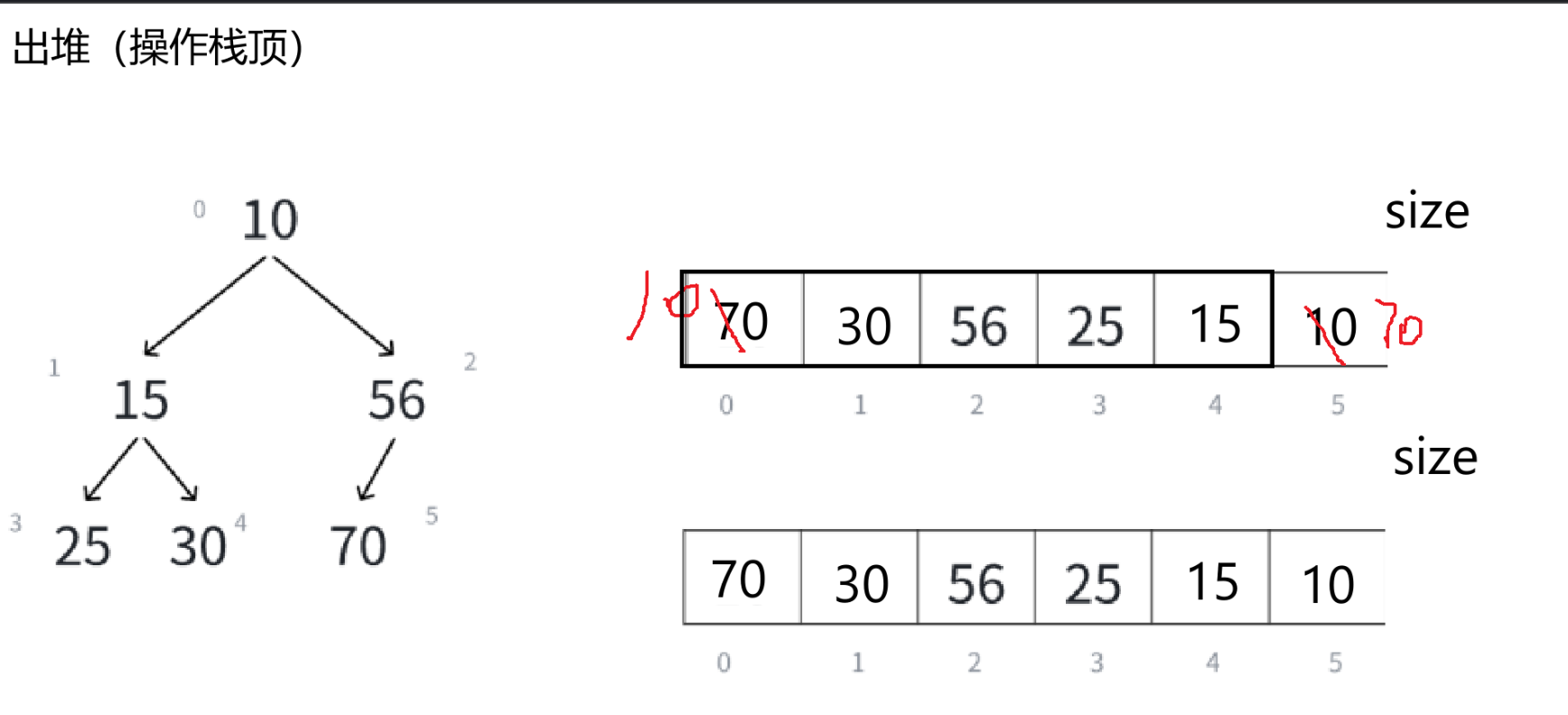
Heap.c:
void HPPop(HP* php)
{assert(!HPEmpty(php));Swap(&php->arr[0], &php->arr[php->size - 1]);--php->size;//堆顶数据需要向下调整AdjustDown(php->arr, 0, php->size);
}test.c:
#include"Heap.h"void test01()
{HP hp;HPInit(&hp);HPPush(&hp, 25);HPPush(&hp, 15);HPPush(&hp, 10);HPPush(&hp, 56);HPPush(&hp, 70);HPPush(&hp, 30);HPPrint(&hp);HPPop(&hp);HPPrint(&hp);HPPop(&hp);HPPrint(&hp);HPPop(&hp);HPPrint(&hp);HPPop(&hp);HPPrint(&hp);HPPop(&hp);HPPrint(&hp);HPDesTroy(&hp);
}
int main()
{test01();return 0;
}
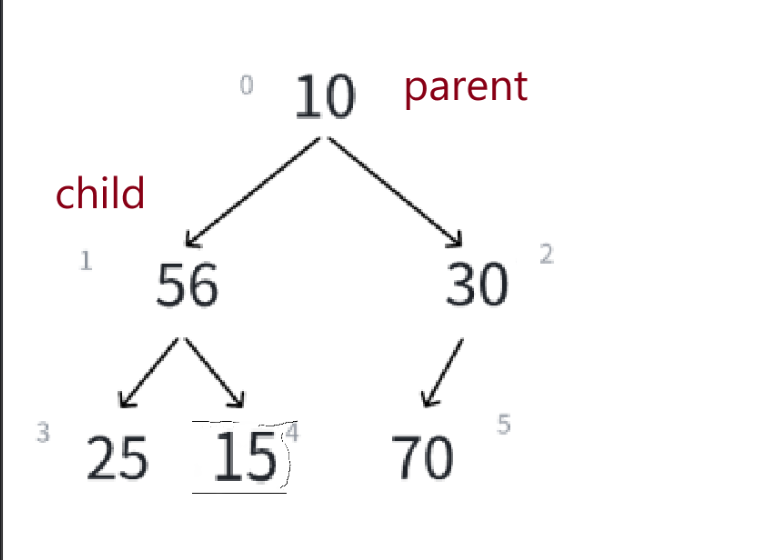
先删除一次——
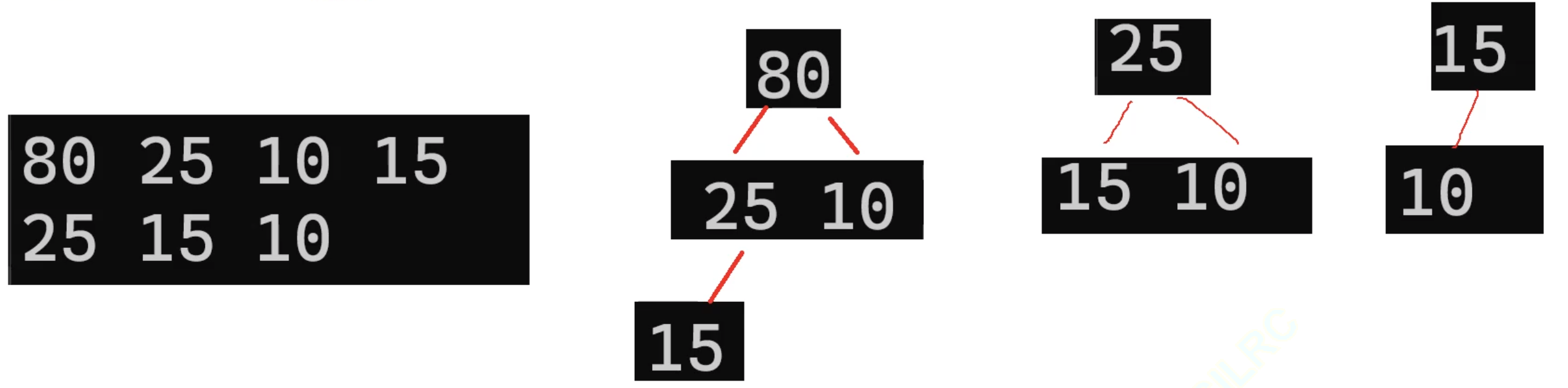
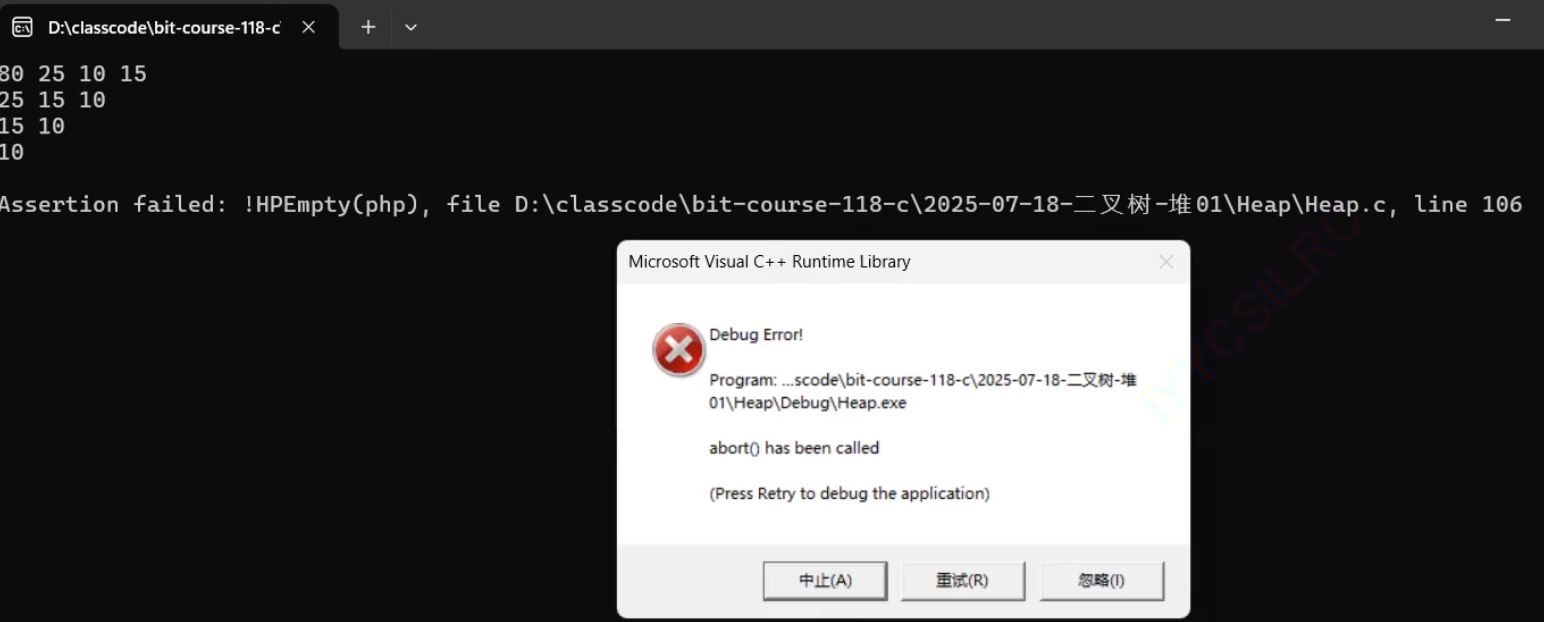
我们期望断言报错,事实上确实如此,那么出堆的代码就写好了。
(11)取堆顶元素
Heap.c:
HPDataType HPTop(HP* php)
{assert(!HPEmpty(php));return php->arr[0];
}test.c:
#include"Heap.h"void test01()
{HP hp;HPInit(&hp);HPPush(&hp, 25);HPPush(&hp, 15);HPPush(&hp, 10);HPPush(&hp, 56);HPPush(&hp, 70);HPPush(&hp, 30);HPPrint(&hp);while (!HPEmpty(&hp)){int top = HPTop(&hp);printf("%d ", top);HPPop(&hp);}HPDesTroy(&hp);
}
int main()
{test01();return 0;
}(12)循环判断堆为不为空
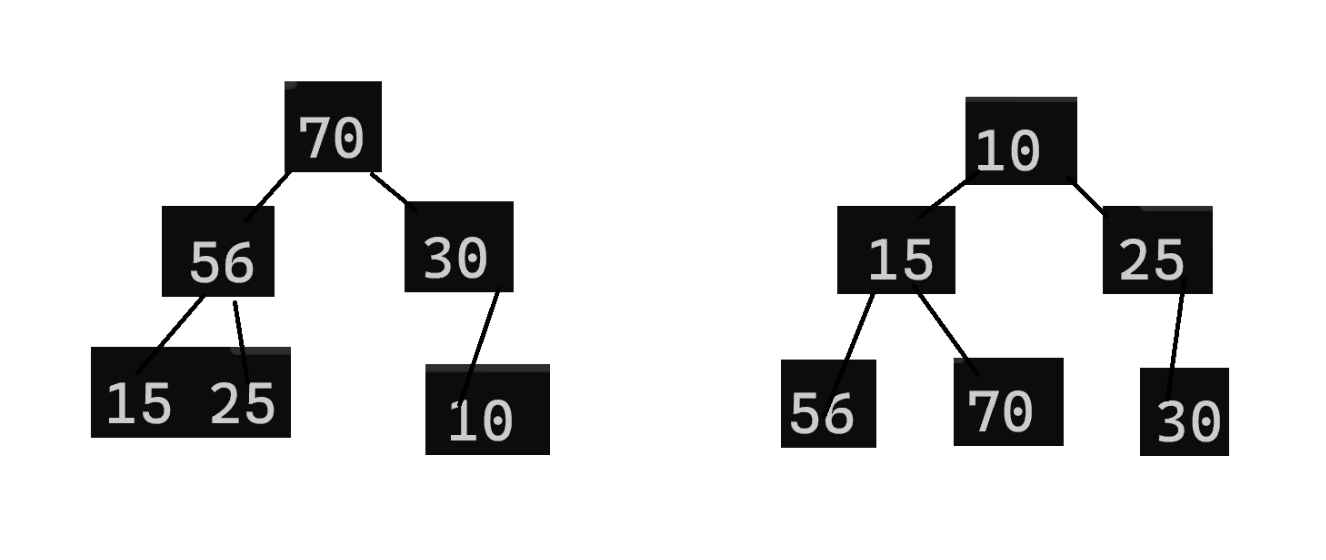
test.c:
while (!HPEmpty(&hp)){int top = HPTop(&hp);printf("%d ", top);HPPop(&hp);}不断循环地判断堆顶为不为空,不为空,出堆顶——

2、完整代码
(1)Heap.h:
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>//定义堆结构
typedef int HPDataType;
typedef struct Heap {HPDataType* arr;int size; //有效数据个数int capaicty;//空间大小
}HP;void HPInit(HP* php);
void HPDesTroy(HP* php);void HPPrint(HP* php);
void Swap(int* x, int* y);
//向下调整算法
void AdjustDown(HPDataType* arr, int parent, int n);
//向上调整算法
void AdjustUp(HPDataType* arr, int child);void HPPush(HP* php, HPDataType x);
void HPPop(HP* php);
HPDataType HPTop(HP* php);bool HPEmpty(HP* php);(2)Heap.c:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1#include"Heap.h"void HPInit(HP* php)
{assert(php);php->arr = NULL;php->size = php->capaicty = 0;
}
void HPDesTroy(HP* php)
{assert(php);if (php->arr)free(php->arr);php->arr = NULL;php->size = php->capaicty = 0;
}
void HPPrint(HP* php)
{for (int i = 0; i < php->size; i++){printf("%d ", php->arr[i]);}printf("\n");
}
void Swap(int* x, int* y)
{int tmp = *x;*x = *y;*y = tmp;
}//向上调整算法
void AdjustUp(HPDataType* arr, int child)
{int parent = (child - 1) / 2;while (child > 0){//建大堆:>//建小堆: <if (arr[child] < arr[parent]){Swap(&arr[child], &arr[parent]);child = parent;parent = (child - 1) / 2;}else {break;}}
}
//向下调整算法
void AdjustDown(HPDataType* arr, int parent, int n)
{int child = parent * 2 + 1;while (child < n){//建大堆:<//建小堆: >if (child + 1 < n && arr[child] > arr[child + 1]){child++;}//孩子和父亲比较//建大堆:>//建小堆:<if (arr[child] < arr[parent]){Swap(&arr[child], &arr[parent]);parent = child;child = parent * 2 + 1;}else {break;}}
}void HPPush(HP* php, HPDataType x)
{assert(php);//空间不够要增容if (php->size == php->capaicty){//增容int newCapacity = php->capaicty == 0 ? 4 : 2 * php->capaicty;HPDataType* tmp = (HPDataType*)realloc(php->arr, newCapacity * sizeof(HPDataType));if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail!");exit(1);}php->arr = tmp;php->capaicty = newCapacity;}//空间足够php->arr[php->size] = x;//向上调整AdjustUp(php->arr, php->size);++php->size;
}bool HPEmpty(HP* php)
{assert(php);return php->size == 0;
}void HPPop(HP* php)
{assert(!HPEmpty(php));Swap(&php->arr[0], &php->arr[php->size - 1]);--php->size;//堆顶数据需要向下调整AdjustDown(php->arr, 0, php->size);
}HPDataType HPTop(HP* php)
{assert(!HPEmpty(php));return php->arr[0];
}(3)test.c:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1#include"Heap.h"void test01()
{HP hp;HPInit(&hp);HPPush(&hp, 25);HPPush(&hp, 15);HPPush(&hp, 10);HPPush(&hp, 56);HPPush(&hp, 70);HPPush(&hp, 30);HPPrint(&hp);while (!HPEmpty(&hp)){int top = HPTop(&hp);printf("%d ", top);HPPop(&hp);}//HPPop(&hp);//HPPrint(&hp);//HPPop(&hp);//HPPrint(&hp);//HPPop(&hp);//HPPrint(&hp);//HPPop(&hp);//HPPrint(&hp);//HPPop(&hp);//HPPrint(&hp);HPDesTroy(&hp);}int main()
{test01();return 0;
}(三)堆的应用——“堆排序”、堆排序和冒泡排序的比较与实现
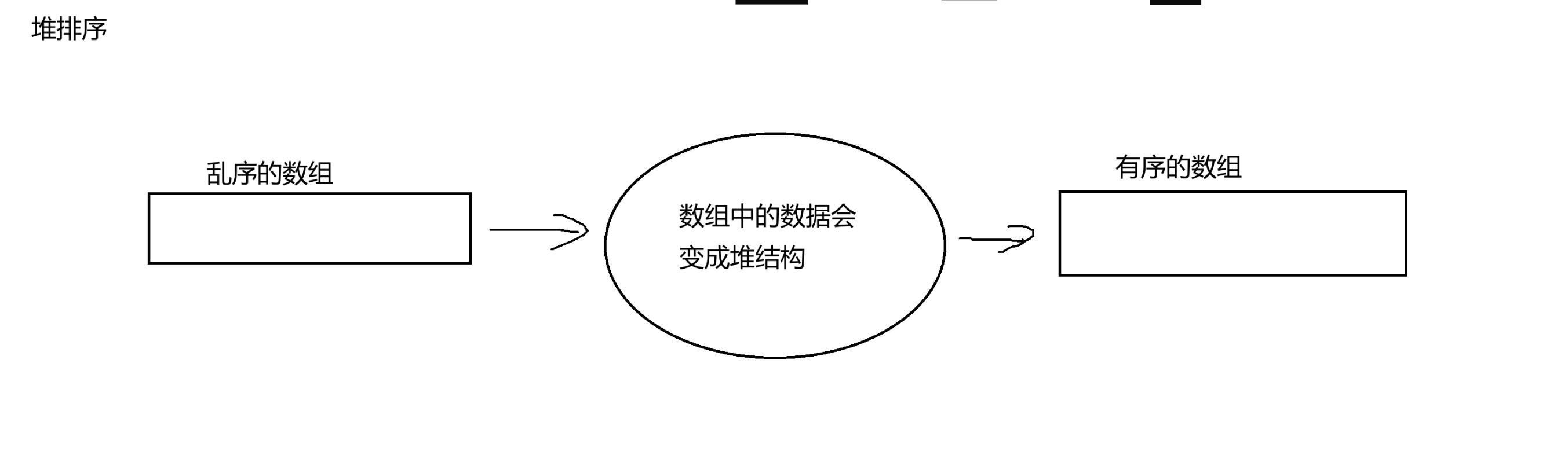
1、冒泡排序
冒泡排序是我们在C语言阶段就介绍过的排序方法——
test.c:
//冒泡排序
void BubbleSort(int* arr, int n)
{for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){for (int j = 0; j < n - i - 1; j++){if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]){Swap(&arr[j], &arr[j + 1]);}}}
}int main()
{//test01();int arr[6] = { 30,56,25,15,70,10 };printf("排序之前:\n");for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++){printf("%d ", arr[i]);}printf("\n");//HeapSort(arr, 6);BubbleSort(arr, 6);printf("排序之后:\n");for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++){printf("%d ", arr[i]);}printf("\n");return 0;
}2、“堆排序”
“堆排序“”——这不是实际的堆排序,调用了堆的结构。
test.c:
//堆排序----这不是实际的堆排序
void HeapSort01(int* arr, int n)
{HP hp;//-----使用数据结构-堆HPInit(&hp);//调用push将数组中的数据放入到堆中for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){HPPush(&hp, arr[i]);}int i = 0;while (!HPEmpty(&hp)){int top = HPTop(&hp);arr[i++] = top;HPPop(&hp);}HPDesTroy(&hp);
}3、堆排序
这个才是堆排序————使用的是堆结构的思想,而不是调用堆的结构。
排升序——建大堆;
排降序——建小堆。
(1)降序
test.c:
//堆排序————使用的是堆结构的思想
void HeapSort(int* arr, int n)
{//乱序数组————建堆for (int i = (n - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--){AdjustDown(arr, i, n);}int end = n - 1;while (end > 0){Swap(&arr[0], &arr[end]);AdjustDown(arr, 0, end);end--;}
}int main()
{//test01();int arr[6] = { 30,56,25,15,70,10 };printf("排序之前:\n");for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++){printf("%d ", arr[i]);}printf("\n");HeapSort(arr, 6);//BubbleSort(arr, 6);printf("排序之后:\n");for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++){printf("%d ", arr[i]);}printf("\n");return 0;
}这里我们打印出来结果是降序的——

(2)升序
也可以是升序的——
test.c:
//堆排序————使用的是堆结构的思想
void HeapSort(int* arr, int n)
{//乱序数组————建堆for (int i = (n - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--){AdjustDown(arr, i, n);}int end = n - 1;while (end > 0){Swap(&arr[0], &arr[end]);AdjustDown(arr, 0, end);end--;}
}
int main()
{//test01();int arr[6] = { 30,56,25,15,70,10 };printf("排序之前:\n");for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++){printf("%d ", arr[i]);}printf("\n");HeapSort(arr, 6);//BubbleSort(arr, 6);printf("排序之后:\n");for (int i = 5; i >= 0; i--){printf("%d ", arr[i]);}printf("\n");return 0;
}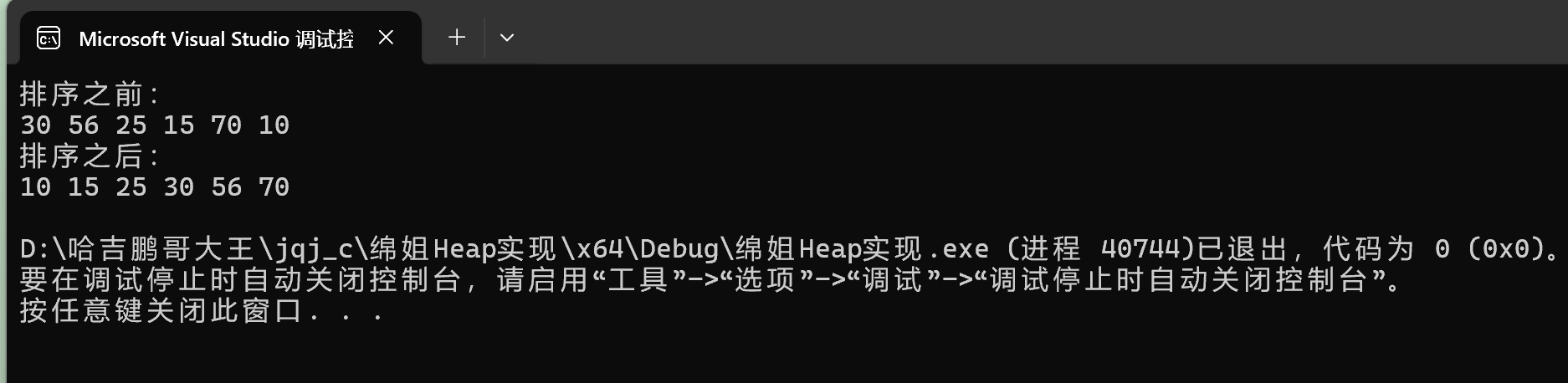
现在就是升序的了。
结尾
函数栈帧的创建与销毁相关博客的链接,博主已经放在正文前面了,有需要的友友自取。
往期回顾:
【数据结构与算法】数据结构初阶:详解二叉树(一)
【数据结构与算法】数据结构初阶:详解栈和队列(下)——队列
【数据结构与算法】数据结构初阶:详解栈和队列(上)——栈
【数据结构与算法】数据结构初阶:详解顺序表和链表(五)——双向链表
【数据结构与算法】数据结构初阶:详解顺序表和链表(四)——单链表(下)
【数据结构与算法】数据结构初阶:详解顺序表和链表(三)——单链表(上)
本期内容需要回顾的C语言知识如下面的截图中所示(指针博主写了6篇,列出来有水字数嫌疑了,就只放指针第六篇的网址,博主在指针(六)把指针部分的前五篇的网址都放在【往期回顾】了,点击【传送门】就可以看了)。
大家如果对前面部分的知识点印象不深,可以去上一篇文章的结尾部分看看,博主把需要回顾的知识点相关的博客的链接都放在上一篇文章了,上一篇文章的链接博主放在下面了:
【数据结构与算法】数据结构初阶:详解顺序表和链表(三)——单链表(上)
结语:本篇文章到这里就结束了,对数据结构的二叉树知识感兴趣的友友们可以在评论区留言,博主创作时可能存在笔误,或者知识点不严谨的地方,大家多担待,如果大家在阅读的时候发现了行文有什么错误欢迎在评论区斧正,再次感谢友友们的关注和支持!
