09-堆
1. 堆的定义
堆: 一颗父节点大于等于(或小于等于)子树中所有节点的特殊完全二叉树.
2. 堆的存储
堆的存储 -- 二叉树的顺序存储
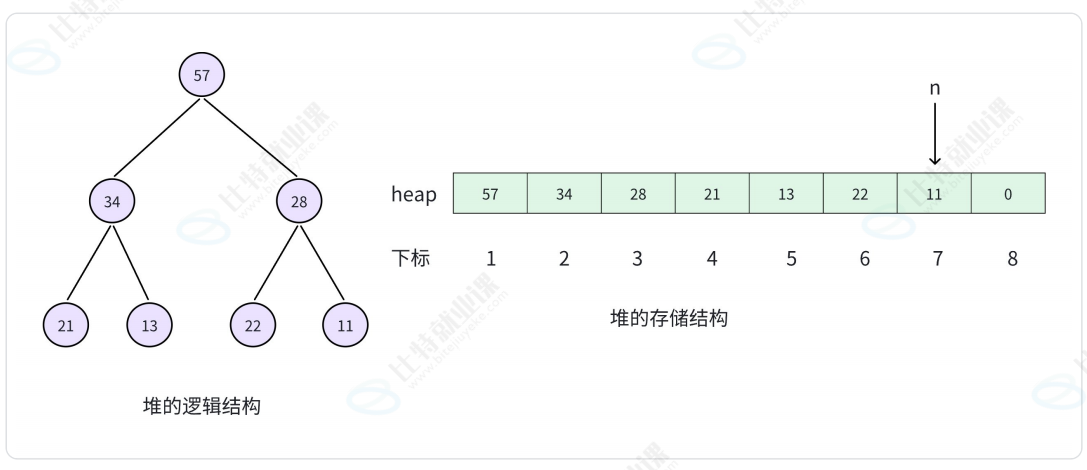
结点下标为:
- 如果父存在,父下标为i/2;
- 如果左孩子存在,左孩子下标为×2;
- 如果右孩子存在,右孩子下标为× 2+1。
3. 堆的核心操作 -- 向上向下调整算法
int n;
int heap[N];// 向上调整算法
void up(int child)
{int parent = child / 2;// 当父结点存在,并且大于父结点的权值时while(parent >= 1 && heap[child] > heap[parent]){swap(heap[child], heap[parent]);child = parent;parent = child / 2;}
}// 向下调整算法
void down(int parent)
{int child = parent * 2;// 如果存在孩子while(child <= n){// 找出最大的孩子if(child + 1 <= n && heap[child + 1] > heap[child]) child++;if(heap[parent] >= heap[child]) return;swap(heap[parent], heap[child]);parent = child;child = parent * 2;}
}4. 堆的模拟实现
#include <iostream>using namespace std;const int N = 1e6 + 10;int n;
int heap[N];// 向上调整算法
void up(int child)
{int parent = child / 2;// 当父结点存在,并且大于父结点的权值时while(parent >= 1 && heap[child] > heap[parent]){swap(heap[child], heap[parent]);child = parent;parent = child / 2;}
}// 向下调整算法
void down(int parent)
{int child = parent * 2;// 如果存在孩子while(child <= n){// 找出最大的孩子if(child + 1 <= n && heap[child + 1] > heap[child]) child++;if(heap[parent] >= heap[child]) return;swap(heap[parent], heap[child]);parent = child;child = parent * 2;}
}// 插入元素
void push(int x)
{heap[++n] = x;up(n);
}// 删除堆顶元素
void pop()
{swap(heap[1], heap[n]);n--;down(1);
}// 查询堆顶元素
int top()
{return heap[1];
}// 堆的大小
int size()
{return n;
}int main()
{// 测试堆int a[10] = {1, 41, 23, 10, 11, 2, -1, 99, 14, 0};// 将这 10 个数依次放入堆中for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){push(a[i]);}while(size()){cout << top() << " ";pop();}return 0;
}5. STL -- 堆的实现 priority_queue
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue> // 优先级队列的头文件using namespace std;int a[10] = {1, 41, 23, 10, 11, 2, -1, 99, 14, 0};struct node
{int a, b, c;// 重载 < 运算符// 按照 b 为基准,创建大根堆// bool operator < (const node& x) const// {// return b < x.b;// }// 按照 b 为基准,创建小根堆bool operator < (const node& x) const{return b > x.b;}
};// 结构体类型
void test2()
{priority_queue<node> heap;for(int i = 1; i <= 5; i++){heap.push({i + 5, i + 1, i + 2});}while(heap.size()){node t = heap.top(); heap.pop();cout << t.a << " " << t.b << " " << t.c << endl;}
}// 内置类型
void test1()
{// 大根堆priority_queue<int> heap1; // 默认就是大根堆// priority_queue<数据类型, 存储结构, 比较方式>// less 和 greaterpriority_queue<int, vector<int>, less<int>> heap2;// 小根堆priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> heap3;// 记忆方式:// 大根堆用小于// 小根堆用大于for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){heap2.push(a[i]);heap3.push(a[i]);}cout << "大根堆:";while(heap2.size()){cout << heap2.top() << " ";heap2.pop();}cout << endl;cout << "小根堆:";while(!heap3.empty()){cout << heap3.top() << " ";heap3.pop();}}6. 算法习题
6.1. P3378 【模板】堆
模拟一个堆
P3378 【模板】堆 - 洛谷
#include <iostream>using namespace std;const int N = 1e6 + 10;int n; // 标记堆的大小
int heap[N]; // 小根堆// 向上调整算法
void up(int child)
{int parent = child / 2;while(parent >= 1 && heap[child] < heap[parent]){swap(heap[child], heap[parent]);child = parent;parent = child / 2;}
}// 向下调整算法
void down(int parent)
{int child = parent * 2; // 左孩子while(child <= n){// 找出两个孩子中的最小值if(child + 1 <= n && heap[child + 1] < heap[child]) child++;if(heap[child] >= heap[parent]) return;swap(heap[child], heap[parent]);parent = child;child = parent * 2;}
}// 进堆
void push(int x)
{n++;heap[n] = x;up(n);
}// 删除堆顶元素
void pop()
{swap(heap[1], heap[n]);n--;down(1);
}int main()
{int T; cin >> T;while(T--){int op; cin >> op;if(op == 1) // 进堆{int x; cin >> x;push(x);}else if(op == 2) // 输出堆顶{cout << heap[1] << endl;}else // 删除堆顶元素{pop();}}return 0;
}6.2. 第k小
TopK问题
第 k 小
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>using namespace std;int n, m, k;
priority_queue<int> heap; // 默认就是大根堆int main()
{cin >> n >> m >> k;for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){int x; cin >> x;heap.push(x);if(heap.size() > k) heap.pop();}while(m--){int op; cin >> op;if(op == 1) // 来了一个数{int x; cin >> x;heap.push(x);if(heap.size() > k) heap.pop();}else if(op == 2) // 查询第 k 小{if(heap.size() == k) cout << heap.top() << endl;else cout << -1 << endl;}}return 0;
}6.3. 除2!
用堆取最值
除2!
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>using namespace std;typedef long long LL;int n, k;
priority_queue<int> heap; // 默认就是大根堆int main()
{cin >> n >> k;LL sum = 0; // 标记所有元素的和for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){int x; cin >> x;sum += x;if(x % 2 == 0) heap.push(x);}while(heap.size() && k--){int t = heap.top() / 2;heap.pop();sum -= t;if(t % 2 == 0) heap.push(t);}cout << sum << endl;return 0;
}6.4. P2085 最小函数值
ideas: {函数取值, 函数本身, 函数值} 为单位push 到堆中, 用堆快速找最值, 然后对应位置函数取值+=1即可.
P2085 最小函数值 - 洛谷
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>using namespace std;typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e4 + 10;int n, m;
LL a[N], b[N], c[N];struct node
{LL f; // 函数值LL num; // 函数编号LL x; // 代入值bool operator <(const node& x) const{// 小根堆,大元素下坠return f > x.f;}
};priority_queue<node> heap;LL calc(LL i, LL x)
{return a[i] * x * x + b[i] * x + c[i];
}int main()
{cin >> n >> m;for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){cin >> a[i] >> b[i] >> c[i];}// 1. 把 x = 1 的值放入堆中for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){heap.push({calc(i, 1), i, 1});}// 2. 依次拿出 m 个值while(m--){auto t = heap.top(); heap.pop();LL f = t.f, num = t.num, x = t.x;cout << f << " ";// 把下一个函数值放入堆中heap.push({calc(num, x + 1), num, x + 1});}return 0;
}6.5. P1631 序列合并
ideas: 固定A, 把所有A的情况push到堆中, 用堆快速取最值, 然后不断测试b(b+=1)即可.
P1631 序列合并 - 洛谷
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>using namespace std;const int N = 1e5 + 10;int n;
int a[N], b[N];struct node
{int sum; // 当前的和int i, j; // a 和 b 的编号bool operator < (const node& x) const{// 小根堆,大元素下坠return sum > x.sum;}
};priority_queue<node> heap; // 小根堆int main()
{cin >> n;for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> b[i];// 1. 将 a[i] + b[1] 放进堆里面for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){heap.push({a[i] + b[1], i, 1});}// 2. 依次拿出 n 的数for(int k = 1; k <= n; k++){node t = heap.top(); heap.pop();int sum = t.sum, i = t.i, j = t.j;cout << sum << " ";if(j + 1 <= n) heap.push({a[i] + b[j + 1], i, j + 1});}return 0;
}6.6. P1878 舞蹈课
ideas: 舞伴配对, 以相邻异性差值为单位push堆, 用堆快速找最值, 然后pop出对应的差值即可.
note: pop堆的时候, 可能会重新push差值 并 某些差值失效
P1878 舞蹈课 - 洛谷
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>using namespace std;const int N = 2e5 + 10;int n;
int s[N]; // 标记男女 - 0/1// 双向链表存数据 -> 用来快速get新的差值
int e[N];
int pre[N], ne[N];struct node
{int d; // 技术差int l, r; // 左右编号// 小根堆,大元素下坠bool operator < (const node& x) const{if(d != x.d) return d > x.d;else if(l != x.l) return l > x.l;else return r > x.r;}
};priority_queue<node> heap;
bool st[N]; // 标记已经出队的人int main()
{cin >> n;for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){char ch; cin >> ch;if(ch == 'B') s[i] = 1;}for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){cin >> e[i];// 创建双向链表pre[i] = i - 1;ne[i] = i + 1;}pre[1] = ne[n] = 0; // 0 表示后面没有元素// 1. 先把所有的异性差放进堆中for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++){if(s[i] != s[i - 1]){heap.push({abs(e[i] - e[i - 1]), i - 1, i});}}// 2. 提取结果vector<node> ret; // 暂存结果while(heap.size()){node t = heap.top(); heap.pop();int d = t.d, l = t.l, r = t.r;if(st[l] || st[r]) continue;ret.push_back(t);st[l] = st[r] = true; // 标记 l 和 r 已经出列// 修改指针,还原新的队列ne[pre[l]] = ne[r];pre[ne[r]] = pre[l];// 判断新的左右是否会成为一对int left = pre[l], right = ne[r];if(left && right && s[left] != s[right]){heap.push({abs(e[left] - e[right]), left, right});}}cout << ret.size() << endl;for(auto& x : ret){cout << x.l << " " << x.r << endl;}return 0;
}