一些运算符重载的例子
一些运算符重载的例子
目录
- 一些运算符重载的例子
- DoubleSubscriptedArray类:重载函数调用运算符()
- HugeInt类:大整数类
DoubleSubscriptedArray类:重载函数调用运算符()
类的需求:
DoubleSubscriptedArray.h
#include <iostream>class DoubleSubscriptedArray
{friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream&, const DoubleSubscriptedArray&);friend std::istream& operator>>(std::istream&, DoubleSubscriptedArray&);
public:DoubleSubscriptedArray(int = 3, int = 3); // 默认构造函数,默认生成一个 3 * 5 的二维数组DoubleSubscriptedArray(const DoubleSubscriptedArray&); // 拷贝构造函数~DoubleSubscriptedArray(); // 析构函数int getSize() const // 返回该二维数组中的元素个数,row * column{return row * column;}int getRow() const // 返回行数{return row;}int getColumn() const // 返回列数{return column;}// 重载的运算符函数const DoubleSubscriptedArray& operator=(const DoubleSubscriptedArray&);bool operator==(const DoubleSubscriptedArray&) const;// 在类声明中直接定义重载的 != 运算符,使其成为内联函数,减少调用它的额外开销bool operator!=(const DoubleSubscriptedArray& right) const{return !((*this) == right);}// 两种访问二维数组元素的方法const int& operator()(int, int) const;int& operator()(int, int);// 因为二维数组本质上是由一个内置的一维数组实现,所以可以只使用一个参数来访问二维数组的指定元素const int& operator()(int) const;int& operator()(int);private:// 该二维数组由一个一维数组实现size_t row;size_t column;int* ptr;
};
DoubleSubscriptedArray.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <stdexcept>
#include "DoubleSubscriptedArray.h"
using namespace std;ostream& operator<<(ostream& output, const DoubleSubscriptedArray& array)
{for (size_t i = 0; i < (array.getRow() * array.getColumn()); i++){output << setw(12) << array.ptr[i];if ((i + 1) % array.getColumn() == 0){output << "\n";}}// 如果最后一行没有满,输出结束再输出一个新行if(array.getSize() % array.getColumn() != 0)output << endl;return output;
}istream& operator>>(istream& input, DoubleSubscriptedArray& array)
{for (size_t i = 0; i < (array.getRow() * array.getColumn()); i++){input >> array.ptr[i];}return input;
}DoubleSubscriptedArray::DoubleSubscriptedArray(int rows, int columns): row(rows > 0 ? rows :throw out_of_range("Array row must be greater than 0.")),column(columns > 0 ? columns :throw out_of_range("Array column must be greater than 0.")),ptr(new int[row * column])
{for (size_t i = 0; i < getSize(); i++){ptr[i] = 0;}
}DoubleSubscriptedArray::DoubleSubscriptedArray(const DoubleSubscriptedArray& array): row(array.row),column(array.column),ptr(new int[row * column])
{for (size_t i = 0; i < getSize(); i++){ptr[i] = array.ptr[i];}
}DoubleSubscriptedArray::~DoubleSubscriptedArray()
{delete[] ptr;
}const DoubleSubscriptedArray& DoubleSubscriptedArray::operator=(const DoubleSubscriptedArray& right)
{// 避免自我赋值if (this == &right){return *this;}// 判断两个对象大小是否相同if (getSize() != right.getSize()){delete[] ptr;row = right.row;column = right.column;ptr = new int[getSize()];}for (size_t i = 0; i < getSize(); i++){ptr[i] = right.ptr[i];}return *this;
}bool DoubleSubscriptedArray::operator==(const DoubleSubscriptedArray& right) const
{// 行或列有一个不相同则一定不同if (row != right.getRow() || column != right.getColumn()){return false;}// 行、列都相同,接着判断每个元素是否相同for (int i = 0; i < (row * column); i++){if (ptr[i] != right.ptr[i]){return false;}}return true;
}const int& DoubleSubscriptedArray::operator()(int rows, int columns) const
{// 判断参数是否越界// 参数从1开始if ((rows - 1) < 0 || (rows - 1) >= row){throw out_of_range("row out of range.");}if ((columns - 1) < 0 || (columns - 1) >= column){throw out_of_range("column out of range.");}return ptr[(rows - 1) * columns + (columns - 1)];
}int& DoubleSubscriptedArray::operator()(int rows, int columns)
{// 判断参数是否越界// 参数从1开始if ((rows - 1) < 0 || (rows - 1) >= row){throw out_of_range("row out of range.");}if ((columns - 1) < 0 || (columns - 1) >= column){throw out_of_range("column out of range.");}return ptr[(rows - 1) * columns + (columns - 1)];
}const int& DoubleSubscriptedArray::operator()(int n) const
{// 判断参数是否越界// 参数从1开始if (n < 0 || n >= getSize()){throw out_of_range("Subscript out of range.");}return ptr[n];
}int& DoubleSubscriptedArray::operator()(int n)
{// 判断参数是否越界// 参数从1开始if (n < 0 || n >= getSize()){throw out_of_range("Subscript out of range.");}return ptr[n];
}
test.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <stdexcept>
#include "DoubleSubscriptedArray.h"
using namespace std;int main()
{DoubleSubscriptedArray integers1(3, 5);DoubleSubscriptedArray integers2;cout << "Size of Array integers1 is " << integers1.getSize()<< "\nrow is " << integers1.getRow() << ", column is " << integers1.getColumn()<< "\nArray after initialization:\n" << integers1 << endl;cout << "\nSize of Array integers2 is " << integers2.getSize()<< "\nrow is " << integers2.getRow() << ", column is " << integers2.getColumn()<< "\nArray after initialization:\n" << integers2 << endl;cout << "Enter 24 integers: " << endl;cin >> integers1 >> integers2;cout << "\nAfter input, the arrays contains:\n"<< "integers1:\n" << integers1<< "\nintegers2:\n" << integers2 << endl;cout << "\nEvaluation: integers1 != integers2." << endl;if (integers1 != integers2){cout << "integers1 and integers2 are not equal." << endl;}// 调用拷贝构造函数,创建两个新对象DoubleSubscriptedArray integers3(integers1);DoubleSubscriptedArray integers4 = integers2; // 隐式调用拷贝构造函数,并不是使用重载的赋值运算符cout << "\nSize of Array integers3 is " << integers3.getSize()<< "\nrow is " << integers3.getRow() << ", column is " << integers3.getColumn()<< "\nArray after initialization:\n" << integers3 << endl;cout << "\nSize of Array integers4 is " << integers4.getSize()<< "\nrow is " << integers4.getRow() << ", column is " << integers4.getColumn()<< "\nArray after initialization:\n" << integers4 << endl;cout << "\nEvaluation: Assigning integers2 to integers1." << endl;integers1 = integers2;cout << "integers1:\n" << integers1<< "integers2:\n" << integers2 << endl;cout << "Evaluating: integers1 == integers2." << endl;if (integers1 == integers2){cout << "integers1 and integers2 are equal." << endl;}// 测试重载的 () 运算符cout << "\nintegers1(5) is " << integers1(5) << endl;cout << "\nAssigning 1000 to integers1(5)" << endl;integers1(5) = 1000;cout << "integers1 is:\n" << integers1 << endl;cout << "\nAssigning 2000 to integers1(2, 2)" << endl; // 下标为5的元素处于第二行第二列integers1(2, 2) = 2000;cout << "integers1 is:\n" << integers1 << endl;// 测试该类的对象是否会自动检查边界try{cout << "Attempt to assigne 1000 to integers1[15]." << endl;integers1(15) = 1000;}catch (out_of_range& e){cout << "An exception occured: " << e.what() << endl;}
}
运行结果:
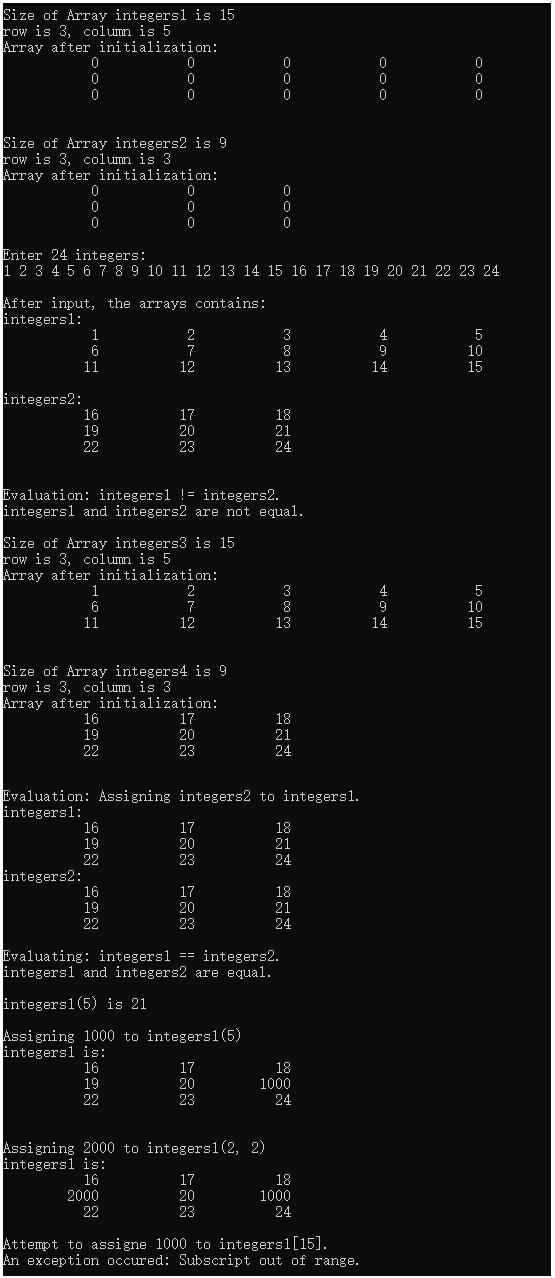
上面代码中并没有重载双方括号运算符,因为它需要创建一个辅助类(管理单行,将一行看成一个一维数组来管理),在该辅助类中重载一个[]运算符,再在二维数组类中重载一个[]运算符,让它访问一行。由链式使用两个[]运算符来实现二维数组的访问,感兴趣的同学可以自己试着实现一下。
HugeInt类:大整数类
HugeInt.h
#include <iostream>
#include <array>
#include <string>class HugeInt
{friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream&, const HugeInt&);
public:static const int digits = 30; // HugeInt类对象的最大长度HugeInt(long = 0); // 默认构造函数,同时也是一个转换构造函数(long->HugeInt)HugeInt(const std::string&); // 转换构造函数,从string类对象转换成HugeInt// 重载加法运算符// 实现 HugeInt + HugeIntHugeInt operator+(const HugeInt&) const;// 实现 HugeInt + HugeIntHugeInt operator+(const int) const;// 实现 HugeInt + HugeIntHugeInt operator+(const std::string&) const;
private:std::array <short, digits> integer;
};
HugeInt.cpp
#include <cctype>
#include "HugeInt.h"
using namespace std;ostream& operator<<(ostream& output, const HugeInt& num)
{int i = 0;// 跳过数组前面的0,最低位放在数组的最后一位for(i = 0; (i < HugeInt::digits) && (num.integer[i] == 0); i++);// 如果此时i指向已经是数组的结尾if(i == HugeInt::digits)output << 0; // 此时该HugeInt对象的值为0else{for(; i < HugeInt::digits; i++)output << num.integer[i];}return output;
}HugeInt::HugeInt(long value)
{// 将数组内容初始化为全0// 必须使用引用,才能修改数据成员array对象的值for(short& element : integer)element = 0;// 获取一个整型类型的数值的最低位是最方便的,%10和/10for (size_t i = digits - 1; value != 0 && i >= 0; i--){integer[i] = value % 10;value /= 10;}
}HugeInt::HugeInt(const string& number)
{for (short& element : integer)element = 0;// HugeInt对象的长度size_t length = number.size();// 获取一个string对象的第一个字符是最容易的for (size_t i = digits - length, j = 0; i < digits; i++, j++){integer[i] = number.at(j) - '0'; // array对象中元素的类型为short,而字符在内存中保存的是ASCII编码的码值// 所以需要将其转换成对应的整型数值}
}HugeInt HugeInt::operator+(const HugeInt& right) const
{HugeInt temp; // 保存计算结果int carry = 0; // 进位数// 从最低位开始计算for (int i = digits - 1; i >= 0; i--){temp.integer[i] = integer[i] + right.integer[i] + carry;if (temp.integer[i] > 9){temp.integer[i] %= 10;carry = 1;}else{carry = 0;}}return temp;
}HugeInt HugeInt::operator+(int right) const
{return (*this) + HugeInt(right); // 使用转换构造函数将参数right转换成HugeInt类型对象// 再使用两个HugeInt对象的加法运算符进行计算
}HugeInt HugeInt::operator+(const string& right) const
{// 同样使用转换构造函数将string对象转换成HugeInt对象,再进行计算return (*this) + HugeInt(right);
}
test.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "HugeInt.h"
using namespace std;int main()
{HugeInt n1(7654321); // 转换构造函数HugeInt n2(7891234); // 转换构造函数 long->HugeIntHugeInt n3("999999999999999999999999999"); // string->HugeIntHugeInt n4("1"); // string->HugeIntHugeInt n5; // 默认构造函数cout << "n1 is " << n1 << "\nn2 is " << n2<< "\nn3 is " << n3 << "\nn4 is " << n4<< "\nn5 is " << n5 << endl;n5 = n1 + n2; // HugeInt + HugeIntcout << "\n" << n1 << " + " << n2 << " = " << n5 << "\n\n";n5 = n3 + n4; // HugeInt + HugeIntcout << "\n" << n3 << " + " << n4 << " = \n" << n5 << "\n\n";n5 = n1 + 9; // HugeInt + intcout << n1 << " + " << 9 << " = " << n5 << "\n\n";n5 = n2 + "10000"; // HugeInt + stringcout << n2 << " + " << "10000" << " = " << n5 << endl;
}
运行结果:
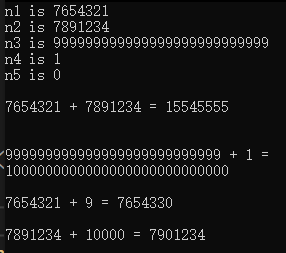
上面代码中只定义了HugeInt类中的加法操作,大家还可以参照上面的形式,补充其他运算。

