SpringBoot的配置文件
一、 Springboot的热部署
spring为开发者提供了一个名为spring-boot-devtools的模块来使Spring Boot应用支持热部署,提高开发者的开发效率,无需手动重启Spring Boot应用。
需要我们在POM.XML文件中引入依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId> <optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
修改java代码或者配置文件模板后可以通过ctrl+f9来实施热部署。
二、配置文件
SpringBoot使用全局的配置文件,配置文件的名称是固定不变的,但是有两种格式他们分别是
application.yamlapplicatioin.properties二者是互补的优先级是 application.properties>application.yaml
配置文件的作用:修改SpringBoot自动配置的默认值;SpringBoot在底层都给我们自动配置好;
三、YAML语法
1. 缩进:YAML使用空格进行缩进,而不是制表符。缩进表示层级关系,通常使用两个或四个空格。缩进必须一致,否则会导致解析错误。

2. k:(空格)v:表示一对键值对(空格必须有;
3. 普通的值(数字,字符串,布尔):K:V 直接来写,字符串默认不加单引号或者双引号。(对于加了双引号的字符串打印出来 例如"hello \n"会换行,但是单引号就不会出现这种情况)
4. 对象、Map(属性和值)(键值对)对象还是使用K:V 的方式
person: #对象名email: exampleex@ample.com #属性:(空格)属性值last-name: "hello \n"age: 18lists:lisizhaoliudog:name: 花花age: 12 用- 值表示数组中的一个元素
三、 配置文件注入
我们可以导入配置文件处理器,以后编写配置就有提示了
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring‐boot‐configuration‐processor</artifactId><optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
#application.yaml
person:email: exampleex@ample.comlast-name: "hello \n"age: 18lists:lisizhaoliudog:name: 花花age: 12
server:port: 8081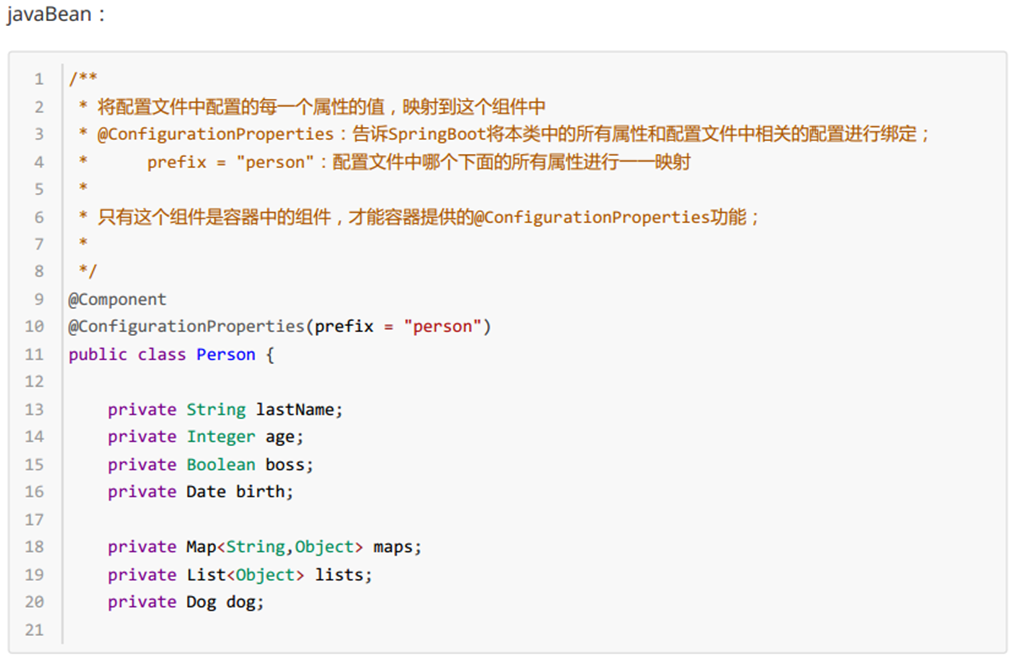
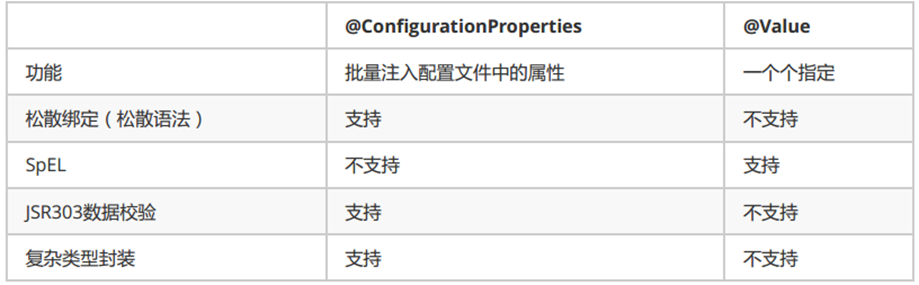
@Value获取值和@ConfigurationProperties获取值比较
4.1 @value注入值
package com.qcby.springboot0720.entity;public class Dog {private String name;private Integer age;public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public Integer getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(Integer age) {this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Dog{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}
}
package com.qcby.springboot0720.entity;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;import javax.validation.constraints.Email;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
@Component//@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
//@Validated
public class Person {@Value("张三")
// @Value("${person.last-name}")private String lastName;private Integer age;
// @Email(message = "邮箱格式无效")private String email;private Boolean boss;
// @Value("2025/11/11")private Date birthday;private Map<String,Object> maps;private List<Object> lists;private Dog dog;@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Person{" +"lastName='" + lastName + '\'' +", age=" + age +", email='" + email + '\'' +", boss=" + boss +", birthday=" + birthday +", maps=" + maps +", lists=" + lists +", dog=" + dog +'}';}public String getLastName() {return lastName;}public void setLastName(String lastName) {this.lastName = lastName;}public Integer getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(Integer age) {this.age = age;}public Boolean getBoss() {return boss;}public void setBoss(Boolean boss) {this.boss = boss;}public Date getBirthday() {return birthday;}public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {this.birthday = birthday;}public Map<String, Object> getMaps() {return maps;}public void setMaps(Map<String, Object> maps) {this.maps = maps;}public List<Object> getLists() {return lists;}public void setLists(List<Object> lists) {this.lists = lists;}public Dog getDog() {return dog;}public void setDog(Dog dog) {this.dog = dog;}public String getEmail() {return email;}public void setEmail(String email) {this.email = email;}
}
测试类
package com.qcby.springboot0720; import com.qcby.springboot0720.entity.Person;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
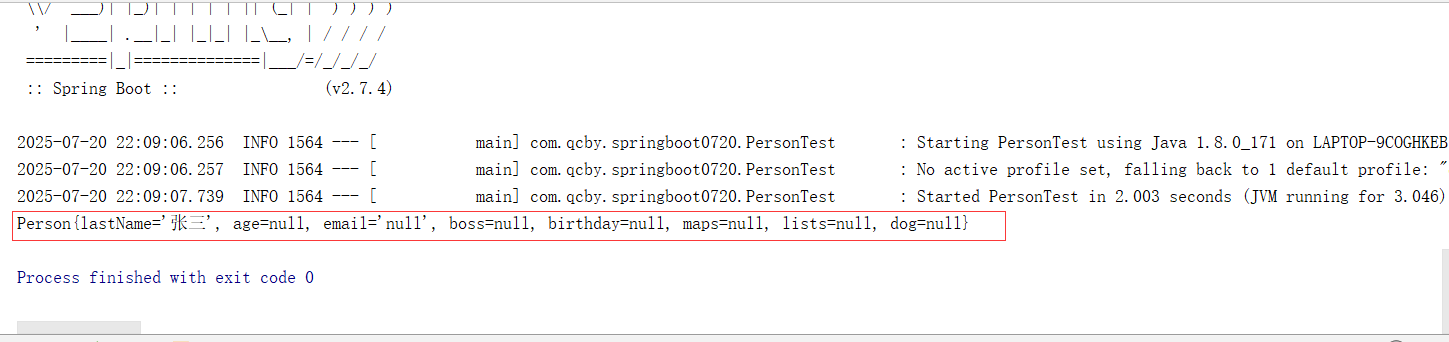
public class PersonTest { @Autowiredprivate Person person;@Testpublic void testPersonInjection() {System.out.println(person.toString());}
}
将先有的注释改为非注释
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")从配置文件前缀是person中拿数据
三、配置文件占位符
1、随机数
${random.value}、${random.int}、${random.long}
${random.int(10)}、${random.int[1024,65536]}
2、占位符获取之前配置的值,如果没有可以是用:指定默认值
person.last‐name=张三${random.uuid}
person.age=${random.int}
person.birth=2017/12/15
person.boss=false
person.maps.k1=v1
person.maps.k2=14
person.lists=a,b,c
person.dog.name=${person.hello:hello}_dog
person.dog.age=15
四、Profile
1、多Profile文件
我们在主配置文件编写的时候,文件名可以是 application-{profile}.properties/yml
默认使用application.properties的配置;
2、yml支持多文档块方式
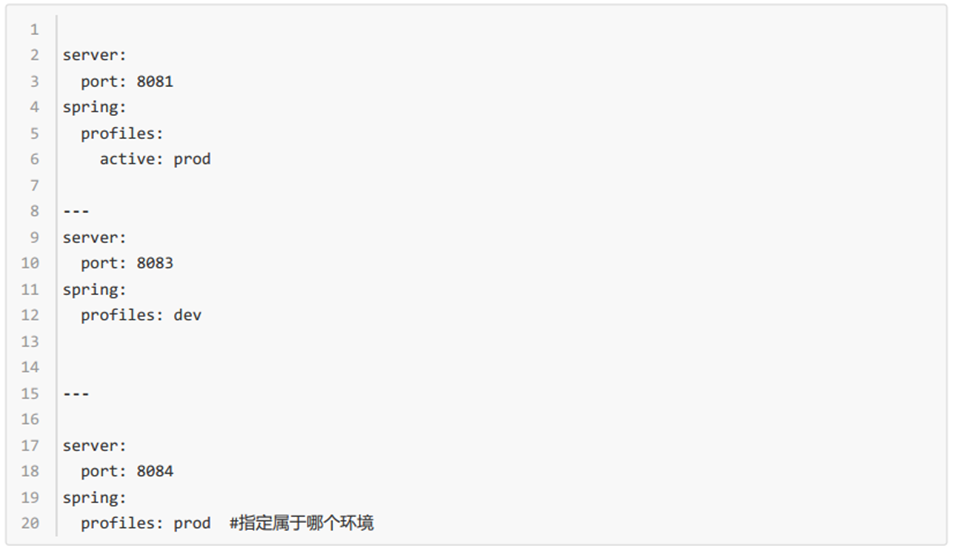
3、激活指定profile
- 在配置文件中指定 spring.profiles.active=dev
- 命令行:
- java -jar spring-boot-02-config-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --spring.profiles.active=dev;
- 可以直接在测试的时候,配置传入命令行参数
- 虚拟机参数;
- -Dspring.profiles.active=dev
