JUC入门(一)
JUC
1、什么是JUC
就是java.util工具包里面的 子包
2、进程和线程
线程和进程
进程:就是一个程序,类似于QQ.exe 等程序的集合
一个进程课以包含多个线程,至少包含一个!
java默认有几个线程?2个 main,GC
线程:一个进程中负责一项职责
对java来说如何使用线程:Thread、Runnable、Callable
Java真的可以开线程嘛?不可以
public synchronized void start() {/*** This method is not invoked for the main method thread or "system"* group threads created/set up by the VM. Any new functionality added* to this method in the future may have to also be added to the VM.** A zero status value corresponds to state "NEW".*/if (threadStatus != 0)throw new IllegalThreadStateException();/* Notify the group that this thread is about to be started* so that it can be added to the group's list of threads* and the group's unstarted count can be decremented. */group.add(this);boolean started = false;try {start0();started = true;} finally {try {if (!started) {group.threadStartFailed(this);}} catch (Throwable ignore) {/* do nothing. If start0 threw a Throwable thenit will be passed up the call stack */}}
}//查看start方法的底层,开启线程调用的是native(本地方法),底层是c++,Java无法直接操作硬件,因为他是
//运行在jvm虚拟机上的
private native void start0();并发、并行
并发:强调多个任务在同一时间段内同时发生,但它们可能并不是同时执行的。例如,操作系统通过时间片轮转的方式让多个任务看起来像是同时运行的,但实际上它们是交替占用CPU的。
并行:强调多个任务同时执行,通常需要硬件支持(如多核处理器)。并行可以看作是并发的一种特例,当多个任务真正同时运行时,就是并行。
并发编程的本质:充分利用cpu
public class Test1 {public static void main(String[] args) {//获取cpu核数System.out.println(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());}
}线程有几个状态?
查看源码,我们得治有6个状态
public enum State {//新生NEW,//运行RUNNABLE,//阻塞BLOCKED,//等待WAITING,//超时等待TIMED_WAITING,终止TERMINATED;
}wait/sleep区别
-
来自不同的类
wait=>Object
sleep=>Thread
-
关于锁的释放
wait:会释放锁
sleep:不会释放锁
-
使用的范围不同
wait:必须在同步代码块中
sleep:可以在任何地方
-
是否需要捕获异常
wait:不需要捕获异常
sleep:必须捕获异常
3、Lock锁(重点)
先了解两个不同的锁
公平锁:需要排队
非公平锁:可以插队
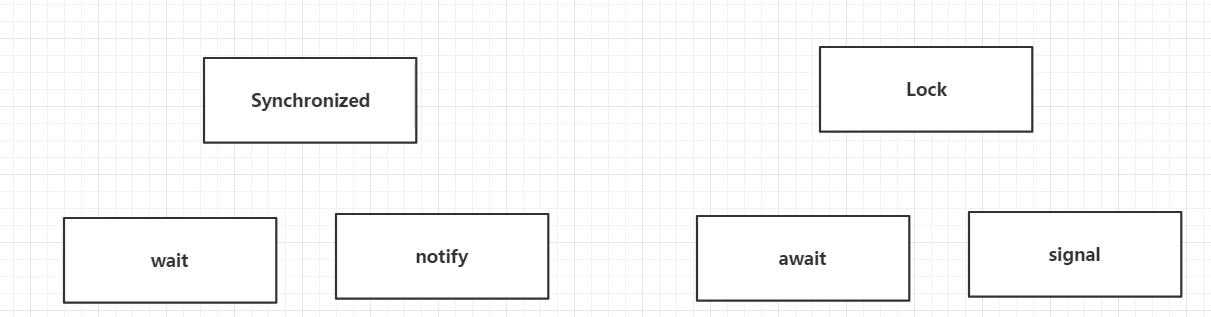
Synachronized和Lock区别
-
Synachronized是内置的Java关键字,Lock是一个Java类
-
Synachronized无法获取锁的状态,Lock可以判断是否获取到了锁
-
Synachronized会自动释放锁,lock必须要手动释放锁!如果不释放就是死锁
-
Synachronized线程1(获得锁,阻塞)、线程2(一直处于等待状态),lock锁就不一定会等待下去
-
Synachronized可重入锁,不可中断的,非公平;Lock,可重入锁,可以判断锁,非公平(可以自己设置)
-
Synachronized适合锁少量的代码同步问题,lock适合锁大量的同步代码
4、生产者和消费者
传统的生产者消费者
package com.yw.pc;public class PCDemo1 {public static void main(String[] args) {Data data = new Data();new Thread(()->{for (int i = 0;i < 10;i++){try {data.increment();} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}},"A").start();new Thread(()->{for (int i = 0;i < 10;i++){try {data.decrement();} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}},"C").start();new Thread(()->{for (int i = 0;i < 10;i++){try {data.increment();} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}},"D").start();new Thread(()->{for (int i = 0;i < 10;i++){try {data.decrement();} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}},"B").start();}
}//生产者消费者三部曲:判断,等待,通知
class Data{private int number = 0;public synchronized void increment() throws InterruptedException {if (number != 0){//判断this.wait();//等待}number++;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=>" + number);//通知this.notifyAll();}public synchronized void decrement() throws InterruptedException {if (number == 0){this.wait();}number--;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=>" + number);this.notifyAll();}
}如果只是一个线程进行一个方法还好,但是像上诉并发的情况下,可能就会发生虚假唤醒,此时查阅官方文档可以得到解决办法=》忙等待

所以使用while忙等待可以解决这个问题,只需要将if改为while即可
提出问题:什么是忙等待?
忙等待(Busy Waiting)是一种编程技术,通常用于实现线程间的同步或等待某个条件成立。它通过在一个循环中不断检查某个条件是否满足,而不是让线程进入阻塞状态来实现等待。
class Data{private int number = 0;public synchronized void increment() throws InterruptedException {while (number != 0){//判断this.wait();//等待}number++;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=>" + number);//通知this.notifyAll();}public synchronized void decrement() throws InterruptedException {while (number == 0){this.wait();}number--;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=>" + number);this.notifyAll();}
}JUC版本的生产者消费者问题
传统与juc 生产者消费者问题三件套
package com.yw.pc;import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;public class PCDemo2 {public static void main(String[] args) {Data2 data = new Data2();new Thread(()->{for (int i = 0;i < 10;i++){try {data.increment();} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}},"A").start();new Thread(()->{for (int i = 0;i < 10;i++){try {data.decrement();} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}},"B").start();new Thread(()->{for (int i = 0;i < 10;i++){try {data.increment();} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}},"C").start();new Thread(()->{for (int i = 0;i < 10;i++){try {data.decrement();} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}},"D").start();}}//生产者消费者三部曲:判断,等待,通知依旧不会改变
class Data2{private int number = 0;Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();Condition condition = lock.newCondition();public void increment() throws InterruptedException {lock.lock();try {while (number != 0){//判断//等待condition.await();}number++;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=>" + number);//通知condition.signalAll();} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} finally {lock.unlock();}}public void decrement() throws InterruptedException {lock.lock();try {Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();Condition condition = lock.newCondition();while (number == 0){condition.await();}number--;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=>" + number);condition.signalAll();} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} finally {lock.unlock();}}}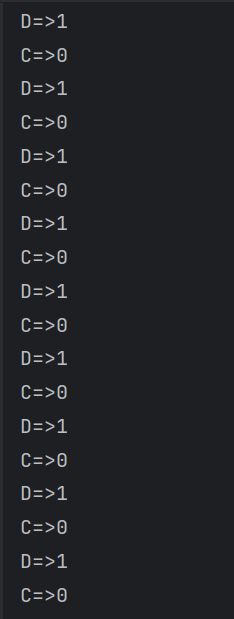
两者执行结果都如下,那么我们为什么要用lock方式?
Condition (同步监视器)精准的通知和唤醒线程
此时我们如果有三个线程A,B,C,这时,我们想A执行完通知B,B执行完通知C,用Condition 实现精准的通知和唤醒线程
package com.yw.pc;import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;public class PCDemo3 {public static void main(String[] args) {Data3 data3 = new Data3();new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i <10 ;i++){data3.printA();}}, "A").start();new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i <10 ;i++){data3.printB();}}, "B").start();new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i <10 ;i++){data3.printC();}}, "C").start();}
}class Data3{private int number = 1;Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();Condition condition1 = lock.newCondition();Condition condition2 = lock.newCondition();Condition condition3 = lock.newCondition();public void printA(){lock.lock();//加锁try {while (number != 1){//判断condition1.await();//等待}number = 2;System.out.println("我是AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA");condition2.signal();//指定唤醒哪个监视器} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} finally {lock.unlock();//解锁}}public void printB(){lock.lock();//加锁try {while (number != 2){//判断condition2.await();//等待}number = 3;System.out.println("我是BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB");condition3.signal();//指定唤醒哪个监视器} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} finally {lock.unlock();//解锁}}public void printC(){lock.lock();//加锁try {while (number != 3){//判断condition3.await();//等待}number = 1;System.out.println("我是CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC");condition1.signal();//指定唤醒哪个监视器} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} finally {lock.unlock();//解锁}}}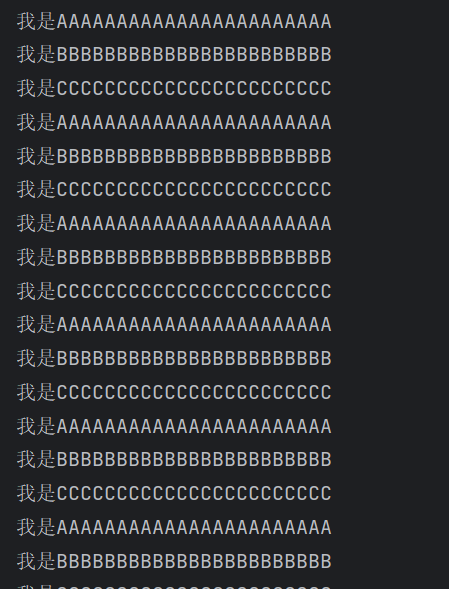
发现实现了我们想要的效果
