单链表的排序
单链表的排序_牛客题霸_牛客网 (nowcoder.com)
这题主要的难点是链表只能按顺序访问,无法通过下标进行排序。
方法2:既然我们无法通过下标进行访问,那我们就将链表转成数组进行排序,数组排序有sort方法,不需要我们手动实现。
方法1:我们还可以将这个n个节点的单链表分成含n个一个节点的链表, 再将这n个单链表合并成一个有序链表。这个方法就是分治思想,分治算法通常是递归实现的;
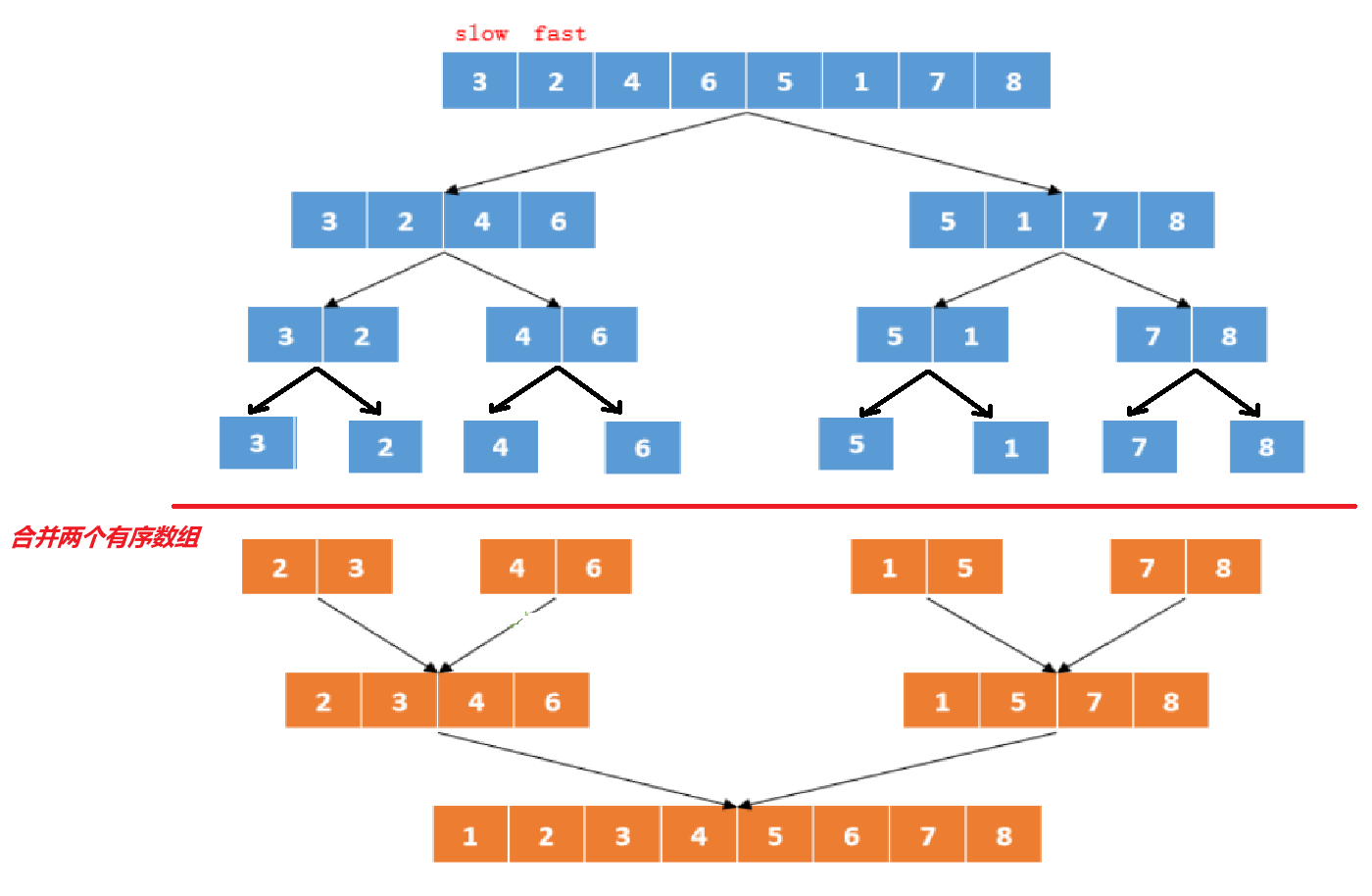
方法1:分治法
public ListNode merge(ListNode h1, ListNode h2) {ListNode vhead = new ListNode(-1);ListNode cur = vhead;while (h1 != null && h2 != null) {if (h1.val < h2.val) {cur.next = h1;h1 = h1.next;} else {cur.next = h2;h2 = h2.next;}cur = cur.next;}if (h1 != null) {cur.next = h1;} else {cur.next = h2;}return vhead.next;
}
//方法1:单链表通过分治思想进行排序,分治的过程通过递归实现的
public ListNode sortInList (ListNode head) {// write code hereif (head == null || head.next == null){return head;//当链表为空或者只有一个元素时,此时的链表时有序的}ListNode slow = head;//慢指针指向头结点ListNode fast = head.next;//快指针在头结点的下一个节点,这样可以的话如果链表的长度为偶数个就可以指向中间节点的左边而不是右边while (fast != null && fast.next != null){slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next.next;}ListNode head2 = slow.next;//记录右半边链表的头结点slow.next = null;//将左右两边链表断开return merge(sortInList(head),sortInList(head2));//将左右两边链表合并成一个有序链表
}同样使用分治思想的链表题:合并k个已排序的链表_牛客题霸_牛客网 (nowcoder.com)
这题也同样使用分治思想,不用的是它可以通过下标查询链表的头结点,所以可以使用二分查找;还可以通过建立小根堆(lamdba表达式)的方式,每出一个节点就放进该节点的下一个节点。
方法2:借助数组 --》改进(使用ArrayList进行存储)
//方法2.通过数组排序的方法对单链表进行排序
public int length(ListNode head){int count = 0;while (head != null){count++;head = head.next;}return count;
}
public ListNode sortInList (ListNode head) {// write code hereint len = length(head);//计算链表长度ListNode cur = head;int[] arr = new int[len];//创建一个相同长度的数组用于存储链表中的数据for (int i = 0; i < len; i++){arr[i] = cur.val;cur = cur.next;}Arrays.sort(arr);//对数组进行排序ListNode vhead = new ListNode(-1);//创建虚拟头结点cur = vhead;for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){cur.next = new ListNode(arr[i]);//创建新结点用于存放排序完数组中的数据cur = cur.next;}return vhead.next;
}//方法2的改进:使用顺序表ArrayList 存储数据
public ListNode sortInList (ListNode head) {// write code hereArrayList<Integer> nums = new ArrayList<>();ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null){nums.add(cur.val);cur = cur.next;}Collections.sort(nums);cur = head;for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++){cur.val = nums.get(i);cur = cur.next;}return head;
}
