C++二叉树常见OJ题分析
OJ(一):根据二叉树创建字符串
606. 根据二叉树创建字符串 - 力扣(LeetCode)

1.(ps:接下来的解答来自LeetCode的官方解释:这里只是为了让以后复习便利而已。)
如果当前节点有两个孩子,那我们在递归时,需要在两个孩子的结果外都加上一层括号;
如果当前节点没有孩子,那我们不需要在节点后面加上任何括号;
- 如果当前节点只有左孩子,那我们在递归时,只需要在左孩子的结果外加上一层括号,而不需要给右孩子加上任何括号;
- 如果当前节点只有右孩子,那我们在递归时,需要先加上一层空的括号 ‘()’ 表示左孩子为空,再对右孩子进行递归,并在结果外加上一层括号。
class Solution {
public:string tree2str(TreeNode* root) {if(root==nullptr)return "";string str=to_string(root->val);if(root->left ||root->right){str+="(";str+=tree2str(root->left);str+=")";}if(root->right){str+="(";str+=tree2str(root->right);str+=")";}return str;}
};OJ(二):二叉树的最近公共祖先
情况一:它们其中一个是根节点,就直接返回根。
情况二:
根据上面我们图知:如果一个在左树,一个在右树,那么当前根就是它们最近的公共祖先。
解释:
1.我们要写一个find函数,用来找它们是符合哪种情况:即找它们是在那支树里
若一个在左树,一个在右树,直接返回它们的当前根
若两个都在当前树的同一支树,则继续去递归,进去下一个更近的树。
2.所以我们可以定义四个变量:即代码中的pInLeft,pInRight,qInLeft,qInRight,返回类型是bool
其中,按照上面的变量名,到下面,你就会很清晰地看到它的优势。
class Solution { public:bool Find(TreeNode*tree,TreeNode* x){if(tree==nullptr)return false;return tree==x||Find(tree->left,x)||Find(tree->right,x);}TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {if(root==nullptr)return nullptr;if(root==p||root==q)return root;bool pInLeft,pInRight,qInLeft,qInRight;pInLeft=Find(root->left,p);//这里就直接逻辑取反即可,因为p不是左就是右pInRight=!pInLeft;qInLeft=Find(root->left,q);//这里就直接逻辑取反即可,因为q不是左就是右qInRight=!qInLeft;//如果都在左边if(pInLeft &&qInLeft){return lowestCommonAncestor(root->left,p,q);}//都在右边else if(pInRight &&qInRight){return lowestCommonAncestor(root->right,p,q);}return root;} };
法二:利用栈去完成。
1.建立两个栈,分别把它们经过遍历的值都push进去各自的栈中,知道找到它们的值为止。
接着,如果它们栈的长度不一样的话,先pop掉长的那个栈,令它们的长度相等,再去比较
比较时,如果它们两个的栈顶值不一样时,就pop掉,反之,它们两个栈顶的值相等时,即找到了它们的最近公共祖先了。
class Solution {
public://找路径的函数bool Findpath(TreeNode*root,TreeNode*x,stack<TreeNode*>& path){if(root==nullptr)return false;path.push(root);if(root==x){return true;}//如果不为空,说明找到了if(Findpath(root->left,x,path)){return true;} if(Findpath(root->right,x,path)){return true;}//如果到最后都找不到,所以没有,就需要pop掉一开始的值path.pop();return false;}TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {stack<TreeNode*>ppath,qpath;Findpath(root,p,ppath);Findpath(root,q,qpath);while(ppath.size()>qpath.size()){ppath.pop();}while(ppath.size()<qpath.size()){qpath.pop();}while(ppath.top()!=qpath.top()){qpath.pop();ppath.pop();}return ppath.top();}
};OJ(三):二叉树的分层遍历
102. 二叉树的层序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)

层序遍历:一层一层地遍历
1.这里使用到了队列来借助完成
2.开始时先入它的根,接着进入循环(条件是:队列不为空)
记录下队列的头结点,再从队列里删去。接着再从已经记录的头节点,去看它的左子树和右子树为不为空,不为空的话,就push进去队列(记得按照左->的顺序入队列)
把每一层的值放进去vector<int>后,再统一把这一层的值push进去ret中。
class Solution { public:vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {vector<vector<int>> ret;//注意这里放的是它的结点,所以类型不要弄成int了queue<TreeNode*> q;if(root)q.push(root);while(!q.empty()){vector<int >ans;int size=q.size();for(int i=1;i<=size;i++){//这里也是注意是结点,而不是intTreeNode*cur=q.front();q.pop();ans.push_back(cur->val);if(cur->left){q.push(cur->left);}if(cur->right){q.push(cur->right);}} ret.push_back(ans);}return ret;} };
OJ(四):二叉树的层序遍历2
107. 二叉树的层序遍历 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
这里跟上面的一样的,只是这道题的最后需要你逆置一下即可
多了一行与上一题:reverse(vv.begin(),vv.end());class Solution { public:vector<vector<int>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode* root) {vector<vector<int>> vv;queue<TreeNode*>q;if(root)q.push(root);while(!q.empty()){vector<int> v;int size=q.size();for(int i=0;i<size;i++){TreeNode*cur=q.front();q.pop();v.push_back(cur->val);if(cur->left)q.push(cur->left);if(cur->right)q.push(cur->right);}vv.push_back(v);}reverse(vv.begin(),vv.end());return vv;} };
OJ(四):二叉搜索树与双向链表
二叉搜索树与双向链表_牛客题霸_牛客网
left:中序上一个
right:中序下一个
画递归图:就可以更加直观了,这里就并不画了。
class Solution { public:void Inorder(TreeNode*cur,TreeNode*&prev){if(cur==nullptr)return;Inorder(cur->left, prev);cur->left=prev;if(prev)prev->right=cur;prev=cur;Inorder(cur->right, prev);}TreeNode* Convert(TreeNode* pRootOfTree) {TreeNode*prev=nullptr;Inorder(pRootOfTree,prev);TreeNode*head=pRootOfTree;while(head &&head->left){head=head->left;}return head;} };
OJ(五):从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
1.
注意:previ加&
class Solution { public:TreeNode* _buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder,int& previ,int inbegin,int inend){if(inbegin>inend)return nullptr;TreeNode*root=new TreeNode(preorder[previ]);int rooti=inbegin;//找根在中序的那个位置while(rooti<inend){if(preorder[previ]==inorder[rooti])break;rooti++;}previ++;root->left=_buildTree(preorder,inorder,previ,inbegin,rooti-1);root->right=_buildTree(preorder,inorder,previ,rooti+1,inend);return root;}TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {int i=0;TreeNode*root=_buildTree(preorder,inorder,i,0,inorder.size()-1);return root;} };
OJ(六):从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
这道题跟上面那道题差不多相似的。
因为我们想想:
后序:左右根 前序:根左右
那么,它们的区别不过只是,后序的根在最后,前序的根在开始而已。并且后序的顺序是从右子树到左子树,前序的顺序是从左子树到右子树。
class Solution { public:TreeNode* _buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder,int& posti,int inbegin,int inend){if(inbegin>inend)return nullptr;TreeNode*root=new TreeNode(postorder[posti]);int rooti=inbegin;while(rooti<inend){if(postorder[posti]==inorder[rooti])break;rooti++;}posti--;//先右再左root->right=_buildTree(inorder,postorder,posti,rooti+1,inend);root->left=_buildTree(inorder,postorder,posti,inbegin,rooti-1);return root;} TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {//最后一个下标int i=postorder.size()-1;TreeNode*root=_buildTree(inorder,postorder,i,0,inorder.size()-1);return root;} };
OJ(七):二叉树的前序遍历(非递归)

1.利用栈来完成:
class Solution { public:vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {stack<TreeNode*>st;vector<int> v;TreeNode*cur=root;while(cur || !st.empty()){while(cur){v.push_back(cur->val);st.push(cur);cur=cur->left;}TreeNode*front=st.top();st.pop();cur=front->right;}return v;} };
OJ(八):二叉树的中序遍历 (非递归)
94. 二叉树的中序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)
这个跟前序差不多很相似:
class Solution { public:vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {stack<TreeNode*>st;vector<int> v;TreeNode*cur=root;while(cur||!st.empty()){while(cur){st.push(cur);cur=cur->left;}TreeNode*front=st.top();st.pop();v.push_back(front->val);cur=front->right;}return v;} };
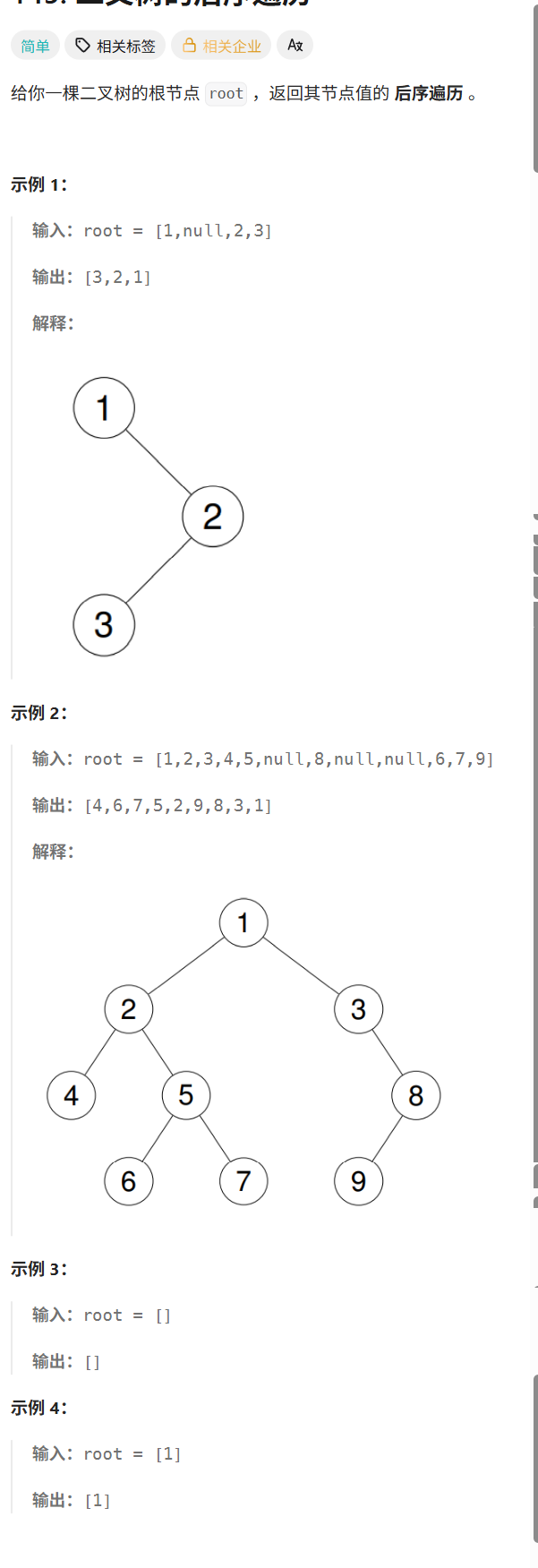
OJ(九):二叉树的后序遍历(非递归)
145. 二叉树的后序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)
这里与前面两道有所差异:
这里后序遍历时:使用到了prev来记录前一个结点
class Solution { public:vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {stack<TreeNode*>st;vector<int>v;TreeNode*cur=root;TreeNode*prev=nullptr;while(cur ||!st.empty()){//左树while(cur){st.push(cur);cur=cur->left;}TreeNode*front=st.top();//因为上面循环中已经知道了cur为空了,即说明左子树已经空了,//左右只需要看它的右子树是否空,如果为空,所以这个是最左边的数了,//就可以进行插入v了,而且第二个是防止它本身就在右子树的,已经遍历完的情况if(front->right==nullptr ||front->right==prev){v.push_back(front->val);prev=front;st.pop();}elsecur=front->right;}return v;} };
好了,关于二叉树的OJ题分析就到此结束了,希望大家都有所收获!
最后,到了本次鸡汤环节:
图片文字与大家共勉!