0806线程
Part 1.梳理思维导图
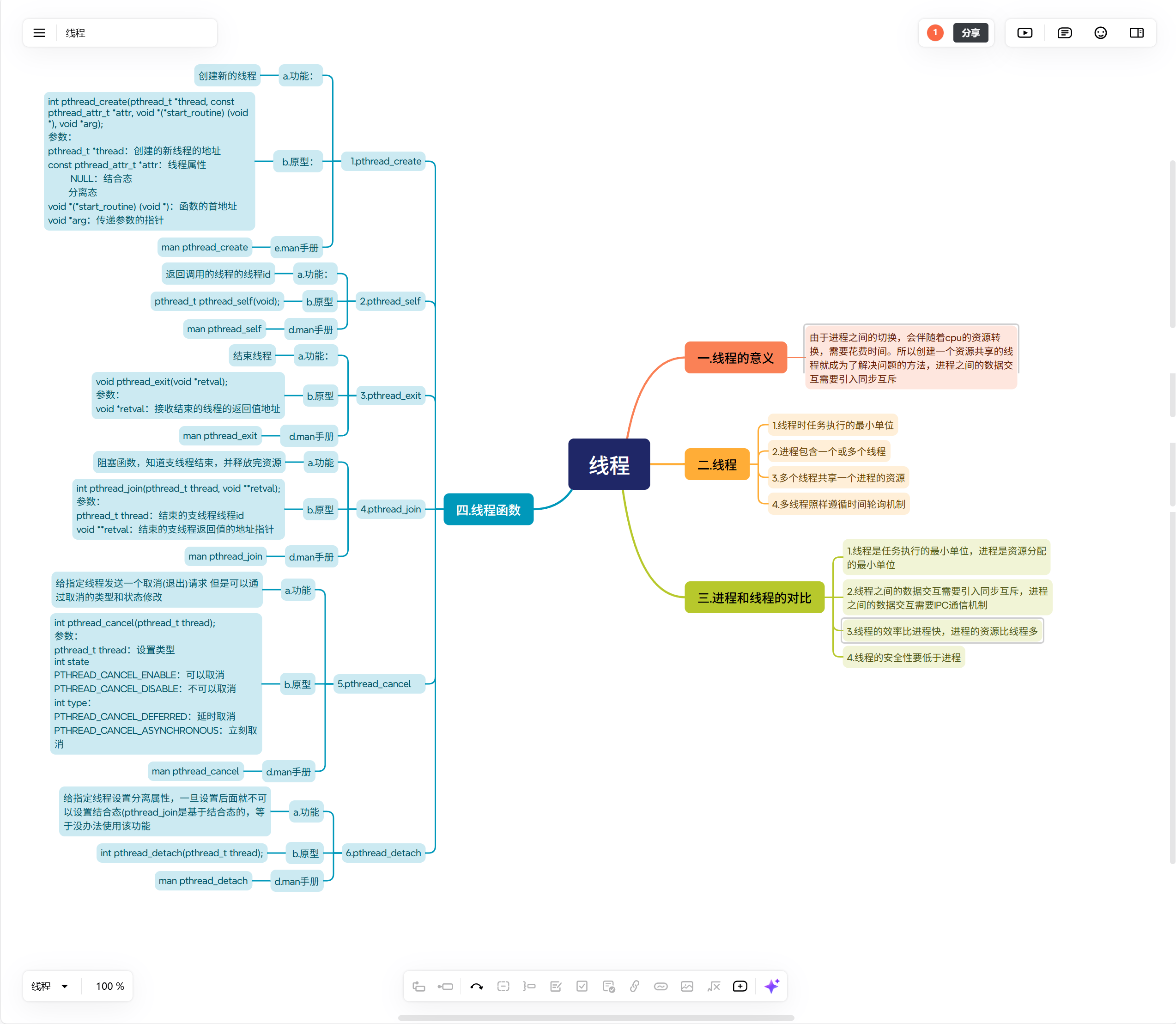
一.线程的意义
由于进程之间的切换,会伴随着cpu的资源转换,需要花费时间。所以创建一个资源共享的线程就成为了解决问题的方法,进程之间的数据交互需要引入同步互斥
二.线程
1.线程时任务执行的最小单位
2.进程包含一个或多个线程
3.多个线程共享一个进程的资源
4.多线程照样遵循时间轮询机制
三.进程和线程的对比
1.线程是任务执行的最小单位,进程是资源分配的最小单位
2.线程之间的数据交互需要引入同步互斥,进程之间的数据交互需要IPC通信机制
3.线程的效率比进程快,进程的资源比线程多
4.线程的安全性要低于进程
四.线程函数
1.pthread_create
a.功能:
创建新的线程
b.原型:
int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread, const pthread_attr_t *attr, void *(*start_routine) (void *), void *arg);
参数:
pthread_t *thread:创建的新线程的地址
const pthread_attr_t *attr:线程属性
NULL:结合态
分离态
void *(*start_routine) (void *):函数的首地址
void *arg:传递参数的指针
c.使用
#include<myhead.h>void *callback1(void *arg)
{//支线程
}int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{pthread_t thread1;//创建的支线程名if(0 != pthread_create(&thread1,NULL,callback1,NULL))//支线程名,结合态,支线程函数名,无返回值{printf("thread1 pthread_create error\n");return -1;}//主线程return 0;
}
d.主线程获得支线程的返回值
#include<myhead.h>void *callback1(void *arg)
{int a = 1;*(int *)arg = &a;printf("支:%d",a);
}int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{pthread_t thread1;//创建的支线程名int b;if(0 != pthread_create(&thread1,NULL,callback1,&b))//支线程名,结合态,支线程函数名,接收返回值存b{printf("thread1 pthread_create error\n");return -1;}printf("%d",b);return 0;
}
e.man手册
man pthread_create
2.pthread_self
a.功能:
返回调用的线程的线程id
b.原型
pthread_t pthread_self(void);
c.使用
#include<myhead.h>void *callback1(void *arg)
{printf("%ld",pthread_self());//输出支线程的线程id
}int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{pthread_t thread1;//创建的支线程名if(0 != pthread_create(&thread1,NULL,callback1,NULL))//支线程名,结合态,支线程函数名,无返回值{printf("thread1 pthread_create error\n");return -1;}//主线程return 0;
}
d.man手册
man pthread_self
3.pthread_exit
a.功能:
结束线程
b.原型
void pthread_exit(void *retval);
参数:
void *retval:接收结束的线程的返回值地址
c.使用
#include<myhead.h>void *callback1(void *arg)
{printf("%ld",pthread_self());pthread_exit(NULL);//不接收返回值
}int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{pthread_t thread1;if(0 != pthread_create(&thread1,NULL,callback1,NULL)){printf("thread1 pthread_create error\n");return -1;}return 0;
}
d.man手册
man pthread_exit
4.pthread_join
a.功能
阻塞函数,知道支线程结束,并释放完资源
b.原型
int pthread_join(pthread_t thread, void **retval);
参数:
pthread_t thread:结束的支线程线程id
void **retval:结束的支线程返回值的地址指针
c.使用
#include<myhead.h>void *callback1(void *arg)
{static int i = 1;printf("%ld",pthread_self());pthread_exit(&i);//不接收返回值
}int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{pthread_t thread1;if(0 != pthread_create(&thread1,NULL,callback1,NULL)){printf("thread1 pthread_create error\n");return -1;}int *i = NULL;pthread_join(thread1,(void**)&i);return 0;
}
d.man手册
man pthread_join
5.pthread_cancel
a.功能
给指定线程发送一个取消(退出)请求 但是可以通过取消的类型和状态修改
b.原型
int pthread_cancel(pthread_t thread);
参数:
pthread_t thread:设置类型
int state
PTHREAD_CANCEL_ENABLE:可以取消
PTHREAD_CANCEL_DISABLE:不可以取消
int type:
PTHREAD_CANCEL_DEFERRED:延时取消
PTHREAD_CANCEL_ASYNCHRONOUS:立刻取消
c.使用
#include<myhead.h>void *callback(void *arg)
{//pthread_setcancelstate(PTHREAD_CANCEL_DISABLE,NULL);//pthread_setcancelstate(PTHREAD_CANCEL_ENABLE,NULL);//pthread_setcanceltype(PTHREAD_CANCEL_ASYNCHRONOUS,NULL);pthread_setcanceltype(PTHREAD_CANCEL_DEFERRED,NULL);static int i = 0;while(1){printf("1\n");sleep(1);}printf("支 = %ld\n",pthread_self());pthread_exit(&i);
}int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{pthread_t thread;if(0 != pthread_create(&thread,NULL,callback,NULL)){printf("pthread_create error\n");return -1;}sleep(3);while(1){//printf("1\n");sleep(1);}pthread_join(thread,NULL);while(1);return 0;
}
d.man手册
man pthread_cancel
6.pthread_detach
a.功能
给指定线程设置分离属性,一旦设置后面就不可以设置结合态(pthread_join是基于结合态的,等于没办法使用该功能
b.原型
int pthread_detach(pthread_t thread);
c.使用
#include<myhead.h>void *callback(void *arg)
{static int i = 0;while(1){printf("1\n");sleep(1);}printf("支 = %ld\n",pthread_self());pthread_exit(&i);
}int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{pthread_t thread;if(0 != pthread_create(&thread,NULL,callback,NULL)){printf("pthread_create error\n");return -1;}sleep(3);pthread_cancel(thread);while(1){//printf("1\n");sleep(1);}pthread_join(thread,NULL);while(1);return 0;
}
d.man手册
man pthread_detach
Part 2.使用创建两个线程,一个线程拷贝文件的前一部分,另一个线程拷贝文件的后一部分
#include<myhead.h>void *callback1(void *arg)
{FILE *fp = fopen("./protect.c","r");FILE *fp2 = fopen("./cp_protect.c","w");fseek(fp,0,SEEK_END);int len = ftell(fp);rewind(fp);rewind(fp2);char a;for(int i = 0; i < len / 2; i++){if( 1 > fread(&a,1,1,fp))break;fwrite(&a,1,1,fp2);}printf("1\n");fclose(fp);fclose(fp2);pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void *callback2(void *arg)
{ sleep(1);FILE *fp = fopen("./protect.c","r");FILE *fp2 = fopen("./cp_protect.c","a");fseek(fp,0,SEEK_END);int len = ftell(fp);fseek(fp,len/2,SEEK_SET);fseek(fp2,len/2,SEEK_SET);char a;for(int i = len / 2; i < len; i++){if( 1 > fread(&a,1,1,fp))break;fwrite(&a,1,1,fp2);}printf("2\n");fclose(fp);fclose(fp2);pthread_exit(NULL);
}int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{pthread_t thread1;if(0 != pthread_create(&thread1,NULL,callback1,NULL)){printf("thread1 pthread_create error\n");return -1;}pthread_t thread2;if(0 != pthread_create(&thread2,NULL,callback2,NULL)){printf("thread2 pthread_create error\n");return -1;}pthread_join(thread1,NULL); pthread_join(thread2,NULL);return 0;
}
Part 3.创建两个线程,一个线程实现字符串的逆置,另一个线程打印字符串,并要求打印顺序是一正一反交替打印 flag
eg:
hello
olleh
hello
olleh
#include<myhead.h>
char a[] = "hello";
void *callback1(void *arg)
{ char *b = (char *)arg;strcpy(b,a);int len = strlen(b);for(int i = 0; i < len/2; i++){char s = b[i];b[i] = b[len-i-1];b[len-i-1] = s;}pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void *callback2(void *arg)
{ sleep(1);int flag = 0;for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){if(flag){printf("%s\n",(char *)arg);flag = 0;}else if (flag == 0){printf("%s\n",a);flag = 1;}}pthread_exit(NULL);
}int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{char arr[128] = "";pthread_t thread1;if(0 != pthread_create(&thread1,NULL,callback1,arr)){printf("thread1 pthread_create error\n");return -1;}pthread_t thread2;if(0 != pthread_create(&thread2,NULL,callback2,arr)){printf("thread2 pthread_create error\n");return -1;}pthread_join(thread1,NULL); pthread_join(thread2,NULL);return 0;
}
