0904 类的继承
Part 1.梳理思维导图
一.继承中的特殊成员函数
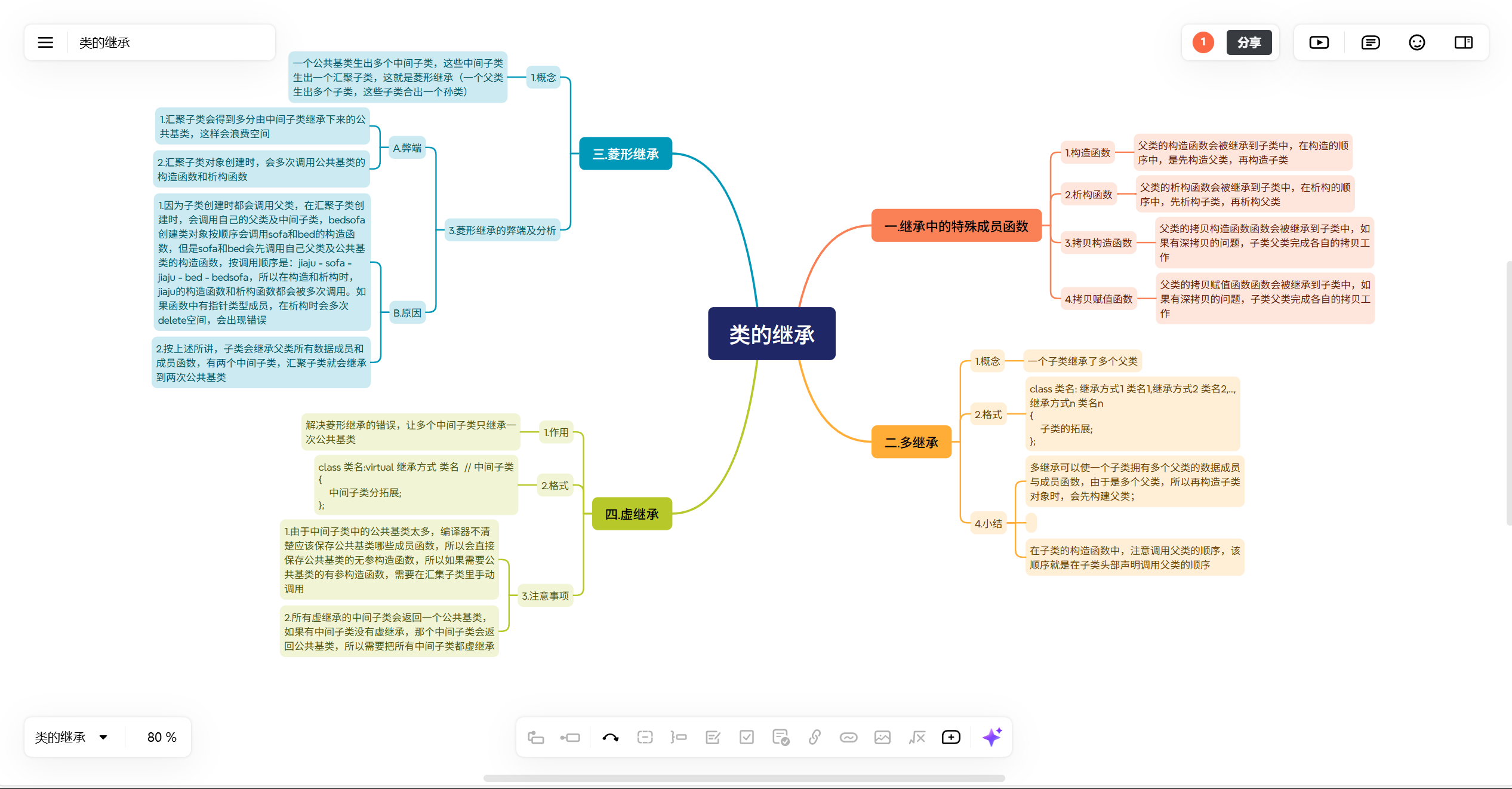
1.构造函数
父类的构造函数会被继承到子类中,在构造的顺序中,是先构造父类,再构造子类
#include <iostream>using namespace std;class Father
{
public:string name;
protected:int *age;
private:int weight;
public:Father(){age = nullptr;cout << "Father::无参构造函数" << endl;}Father(string n,int a,int w):name(n),age(new int(a)),weight(w){cout << "Father::有参构造函数" << endl;}void show(){cout << name << " " << *age << " " << weight << endl;}
};class Son:public Father
{
private:string sonname;int *sonage;
public:Son(){sonage = nullptr;cout << "Son::无参构造函数" << endl;}Son(string sn,int sa,string fn,int a,int w):Father(fn,a,w),sonname(sn),sonage(new int(sa)){cout << "Son::有参构造函数" << endl;}void show(){cout << sonname << " " << *sonage << " ";Father::show();}
};int main()
{Son s1("张四",18,"张三",40,100);s1.show();return 0;
}
在创建子类时,会先调用父类的构造函数,再调用子类的构造函数
2.析构函数
父类的析构函数会被继承到子类中,在析构的顺序中,先析构子类,再析构父类
#include <iostream>using namespace std;class Father
{
public:string name;
protected:int *age;
private:int weight;
public:Father(){age = nullptr;cout << "Father::无参构造函数" << endl;}Father(string n,int a,int w):name(n),age(new int(a)),weight(w){cout << "Father::有参构造函数" << endl;}~Father(){delete age;age = nullptr;cout << "Father::析构函数" << endl;}void show(){cout << name << " " << *age << " " << weight << endl;}
};class Son:public Father
{
private:string sonname;int *sonage;
public:Son(){sonage = nullptr;cout << "Son::无参构造函数" << endl;}Son(string sn,int sa,string fn,int a,int w):Father(fn,a,w),sonname(sn),sonage(new int(sa)){cout << "Son::有参构造函数" << endl;}~Son(){delete sonage;sonage = nullptr;cout << "Son::析构函数" << endl;}void show(){cout << sonname << " " << *sonage << " ";Father::show();}
};int main()
{Son s1("张四",18,"张三",40,100);s1.show();return 0;
}
在函数结束时,释放子类,会先调用子类的析构函数,再调用父类的析构函数
3.拷贝构造函数
父类的拷贝构造函数函数会被继承到子类中,如果有深拷贝的问题,子类父类完成各自的拷贝工作
#include <iostream>using namespace std;class Father
{
public:string name;
protected:int *age;
private:int weight;
public:Father(){age = nullptr;cout << "Father::无参构造函数" << endl;}Father(string n,int a,int w):name(n),age(new int(a)),weight(w){cout << "Father::有参构造函数" << endl;}~Father(){delete age;age = nullptr;cout << "Father::析构函数" << endl;}Father(const Father &other):name(other.name),age(new int(*(other.age))),weight(other.weight){cout << "Father::拷贝构造函数" << endl;}void show(){cout << name << " " << *age << " " << weight << endl;}
};class Son:public Father
{
private:string sonname;int *sonage;
public:Son(){sonage = nullptr;cout << "Son::无参构造函数" << endl;}Son(string sn,int sa,string fn,int a,int w):Father(fn,a,w),sonname(sn),sonage(new int(sa)){cout << "Son::有参构造函数" << endl;}~Son(){delete sonage;sonage = nullptr;cout << "Son::析构函数" << endl;}Son(const Son &other):Father(other),sonname(other.sonname),sonage(new int(*(other.sonage))){cout << "Son::拷贝构造函数" << endl;}void show(){cout << sonname << " " << *sonage << " ";Father::show();}
};int main()
{Son s1("张四",18,"张三",40,100);s1.show();Son s2 = s1;s2.show();return 0;
}
在子类对象就行拷贝构造时,会调用子类的拷贝构造函数拷贝子类的内容,并调用父类的拷贝构造函数拷贝父类内容,最后构造另一个子类对象
4.拷贝赋值函数
父类的拷贝赋值函数函数会被继承到子类中,如果有深拷贝的问题,子类父类完成各自的拷贝工作
#include <iostream>using namespace std;class Father
{
public:string name;
protected:int *age;
private:int weight;
public:Father(){age = nullptr;cout << "Father::无参构造函数" << endl;}Father(string n,int a,int w):name(n),age(new int(a)),weight(w){cout << "Father::有参构造函数" << endl;}Father &operator=(const Father &other){if(this != &other){name = other.name;age = new int(*(other.age));weight = other.weight;}cout << "Father::拷贝赋值函数" << endl;return *this;}void show(){cout << name << " " << *age << " " << weight << endl;}
};class Son:public Father
{
private:string sonname;int *sonage;
public:Son(){sonage = nullptr;cout << "Son::无参构造函数" << endl;}Son(string sn,int sa,string fn,int a,int w):Father(fn,a,w),sonname(sn),sonage(new int(sa)){cout << "Son::有参构造函数" << endl;}Son &operator=(const Son &other){if(this != &other){sonname = other.sonname;sonage = new int(*(other.sonage));Father::operator = (other);}cout << "Son::拷贝赋值函数" << endl;return *this;}void show(){cout << sonname << " " << *sonage << " ";Father::show();}
};int main()
{Son s1("张四",18,"张三",40,100);s1.show();Son s3;s3 = s1;s3.show();return 0;
}
二.多继承
1.概念
一个子类继承了多个父类
2.格式
class 类名: 继承方式1 类名1,继承方式2 类名2,...,继承方式n 类名n
{子类的拓展;
};3.例子
#include <iostream>using namespace std;class Sofa
{
private:string sit;
public:Sofa(){cout << "Sofa::无参构造函数" << endl;}Sofa(string sit):sit(sit){cout << "Sofa::有参构造函数" << endl;}~Sofa(){cout << "Sofa::析构函数" << endl;}void show(){Jiaju::show();cout << sit << endl;}
};class Bed
{
private:string sleep;
public:Bed(){cout << "Bed::无参构造函数" << endl;}Bed(string sleep):sleep(sleep){cout << "Bed::有参构造函数" << endl;}~Bed(){cout << "Bed::析构函数" << endl;}void show(){Jiaju::show();cout << sleep << endl;}
};class Bedsofa:public Sofa,public Bed
{
private:string color;
public:Bedsofa(){cout << "Bedsofa::无参构造函数" << endl;}Bedsofa(string sit,string sleep,string color,):Sofa(sit),Bed(sleep),color(color){cout << "Bedsofa::有参构造函数" << endl;}~Bedsofa(){cout << "Bedsofa::析构函数" << endl;}void show(){Bed::show();Sofa::show();cout << color << endl;}
};int main()
{Bedsofa b1("能坐","能躺","白色",100);b1.show();return 0;
}
4.小结
多继承可以使一个子类拥有多个父类的数据成员与成员函数,由于是多个父类,所以再构造子类对象时,会先构建父类;
在子类的构造函数中,注意调用父类的顺序,该顺序就是在子类头部声明调用父类的顺序
三.菱形继承
1.概念
一个公共基类生出多个中间子类,这些中间子类生出一个汇聚子类,这就是菱形继承
(一个父类生出多个子类,这些子类合出一个孙类)
2.例子
#include <iostream>using namespace std;
class Jiaju
{
private:int weight;
public:Jiaju(){cout << "Jiaju::无参构造函数" << endl;}Jiaju(int weight):weight(weight){cout << "Jiaju::有参构造函数" << endl;}~Jiaju(){cout << "Jiaju::析构函数" << endl;}void show(){cout << weight << endl;}
};class Sofa:public Jiaju
{
private:string sit;
public:Sofa(){cout << "Sofa::无参构造函数" << endl;}Sofa(string sit,int weight):Jiaju(weight),sit(sit){cout << "Sofa::有参构造函数" << endl;}~Sofa(){cout << "Sofa::析构函数" << endl;}void show(){Jiaju::show();cout << sit << endl;}
};class Bed:public Jiaju
{
private:string sleep;
public:Bed(){cout << "Bed::无参构造函数" << endl;}Bed(string sleep,int weight):Jiaju(weight),sleep(sleep){cout << "Bed::有参构造函数" << endl;}~Bed(){cout << "Bed::析构函数" << endl;}void show(){Jiaju::show();cout << sleep << endl;}
};class Bedsofa:public Sofa,public Bed
{
private:string color;
public:Bedsofa(){cout << "Bedsofa::无参构造函数" << endl;}Bedsofa(string sit,string sleep,string color,int weight):Sofa(sit,weight),Bed(sleep,weight),color(color){cout << "Bedsofa::有参构造函数" << endl;}~Bedsofa(){cout << "Bedsofa::析构函数" << endl;}void show(){Bed::show();Sofa::show();cout << color << endl;}
};int main()
{Bedsofa b1("能坐","能躺","白色",100);b1.show();return 0;
}
在该函数中,公共基类(jiaju)生出两个中间子类(bed和sofa),最后俩中间子类生出一个汇聚子类(bedsofa),汇聚子类用到了多继承,继承两个父类及两个中间子类,俩中间子类的共同父类及公共基类
3.菱形继承的弊端及分析
A.弊端
1.汇聚子类会得到多分由中间子类继承下来的公共基类,这样会浪费空间
2.汇聚子类对象创建时,会多次调用公共基类的构造函数和析构函数
B.原因
1.因为子类创建时都会调用父类,在汇聚子类创建时,会调用自己的父类及中间子类,bedsofa创建类对象按顺序会调用sofa和bed的构造函数,但是sofa和bed会先调用自己父类及公共基类的构造函数,按调用顺序是:jiaju - sofa - jiaju - bed - bedsofa,所以在构造和析构时,jiaju的构造函数和析构函数都会被多次调用。如果函数中有指针类型成员,在析构时会多次delete空间,会出现错误
2.按上述所讲,子类会继承父类所有数据成员和成员函数,有两个中间子类,汇聚子类就会继承到两次公共基类
四.虚继承
1.作用
解决菱形继承的错误,让多个中间子类只继承一次公共基类
2.格式
在中间子类继承前面加上virtual
class 类名:virtual 继承方式 类名 // 中间子类
{中间子类分拓展;
};3.注意事项
1.由于中间子类中的公共基类太多,编译器不清楚应该保存公共基类哪些成员函数,所以会直接保存公共基类的无参构造函数,所以如果需要公共基类的有参构造函数,需要在汇集子类里手动调用
2.所有虚继承的中间子类会返回一个公共基类,如果有中间子类没有虚继承,那个中间子类会返回公共基类,所以需要把所有中间子类都虚继承
4.示例
#include <iostream>using namespace std;
class Jiaju
{
private:int weight;
public:Jiaju(){cout << "Jiaju::无参构造函数" << endl;}Jiaju(int weight):weight(weight){cout << "Jiaju::有参构造函数" << endl;}~Jiaju(){cout << "Jiaju::析构函数" << endl;}void show(){cout << weight << endl;}
};class Sofa:virtual public Jiaju//虚继承
{
private:string sit;
public:Sofa(){cout << "Sofa::无参构造函数" << endl;}Sofa(string sit,int weight):Jiaju(weight),sit(sit){cout << "Sofa::有参构造函数" << endl;}~Sofa(){cout << "Sofa::析构函数" << endl;}void show(){Jiaju::show();cout << sit << endl;}
};class Bed:virtual public Jiaju//虚继承
{
private:string sleep;
public:Bed(){cout << "Bed::无参构造函数" << endl;}Bed(string sleep,int weight):Jiaju(weight),sleep(sleep){cout << "Bed::有参构造函数" << endl;}~Bed(){cout << "Bed::析构函数" << endl;}void show(){Jiaju::show();cout << sleep << endl;}
};class Bedsofa:public Sofa,public Bed
{
private:string color;
public:Bedsofa(){cout << "Bedsofa::无参构造函数" << endl;}Bedsofa(string sit,string sleep,string color,int weight):Jiaju(weight),Sofa(sit,weight),Bed(sleep,weight),color(color)//汇聚子类手动调用公共基类{cout << "Bedsofa::有参构造函数" << endl;}~Bedsofa(){cout << "Bedsofa::析构函数" << endl;}void show(){Bed::show();Sofa::show();cout << color << endl;}
};int main()
{Bedsofa b1("能坐","能躺","白色",100);b1.show();return 0;
}
