Java I/O知识归纳
Java I/O(输入/输出)是处理数据输入输出的核心 API,用于文件读写、网络通信等操作。Java I/O 分为 传统 I/O(java.io) 和 NIO(New I/O, java.nio) 两大类。下面详细讲解关键概念和用法:
一、核心概念
流(Stream)
字节流:以字节为单位(8位),处理二进制数据
InputStream/OutputStream(抽象基类)
字符流:以字符为单位(16位 Unicode),处理文本数据
Reader/Writer(抽象基类)
缓冲(Buffering) 通过缓冲区减少物理读写次数,提升性能(如
BufferedInputStream)。装饰者模式 Java I/O 使用装饰者模式动态增强流的功能(如缓冲、字符转换)。
字节流(Byte Streams)深度解析
Java 字节流是处理二进制数据的核心 API,以 8 位字节为单位进行数据读写,适用于所有类型的数据(包括文本、图片、音视频等)。字节流的核心抽象类是 InputStream 和 OutputStream。
一、字节流核心类体系
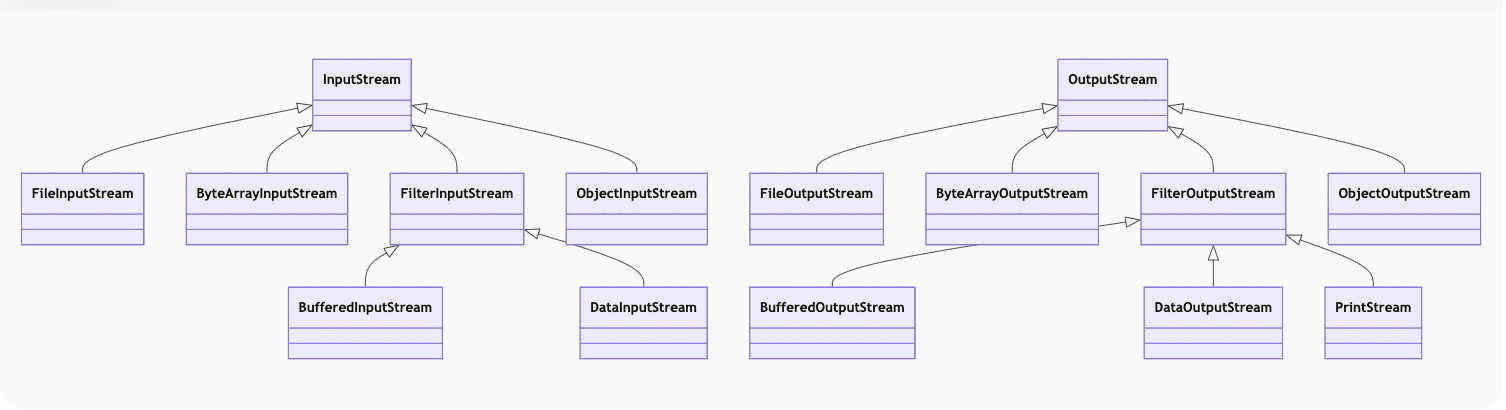
二、关键类详解
1. 基础文件流
FileInputStream:从文件读取字节
try (InputStream is = new FileInputStream("photo.jpg")) {int byteData;while ((byteData = is.read()) != -1) {// 处理每个字节 (0-255)} }FileOutputStream:向文件写入字节
try (OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("copy.jpg")) {byte[] data = {0x48, 0x65, 0x6C, 0x6C, 0x6F}; // Hello 的十六进制os.write(data); }
2. 缓冲流(性能关键)
BufferedInputStream:内置 8KB 缓冲区
try (InputStream is = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("large.bin"), 16384)) { // 16KB 缓冲区// 读取效率提升 5-10 倍 }BufferedOutputStream:写缓冲
try (OutputStream os = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("output.bin"))) {os.write(0xFF); // 不会立即写入磁盘os.flush(); // 强制写入磁盘 }
3. 数据类型处理流
DataInputStream:读取基本数据类型
try (DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("data.bin"))) {int intVal = dis.readInt();double doubleVal = dis.readDouble();boolean boolVal = dis.readBoolean(); }DataOutputStream:写入基本数据类型
try (DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("data.bin"))) {dos.writeInt(1024);dos.writeDouble(3.14);dos.writeBoolean(true); }
4. 对象序列化流
ObjectInputStream / ObjectOutputStream
// 序列化对象 try (ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("user.dat"))) {oos.writeObject(new User("Alice", 25)); } // 反序列化 try (ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("user.dat"))) {User user = (User) ois.readObject(); }注意:被序列化的类必须实现
Serializable接口
5. 内存操作流
ByteArrayInputStream:从内存字节数组读取
byte[] data = "Hello".getBytes(); try (InputStream is = new ByteArrayInputStream(data)) {// 从内存数组读取 }ByteArrayOutputStream:写入内存缓冲区
try (ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream()) {baos.write("World".getBytes());byte[] result = baos.toByteArray(); // 获取内存数据 }
三、核心操作 API
InputStream 关键方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
int read() | 读取单个字节 (0-255),EOF 返回 -1 |
int read(byte[] b) | 读取字节到数组,返回实际读取数 |
int read(byte[] b, int off, int len) | 读取指定长度的字节到数组偏移位置 |
long skip(long n) | 跳过 n 个字节 |
int available() | 返回可读取的字节数(不阻塞) |
void close() | 关闭流 |
mark(int limit) / reset() | 标记/重置读取位置 |
OutputStream 关键方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
void write(int b) | 写入单个字节(低8位) |
void write(byte[] b) | 写入整个字节数组 |
void write(byte[] b, int off, int len) | 写入数组指定范围 |
void flush() | 强制写出缓冲数据 |
void close() | 关闭流 |
四、高效读写模式
1. 缓冲区最佳实践
try (InputStream is = new FileInputStream("source.bin");OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("target.bin")) {byte[] buffer = new byte[8192]; // 8KB缓冲区int bytesRead;while ((bytesRead = is.read(buffer)) != -1) {os.write(buffer, 0, bytesRead); // 写入实际读取量}
}2. 零拷贝技术(Java 9+)
try (InputStream is = new FileInputStream("source.bin");OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("target.bin")) {is.transferTo(os); // 直接传输所有数据,减少拷贝次数
}五、特殊场景处理
1. 大文件分块读取
try (RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile("huge.bin", "r")) {byte[] chunk = new byte[1024 * 1024]; // 1MB 块for (long i = 0; i < raf.length(); i += chunk.length) {raf.seek(i);int read = raf.read(chunk);// 处理数据块}
}2. 资源泄漏防护(try-with-resources)
// 自动关闭多个资源(按声明逆序关闭)
try (InputStream is1 = new FileInputStream("f1.bin");InputStream is2 = new FileInputStream("f2.bin");OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("merged.bin")) {// 合并文件操作
}3. 文件尾部追加
try (OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("log.bin", true)) { // 追加模式os.write("New log entry".getBytes());
}六、字节流 vs 字符流
| 特性 | 字节流 | 字符流 |
|---|---|---|
| 数据单位 | 8位字节 (0-255) | 16位字符 (Unicode) |
| 处理类型 | 二进制数据(所有文件类型) | 文本数据(含编码转换) |
| 核心类 | InputStream/OutputStream | Reader/Writer |
| 性能 | 原始字节操作,速度快 | 需编码转换,稍慢 |
| 缓冲区 | 需手动添加缓冲 | 部分实现内置缓冲 |
| 典型场景 | 图片/视频/压缩文件 | 配置文件/日志/HTML/XML |
最佳实践总结
始终使用缓冲流:用
BufferedInputStream/BufferedOutputStream包装基础流明确指定缓冲区大小:根据文件大小调整(通常 8KB-64KB)
使用 try-with-resources:确保资源关闭,避免泄漏
二进制文件使用字节流:文本文件考虑字符流(需处理编码)
大文件分块处理:避免一次性加载到内存
序列化敏感字段标记 transient:防止敏感数据写入磁盘
NIO 处理高性能场景:如
Files.copy()或FileChannel
