A*寻路算法:原理、实现与优化指南
🧭 A*寻路算法:原理、实现与优化指南
引用:
- A*寻路算法深度解析:原理、实现与优化
- B*算法深度解析:动态避障路径规划的革命性方法
折戟沉沙秋水溟繁花落尽君辞去长坂坡上草木腥沧江一梦镜花影
探索现代游戏开发与机器人导航中的路径规划核心算法
🌐 引言:路径规划的进化之路
人类从古至今一直追求更优的路径解决方案——从最早的星象导航到现代GPS系统。在计算机科学领域,路径规划算法始终占据重要地位,其中A*算法因其高效性和灵活性成为路径规划领域最具影响力的算法之一。本文将深入剖析A*算法的原理、实现细节和优化方向,帮助读者全面掌握这一经典算法的核心思想。
🧩 第一章:A*算法基础理论
🚩 1.1 什么是A*算法
A*(A-Star)算法是一种启发式搜索算法,由Peter Hart、Nils Nilsson和Bertram Raphael于1968年首次提出。该算法在保证找到最短路径的前提下,通过启发式函数(Heuristic Function) 引导搜索方向,显著减少了搜索空间,极大地提高了搜索效率。
📐 1.2 算法核心思想
A*算法使用一个评估函数:F(n) = G(n) + H(n),其中:
- G(n): 从起点到节点n的实际代价(通常用距离表示)
- H(n): 从节点n到目标的估计代价(启发式函数)
- F(n): 通过节点n的路径总代价估计
算法通过维护两个列表工作:
- 开放列表(Open List): 存储待检查的节点集合
- 关闭列表(Closed List): 存储已检查的节点集合
🔍 1.3 算法运行流程
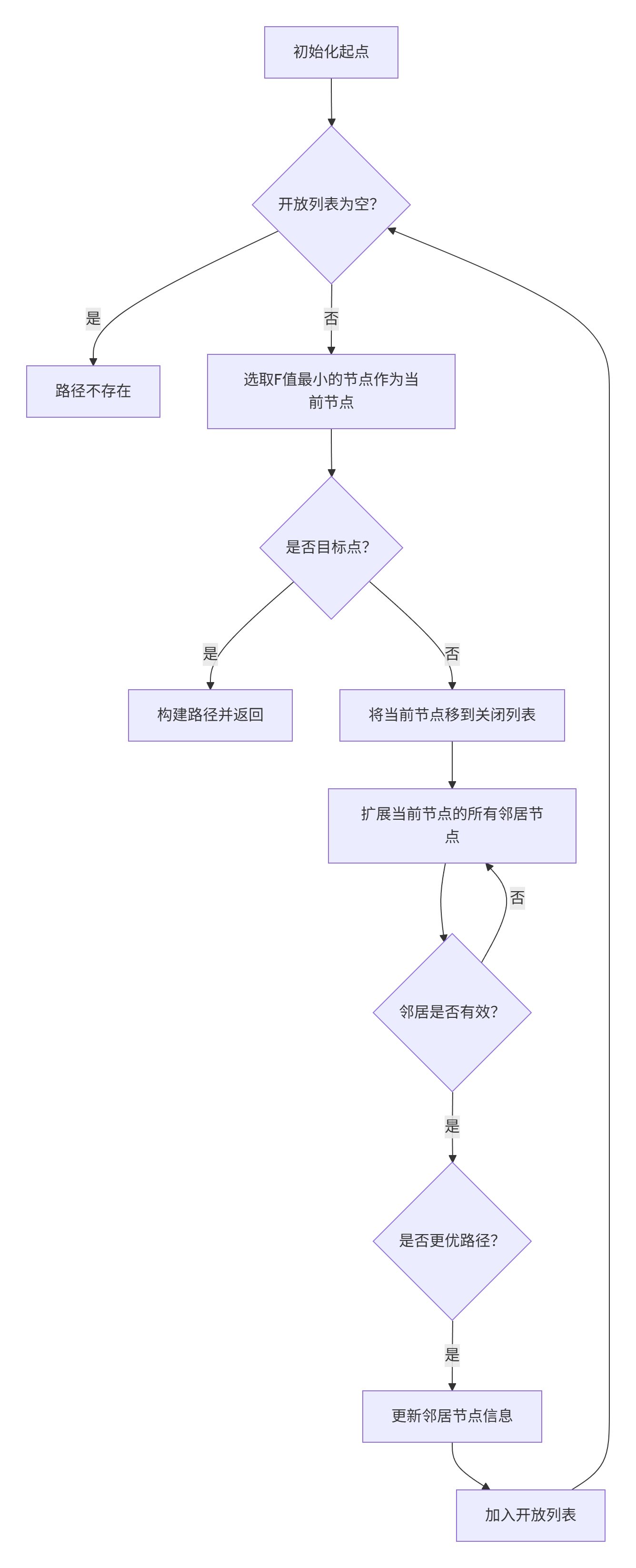
🏗️ 第二章:A*算法C++实现剖析
🔧 2.1 数据结构设计
节点状态枚举
enum class NodeState {UNVISITED, // 未访问状态OPEN, // 在开放列表中(待探索)CLOSED // 在关闭列表中(已探索)
};
节点结构体
struct Node {int x, y; // 节点坐标int g_value; // 起点到当前节点的实际代价int h_value; // 启发式函数估算值Node* parent; // 父节点指针NodeState state; // 节点状态// 计算总代价f = g + hint f_value() const {if (g_value == INT_MAX || h_value == INT_MAX) return INT_MAX;return g_value + h_value;}
};
⚙️ 2.2 关键组件实现
节点比较函数
struct NodeCompare {bool operator()(const Node* a, const Node* b) const {if (a->f_value() != b->f_value())return a->f_value() > b->f_value(); // 小顶堆if (a->h_value != b->h_value)return a->h_value > b->h_value; // Tie-breakerreturn a < b; // 保证唯一性}
};
曼哈顿距离启发函数
int heuristic(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2) const {return std::abs(x1 - x2) + std::abs(y1 - y2);
}
🔄 2.3 主搜索流程核心代码
bool find_path(const std::pair<int, int>& start, const std::pair<int, int>& target,std::vector<std::pair<int, int>>& path) {// 初始化起点start_node->g_value = 0;start_node->h_value = heuristic(...);start_node->state = NodeState::OPEN;open_queue.push(start_node);while (!open_queue.empty()) {Node* current = open_queue.top();open_queue.pop();if (current->state == NodeState::CLOSED) continue;if (current == target_node) {build_path(current, path);return true;}current->state = NodeState::CLOSED;// 探索四个方向的邻居for (const auto& dir : directions) {int nx = current->x + dir.first;int ny = current->y + dir.second;if (!is_valid(nx, ny)) continue;Node* neighbor = node_pool_[ny][nx].get();int new_g = current->g_value + 1;if (new_g < neighbor->g_value) {// 更新邻居节点信息neighbor->parent = current;neighbor->g_value = new_g;neighbor->h_value = heuristic(nx, ny, ...);neighbor->state = NodeState::OPEN;open_queue.push(neighbor);}}}return false;
}
📊 第三章:算法性能与可视化分析
🧪 3.1 测试环境与数据集
我们使用10x10网格地图进行测试:
网格地图 (10x10):
. . . . . . . . . .
. # # . # # # . # .
. # . . . . . . # .
. # . # # # # . # .
. . . # . . . . . .
. # . . . # . # # .
. # # # # # # # # .
. # . . . . . . . .
. # . # # # . # # .
. . . . . . . . . .
⏱ 3.2 性能测试结果
| 测试路径 | 路径步数 | 计算时间(μs) | 是否找到路径 |
|---|---|---|---|
| (0,0) → (9,9) | 19 | 54 | 是 |
| (4,4) → (0,9) | 12 | 29 | 是 |
| (0,0) → (0,0) | 1 | 5 | 是 |
🎨 3.3 路径可视化效果
测试路径1: (0,0) → (9,9)
S > > > > > > v . .
. # # . # # # v # .
. # . . . . . v # .
. # . # # # # v # .
. . . # . . . > > v
. # . . . # . # # v
. # # # # # # # # v
. # . . . . . . . v
. # . # # # . # # v
. . . . . . . . . E
测试路径2: (4,4) → (0,9)
. . . . . . . . . .
. # # . # # # . # .
. # . . . . . . # .
. # . # # # # . # .
v < < # S . . . . .
v # ^ < < # . # # .
v # # # # # # # # .
v # . . . . . . . .
v # . # # # . # # .
E . . . . . . . . .
⚡ 第四章:高级优化技术
🔍 4.1 启发式函数优化
根据不同场景选择合适的启发函数:
-
曼哈顿距离:适用于4方向移动场景
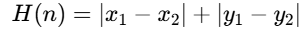
-
对角线距离:适用于8方向移动
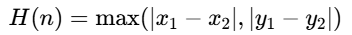
-
欧几里得距离:适用于任意方向移动
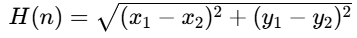
📦 4.2 数据结构优化
优化开放列表数据结构:
🔀 4.3 双向A*算法
双向A*算法从起点和终点同时搜索,显著提高效率:
// 伪代码实现
bool bidirectional_astar() {while (!open_set_start.empty() && !open_set_end.empty()) {// 从起点方向扩展expand_nodes(open_set_start, closed_set_start, true);// 从终点方向扩展expand_nodes(open_set_end, closed_set_end, false);// 检查连接点if (check_intersection()) {merge_paths();return true;}}return false;
}
🛠️ 4.4 JPS跳点搜索优化
Jump Point Search (JPS) 专门优化栅格地图上的路径搜索:
- 利用地图的规则结构跳过冗余节点
- 只检查关键节点(跳点)
- 在大型开放区域效率提升10倍以上
// JPS核心跳点检测
Node* jump(Node* current, Direction dir) {Node* next = current->neighbor(dir);if (!next || next->obstacle) return nullptr;if (next == goal) return next;// 强制邻居检查if (has_forced_neighbors(next, dir)) return next;// 对角线特殊处理if (is_diagonal(dir)) {for (const auto& d : {get_horizontal(dir), get_vertical(dir)}) {if (jump(next, d)) return next;}}return jump(next, dir);
}
💻 第五章:现代应用场景
🎮 5.1 游戏开发中的应用
在游戏AI中使用A*算法的优化策略:
- 动态障碍处理:实时更新路径
- 层级路径规划:先区域后细节
- 路径平滑处理:贝塞尔曲线优化
原始路径: [S] - [ ] - [ ] - [ ] - [E]| | | | |
优化后: [S]-----------[E]
🤖 5.2 机器人导航实践
机器人系统中A*算法的特殊考量:
-
代价地图:整合地形、坡度等因素

-
动力学约束:转弯半径限制
-
实时重规划:处理动态障碍物
🗺️ 5.3 大型地图处理技巧
处理百万级网格地图的技术:
- 分块加载:按需加载地图区域
- 路径缓存:存储常用路径
- HPA*分层规划:创建抽象路径网络
🏁 第六章:总结与展望
A算法作为路径规划领域的里程碑,经过半个世纪的发展依然保持活力。随着现代技术的发展,A算法在以下方向持续进化:
- 机器学习整合:训练启发函数适应复杂环境
- 多智能体协调:解决群体路径冲突
- 量子计算优化:指数级提升搜索效率
“A*算法的优雅在于它完美平衡了最优性与效率,这是算法设计中永恒的追求。” - Dr. Stephen G. Nash
📄 附录:完整实现代码
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <memory>
#include <climits>
#include <functional>
#include <chrono>
#include <queue>// 节点状态枚举
enum class NodeState {UNVISITED, // 未访问状态OPEN, // 在开放列表中(待探索)CLOSED // 在关闭列表中(已探索)
};// 节点结构体
struct Node {int x; // 节点在网格中的x坐标int y; // 节点在网格中的y坐标int g_value; // 从起点到当前节点的实际代价int h_value; // 启发式函数估算的到目标点的代价Node* parent; // 指向父节点的指针(用于回溯路径)NodeState state = NodeState::UNVISITED; // 节点当前状态// 构造函数:初始化节点位置,g值设为最大整数(表示无穷大)Node(int x, int y) : x(x), y(y), g_value(INT_MAX), h_value(0), parent(nullptr) {}// 计算总代价f = g + hint f_value() const {// 避免整数溢出,确保g和h都不是INT_MAXif (g_value == INT_MAX || h_value == INT_MAX)return INT_MAX;return g_value + h_value;}
};// 节点比较函数(用于优先队列)
struct NodeCompare {bool operator()(const Node* a, const Node* b) const {// 优先比较f值(总代价)if (a->f_value() != b->f_value())return a->f_value() > b->f_value(); // 优先队列需要逆序比较// f值相同时使用h值作为tie-breaker(倾向于离目标更近的节点)if (a->h_value != b->h_value)return a->h_value > b->h_value;// 如果f值和h值都相同,使用指针地址确保唯一性return a < b;}
};class AStar {
private:const std::vector<std::vector<int>>& grid_map_; // 网格地图的引用int map_width_; // 地图宽度(列数)int map_height_; // 地图高度(行数)// 节点池:使用unique_ptr管理节点内存std::vector<std::vector<std::unique_ptr<Node>>> node_pool_;// 计算曼哈顿距离(启发式函数)int heuristic(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2) const {// 曼哈顿距离:|x1-x2| + |y1-y2|return std::abs(x1 - x2) + std::abs(y1 - y2);}// 检查坐标是否有效(在地图范围内且可通行)bool is_valid(int x, int y) const {// 检查坐标是否在地图范围内if (x < 0 || x >= map_width_ || y < 0 || y >= map_height_)return false;// 检查是否为可通行区域(0表示可通行)return grid_map_[y][x] == 0;}// 回溯构建路径(从终点到起点)void build_path(Node* target, std::vector<std::pair<int, int>>& path) const {path.clear();Node* current = target;// 从终点回溯到起点while (current != nullptr) {path.emplace_back(current->x, current->y);current = current->parent;}// 反转路径,使其从起点到终点std::reverse(path.begin(), path.end());}public:// 构造函数:初始化地图信息AStar(const std::vector<std::vector<int>>& map): grid_map_(map),map_height_(map.size()),map_width_(map.empty() ? 0 : map[0].size()) {// 初始化节点池reset_nodes();}// 重置所有节点状态(用于多次寻路)void reset_nodes() {node_pool_.clear();node_pool_.resize(map_height_);// 为每个网格位置创建节点for (int y = 0; y < map_height_; ++y) {node_pool_[y].resize(map_width_);for (int x = 0; x < map_width_; ++x) {node_pool_[y][x] = std::make_unique<Node>(x, y);}}}// 查找路径主函数bool find_path(const std::pair<int, int>& start,const std::pair<int, int>& target,std::vector<std::pair<int, int>>& path) {// 验证地图是否有效if (map_height_ == 0 || map_width_ == 0)return false;// 验证起点和终点是否有效if (!is_valid(start.first, start.second) ||!is_valid(target.first, target.second)) {return false;}// 方向数组:上、右、下、左(四个基本方向)static const std::vector<std::pair<int, int>> directions = {{0, 1}, // 向下移动{1, 0}, // 向右移动{0, -1}, // 向上移动{-1, 0} // 向左移动};// 使用优先队列作为开放列表(待探索节点)std::priority_queue<Node*, std::vector<Node*>, NodeCompare> open_queue;// 获取起点和终点节点Node* start_node = node_pool_[start.second][start.first].get();Node* target_node = node_pool_[target.second][target.first].get();// 初始化起点节点start_node->g_value = 0; // 起点到起点的代价为0start_node->h_value = heuristic(start.first, start.second,target.first, target.second);start_node->state = NodeState::OPEN;open_queue.push(start_node);// 主循环:处理开放列表中的节点while (!open_queue.empty()) {// 获取当前最佳节点(f值最小的节点)Node* current = open_queue.top();open_queue.pop();// 跳过已被关闭的节点(避免重复处理)if (current->state == NodeState::CLOSED)continue;// 检查是否到达目标节点if (current == target_node) {build_path(current, path);return true;}// 将当前节点标记为已关闭current->state = NodeState::CLOSED;// 探索当前节点的所有邻居for (const auto& dir : directions) {int nx = current->x + dir.first; // 邻居节点的x坐标int ny = current->y + dir.second; // 邻居节点的y坐标// 跳过无效位置(障碍物或越界)if (!is_valid(nx, ny))continue;// 获取邻居节点Node* neighbor = node_pool_[ny][nx].get();// 计算从起点到邻居的新代价(当前节点代价+1)int new_g = current->g_value + 1;// 如果找到更优路径if (new_g < neighbor->g_value) {// 清除旧状态标记if (neighbor->state == NodeState::OPEN || neighbor->state == NodeState::CLOSED) {neighbor->state = NodeState::UNVISITED;}// 更新邻居节点的父节点和代价neighbor->parent = current;neighbor->g_value = new_g;// 计算启发值(到目标的估算代价)neighbor->h_value = heuristic(nx, ny,target.first, target.second);// 节点加入开放列表neighbor->state = NodeState::OPEN;open_queue.push(neighbor);}}}return false; // 未找到路径}
};// 获取两点间的移动方向
char get_direction(const std::pair<int, int>& from, const std::pair<int, int>& to) {int dx = to.first - from.first; // x方向变化int dy = to.second - from.second; // y方向变化// 根据移动方向返回对应字符if (dx == 1) return '>'; // 向右移动if (dx == -1) return '<'; // 向左移动if (dy == 1) return 'v'; // 向下移动if (dy == -1) return '^'; // 向上移动return '*'; // 默认(通常不会发生)
}// 可视化路径
void visualize_path(const std::vector<std::pair<int, int>>& path,const std::vector<std::vector<int>>& grid) {if (path.empty()) return;// 创建显示网格(初始化为'.')std::vector<std::vector<char>> display(grid.size(),std::vector<char>(grid[0].size(), '.'));// 标记障碍物for (size_t y = 0; y < grid.size(); y++) {for (size_t x = 0; x < grid[0].size(); x++) {if (grid[y][x] == 1) {display[y][x] = '#'; // 障碍物}}}// 当路径只有起点时特殊处理if (path.size() == 1) {display[path[0].second][path[0].first] = 'S';for (const auto& row : display) {for (char cell : row) {std::cout << cell << ' ';}std::cout << std::endl;}return;}// 标记起点和终点display[path.front().second][path.front().first] = 'S'; // 起点display[path.back().second][path.back().first] = 'E'; // 终点// 标记路径方向for (size_t i = 0; i < path.size() - 1; i++) {const auto& curr = path[i];const auto& next = path[i + 1];// 跳过起点(已标记为S)if (i > 0) {char dir = get_direction(curr, next);display[curr.second][curr.first] = dir;}}// 打印可视化地图(增加空格提高可读性)for (const auto& row : display) {for (char cell : row) {std::cout << cell << ' ';}std::cout << std::endl;}
}int main() {// 创建固定10x10网格地图// 0 = 可通行, 1 = 障碍物const std::vector<std::vector<int>> grid = {{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},{0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0},{0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0},{0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0},{0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},{0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0},{0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0},{0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},{0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0},{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}};// 打印地图std::cout << "网格地图 (10x10):\n";for (const auto& row : grid) {for (int cell : row) {std::cout << (cell == 1 ? "# " : ". ");}std::cout << std::endl;}// 创建A*路径查找器AStar pathfinder(grid);std::vector<std::pair<int, int>> path;// 测试路径1: (0,0) -> (9,9)std::cout << "\n测试路径 (0,0) -> (9,9)\n";auto start_time = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();bool found = pathfinder.find_path({ 0, 0 }, { 9, 9 }, path);auto end_time = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();auto duration = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::microseconds>(end_time - start_time);if (found) {std::cout << "路径步数: " << path.size() << "\n计算时间: " << duration.count() << "微秒\n";std::cout << "路径点:";for (const auto& p : path) {std::cout << " (" << p.first << "," << p.second << ")";}std::cout << "\n\n可视化:\n";visualize_path(path, grid);}else {std::cout << "未找到路径!\n";}// 重置节点状态(准备下一次寻路)pathfinder.reset_nodes();path.clear();// 测试路径2: (4,4) -> (0,9)std::cout << "\n测试路径 (4,4) -> (0,9)\n";start_time = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();found = pathfinder.find_path({ 4, 4 }, { 0, 9 }, path);end_time = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();duration = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::microseconds>(end_time - start_time);if (found) {std::cout << "路径步数: " << path.size() << "\n计算时间: " << duration.count() << "微秒\n";std::cout << "路径点:";for (const auto& p : path) {std::cout << " (" << p.first << "," << p.second << ")";}std::cout << "\n\n可视化:\n";visualize_path(path, grid);}else {std::cout << "未找到路径!\n";}// 测试起点即终点的情况std::cout << "\n测试路径 (0,0) -> (0,0)\n";pathfinder.reset_nodes();path.clear();found = pathfinder.find_path({ 0, 0 }, { 0, 0 }, path);if (found) {std::cout << "特殊路径:起点即终点\n";visualize_path(path, grid);}return 0;
}
本文通过对A算法的全面剖析,涵盖了从基础原理到高级优化的完整知识体系,提供了可直接应用的C++实现代码。无论是在游戏开发、机器人导航还是任何路径规划场景,理解并掌握A算法都将为相关领域的项目打下坚实基础。 路径规划之路永无止境,A*算法只是精彩旅程的起点!
