CD73.【C++ Dev】map和set练习题1(有效的括号、复杂链表的复制)
目录
1.有效的括号
分析
代码
提交结果
2.复杂链表的复制
分析
代码
提交结果
编辑
1.有效的括号
之前在L11.【LeetCode题解】有效的括号文章用C语言写过,要求采用C++ STL优化以下代码:
typedef char STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{STDataType* a;int top; int capacity;
}ST;void STInit(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);ps->a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * 4);if (ps->a == NULL){perror("malloc");return;}ps->capacity = 4;ps->top = 0;//top栈顶元素的下一个位置
}void STDestory(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);free(ps->a);ps->a = NULL;ps->top = 0;ps->capacity = 0;
}void STPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{assert(ps);if (ps->top == ps->capacity){STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(STDataType) * ps->capacity * 2);if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc");return;}ps->a = tmp;ps->capacity *= 2;}ps->a[ps->top] = x;ps->top++;
}bool STEmpty(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->top == 0;
}
void STPop(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(!STEmpty(ps));//确保不越界ps->top--;
}STDataType STTop(ST* ps)//访问栈顶元素
{assert(ps);assert(!STEmpty(ps));//确保不越界return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}bool isValid(char* s)
{ST st;STInit(&st);while(*s){if (*s=='('||*s=='['||*s=='{'){STPush(&st,*s);}else{if (STEmpty(&st))return false;char top=STTop(&st);//注意STPop(&st);if ((*s==')'&&top !='(')||(*s==']'&&top !='[')||(*s=='}'&&top !='{'))return false;}s++;}bool ret=STEmpty(&st);STDestory(&st);return ret;
}分析
上方代码手动实现了栈的各个操作,可以改用STL的stack<char>
class Solution {
public:bool isValid(string s) {stack<char> st;for (auto ch:s){if (ch=='('||ch=='['||ch=='{'){st.push(ch);}else{if (st.empty())return false;char top=st.top();st.pop();if ((ch==')'&&top !='(')||(ch==']'&&top !='[')||(ch=='}'&&top !='{'))return false;}}return st.empty();}
};
本题考察括号的匹配,匹配问题可以用map,那么if判断可以用map优化
map中存储正确的匹配:
map<char,char> mp;
//调用operator[]比用insert写起来方便
mp['(']=')';
mp['[']=']';
mp['{']='}';简化if判断:
if (mp.count(ch))//如果ch能在map的所有key中能找到,就push
{st.push(ch);
}
else
{if (st.empty())return false;char top=st.top();st.pop();if (mp[top]!=ch)//左右括号不匹配,返回falsereturn false;
}代码
class Solution {
public:bool isValid(string s) {stack<char> st;map<char,char> mp;//调用operator[]比用insert写起来方便mp['(']=')';mp['[']=']';mp['{']='}';for (auto ch:s){if (mp.count(ch))//如果ch能在map的所有key中能找到,就push{st.push(ch);}else{if (st.empty())return false;char top=st.top();st.pop();if (mp[top]!=ch)//左右括号不匹配,返回falsereturn false;}}return st.empty();}
};
提交结果
2.复杂链表的复制
之前在L34.【LeetCode题解】随机链表的复制(复杂链表的复制)文章用C语言写过,要求采用C++ STL优化以下代码:
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head)
{struct Node* cur=head;//插入新节点while(cur){struct Node* newnode=(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));newnode->next=cur->next;newnode->val=cur->val;cur->next=newnode;cur=cur->next->next;}//设置randomcur=head;while(cur){struct Node* copy=cur->next;if (cur->random==NULL){copy->random=NULL;}else{copy->random=cur->random->next;//重要的一步}cur=cur->next->next;}struct Node* copy_head=NULL;struct Node* copy_tail=NULL;cur=head;while(cur){struct Node* copy=cur->next;struct Node* copy_next=copy->next;if (copy_head==NULL)//空链表尾插{copy_head=copy_tail=copy;}else//非空链表尾插{copy_tail->next=copy;copy_tail=copy_tail->next;//更新尾部}cur->next=copy_next;//恢复原链表cur=cur->next;}return copy_head;
}分析
首先复制链表,暂时`不处理random指针
if (head==nullptr)return nullptr;
Node* cur=head;//遍历要复制的链表
Node* copy=nullptr;
Node* copy_head=nullptr;//保存拷贝链表的头节点
for(;;)
{if (copy==nullptr){copy=new Node(cur->val);copy_head=copy;cur=cur->next;}else if (cur){copy->next=new Node(cur->val);copy=copy->next;cur=cur->next;}else//复制完毕break;
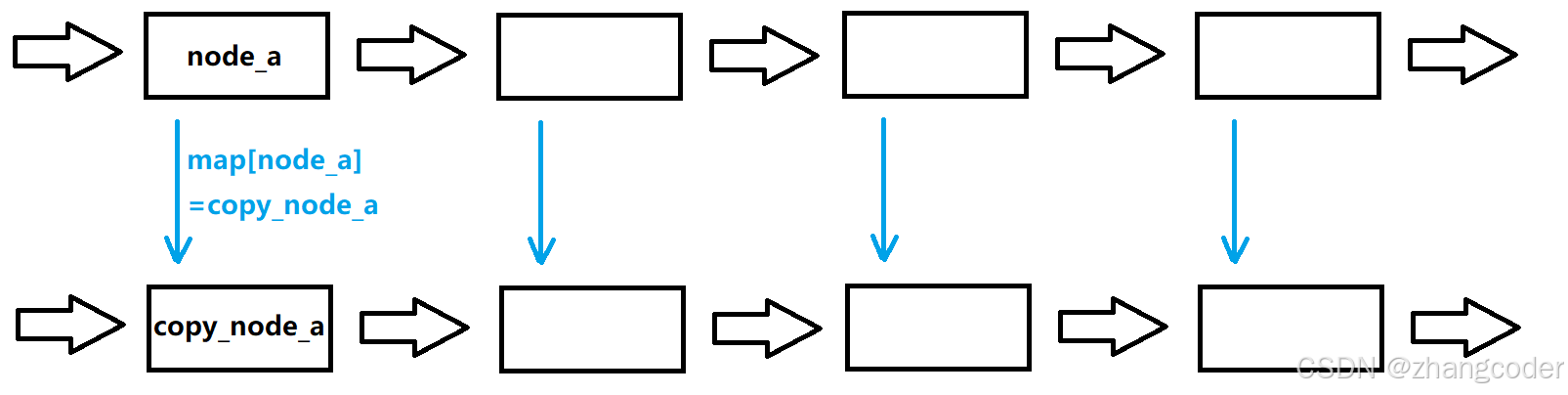
}链表复制中比较难处理的是random指针指向的节点,处理方法: 用map提前存映射,让cur指向的节点和copy指向的节点一一对应
那么在设置random时:
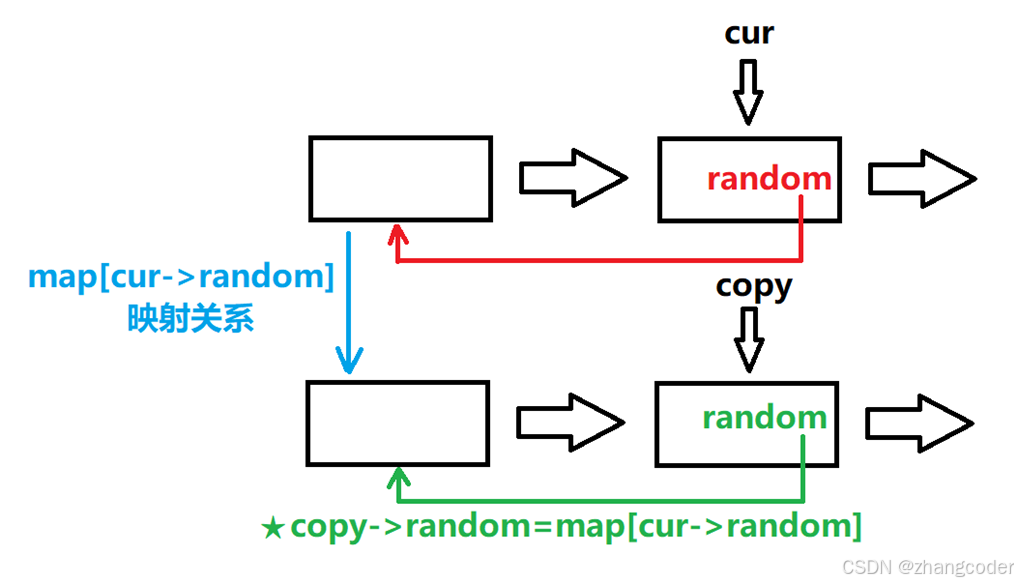
解读图片: cur指向的节点的random的值为cur->random,指向的节点对应在新链表中的位置为map[cur->random],这下copy->random就好设置值了
那么可以边复制链表(不包含设置random指针)边设置map<Node*,Node*>:
if (head==nullptr)return nullptr;
Node* cur=head;//遍历要复制的链表
Node* copy=nullptr;
Node* copy_head=nullptr;//保存拷贝链表的头节点
map<Node*,Node*> mp;
for(;;)
{if (copy==nullptr){copy=new Node(cur->val);mp[cur]=copy;copy_head=copy;cur=cur->next;}else if (cur){copy->next=new Node(cur->val);copy=copy->next;mp[cur]=copy;cur=cur->next;}else//复制完毕break;
}最后依据map的内容设置复制链表的指针:
//设置random
copy=copy_head;
cur=head;
while(copy)
{copy->random=mp[cur->random];cur=cur->next;copy=copy->next;
}代码
class Solution {
public:Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {if (head==nullptr)return nullptr;Node* cur=head;//遍历要复制的链表Node* copy=nullptr;Node* copy_head=nullptr;//保存拷贝链表的头节点map<Node*,Node*> mp;for(;;){if (copy==nullptr){copy=new Node(cur->val);mp[cur]=copy;copy_head=copy;cur=cur->next;}else if (cur){copy->next=new Node(cur->val);copy=copy->next;mp[cur]=copy;cur=cur->next;}else//复制完毕break;}//设置randomcopy=copy_head;cur=head;while(copy){copy->random=mp[cur->random];cur=cur->next;copy=copy->next;}return copy_head;}
};