芝法酱躺平攻略(22)——rabbitmq安装和使用(二)
六、RPC模式
6.1 功能概要
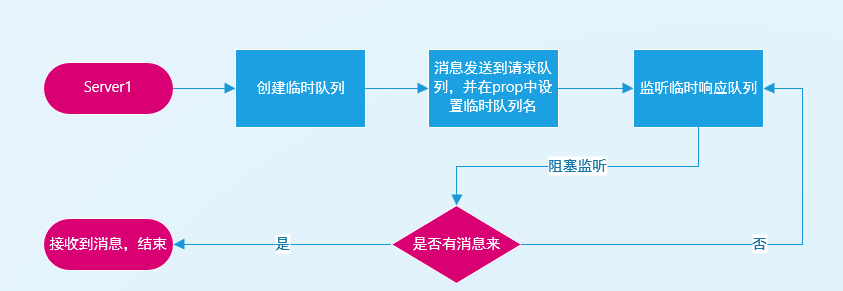
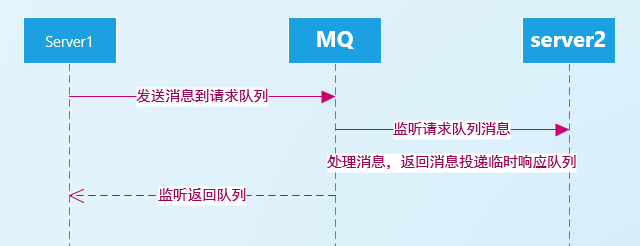
RPC模式,就是用两个队列来实现服务A向服务B的调用。
服务A先创建一个临时的响应队列,而后把消息发送到请求队列,并在prop中附带响应队列的名字。并阻塞监听那个临时的响应队列。
服务B监听请求队列,获得消息,处理后,把处理后的消息发到响应队列。
服务A监听响应队列,拿到对应消息后,放开阻塞,删除临时队列。
6.2 SpringBoot的简单实现
6.1讲的流程看上去有些复杂,而且性能也并不感觉很好。如果想做这种RPC,至少应该基于netty做个响应队列,而不是每次请求创建一个临时队列。不过有兴趣的同学,也可以基于rabbit-mq自己实现一套。但这样何不用dubbo这样专业的RPC框架呢?不过我们这里是学习贴,还是找个简单的方案实现下。
6.1.2 发送方rabbit配置
@Configuration
public class RabbitConfig {@Bean(name = "s1-request")public Queue queue1() {return new Queue(Constant.PRC_QUE_REQUEST_S1,true);}@Bean(name = "default-exchange")public DirectExchange psExchange() {return new DirectExchange(Constant.DEFAULT_EXCHANGE_NAME);}@Beanpublic Binding bindingQue1(@Qualifier("s1-request") Queue myQueue, @Qualifier("default-exchange") DirectExchange exchange) {return BindingBuilder.bind(myQueue).to(exchange).with(Constant.PRC_QUE_REQUEST_S1);}@Beanpublic RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate = new RabbitTemplate(connectionFactory);rabbitTemplate.setReplyTimeout(3000);return rabbitTemplate;}
}
6.1.3 发送方业务逻辑
@Data
public class FabRequest {Double a1 = 1d;Double a2 = 1d;Double k1 = 1d;Double k2 = 1d;int n;
}@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Component
public class FabRpcServiceImpl implements IFabRpcService {private final RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;@Overridepublic Double Fab(FabRequest pFabRequest) throws IOException {String replyQueueName = rabbitTemplate.getConnectionFactory().createConnection().createChannel(false).queueDeclare().getQueue();// correlationId,自己生成String correlationId = UUID.randomUUID().toString();MessageProperties props = new MessageProperties();props.setReplyTo(replyQueueName);props.setCorrelationId(correlationId);String jsonBody = JSON.toJSONString(pFabRequest);Message message = new Message(jsonBody.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8), props);Message rspMsg = rabbitTemplate.sendAndReceive(Constant.PRC_QUE_REQUEST_S1, message);if(null == rspMsg){throw new ServiceException("远程调用失败");}byte[] rspByte = rspMsg.getBody();RestResponse<Double> rsp = JSONObject.parseObject(new String(rspByte),new TypeReference<RestResponse<Double>>(){});if(rsp.getCode().equals(200)){return rsp.getData();}else{throw new ServiceException(rsp.getCode(),rsp.getMessage());}}
}
6.1.4 接收方业务逻辑
public Double fab(FabRequest PFabRequest) {Double a1 = PFabRequest.getA1();Double a2 = PFabRequest.getA2();if(PFabRequest.getN() <= 0){throw new ServiceException("n必须是大于0的整数");}if(PFabRequest.getN() == 1){return a1;}else if(PFabRequest.getN() == 2){return a2;}Double res = a2;for(int i=3;i<PFabRequest.getN();i++){res = a1 * PFabRequest.getK1() + a2 * PFabRequest.getK2();a1 = a2;a2 = res;}return res;}@RabbitListener(queues = Constant.PRC_QUE_REQUEST_S1)public String fabRbc(Message message, Channel channel) {try{FabRequest request = JSONObject.parseObject(message.toString(),FabRequest.class);Double rsp = fab(request);RestResponse<Double> response = RestResponse.<Double>ok(rsp);return JSONObject.toJSONString(response);}catch (ServiceException ex){RestResponse response = RestResponse.error(500,ex.getMessage());return JSONObject.toJSONString(response);}}
七、消费者优先级
消费者,可以通过设置优先级,以及预取消息数量,让消息队列优先把消息投递给优先级高的消费者。
大家请看下面的消费者程序:
我们生产者,向Constant.NW_QUE_PRI_NAME队列中,投递22条数据,并记录数据的idx,每200ms投递一条。
我们的消费者A,B,每1000毫秒消费1条,A预取5条,B预取10条,B优先级比A高。
我们可以观察到,1~10,11,12,16,20,22全给了B,只要B的预消费还有空间,就会尽可能的塞给B。
@Slf4j
public class PriConsumerApplication {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {Connection connection = null;try{connection = NWRabbitUtils.getConnection();if(null == connection){return;}CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(2);final Connection finalConnection = connection;Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{try{Channel channelA = finalConnection.createChannel();Map<String,Object> param = new HashMap<>();param.put("x-priority",1);// 消息预加载channelA.basicQos(5);channelA.basicConsume(Constant.NW_QUE_PRI_NAME,false,param,new DefaultConsumer(channelA){@SneakyThrows@Overridepublic void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {String str = new String(body);OrderMsg orderMsg = JSON.parseObject(str,OrderMsg.class);log.info("channelA#接收到订单信息:"+orderMsg);Thread.sleep(1000);channelA.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag(),false);}});countDownLatch.countDown();}catch (Exception e){System.out.println("channelA error:"+e);}});Thread t2 = new Thread(()->{try{Channel channelB = finalConnection.createChannel();Map<String,Object> param = new HashMap<>();param.put("x-priority",2);// 消息预加载channelB.basicQos(10);channelB.basicConsume(Constant.NW_QUE_PRI_NAME,false,param,new DefaultConsumer(channelB){@SneakyThrows@Overridepublic void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {String str = new String(body);OrderMsg orderMsg = JSON.parseObject(str,OrderMsg.class);log.info("channelB#接收到订单信息:"+orderMsg);Thread.sleep(1000);channelB.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag(),false);}});countDownLatch.countDown();}catch (Exception e){System.out.println("channelB error:"+e);}});t1.start();t2.start();countDownLatch.await();}catch (Exception e){System.out.println(e);}}
}
八、仲裁队列
如果线上环境,并且把MQ用作订单或金融消息等对数据安全性要求极高的场景下,可以考虑使用仲裁队列,把数据存在不同的brocker中。
仲裁队列也是rabbitMQ4.x的新特性,区别于之前镜像队列,对资源的利用率更高。
仲裁队列使用Raft选举算法,是一个CP方案。在可用性方面过半数节点可用,这个集群就可用(多数场景下已足够)。相比原先的镜像队列,只需要过半数的节点完成,就算写入完成。同时,支持把不同的主题的主节点放在不同的brocker上,这样就充分利用的不同机器的数据吞吐能力。
只不过,引入仲裁队列会降低系统吞吐性。不过,要追求高吞吐场景,干嘛不用kafka。
4.x也增加了流式队列,我觉得没太大必要研究,不如用kafka

九、死信队列
死信队列的相关介绍,可以查看官网超时消息,和死信队列的相关介绍。在项目中的私信队列使用,一般有两种情形。一种是设置了队列堆积的上限,超出上限的消息会被投递到私信队列,做兜底处理。另一种则是当一个延迟队列功能使用,先把消息投递到一个普通队列,设置消息的过期时间,而后等消息过期,会自动投递到死信交换机,而后路由到对应的死信队列。
代码示例非常简单:
9.1 生产者
@Slf4j
public class DMProcedureApplication {public static void init(Channel pChannel) throws IOException {// 声明一个 direct 类型的死信交换机pChannel.exchangeDeclare(Constant.DM_EXCHANGE_NAME, BuiltinExchangeType.DIRECT, true);// 定义和死信队列相关的参数Map<String,Object> params = new HashMap<>();// 消息5分钟过期params.put("x-message-ttl",5*60*1000);// 死信交换机名字params.put("x-dead-letter-exchange", Constant.DM_EXCHANGE_NAME);// 死信交换机的键params.put("x-dead-letter-routing-key", Constant.ROUTE_QUE_DM_ORDER_EXPIRE);// 声明 死信队列pChannel.queueDeclare(Constant.DM_QUE_NAME, true, false, false, null);// 声明一个普通队列,接入死信交换机pChannel.queueDeclare(Constant.NW_QUE_DM_NAME, true, false, false, params);// 将 DLQ 绑定到之前声明的 DLXpChannel.queueBind(Constant.DM_QUE_NAME, Constant.DM_EXCHANGE_NAME, Constant.ROUTE_QUE_DM_ORDER_EXPIRE);}public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {Channel channel = null;Connection connection = null;final String queName;queName = Constant.NW_QUE_DM_NAME;//queName = Constant.NW_QUE_NAME;try{connection = NWRabbitUtils.getConnection();channel = connection.createChannel();init(channel);for (int i = 0; i < 22; i++) {String code = RandomUtil.randomString(8);OrderMsg orderMsg = new OrderMsg();orderMsg.setIdx(i+1);orderMsg.setCode(code);orderMsg.setBillTime(LocalDateTime.now());orderMsg.setBillTimeSecond(TimeUtil.nowSecond());orderMsg.setAmount(RandomUtil.randomBigDecimal(BigDecimal.valueOf(10), BigDecimal.valueOf(1000)));String jsonMsg = JSON.toJSONString(orderMsg);channel.basicPublish("", queName, null, jsonMsg.getBytes());log.info("push msg "+orderMsg);Thread.sleep(200);}}catch (Exception e){System.out.println(e);}finally {channel.close();connection.close();}}
}
9.2 消费者
@Slf4j
public class DMConsumerApplication {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {Connection connection = null;try{connection = NWRabbitUtils.getConnection();if(null == connection){return;}Channel channel = connection.createChannel();// 消息预加载channel.basicQos(1);channel.basicConsume(Constant.DM_QUE_NAME,false,new DefaultConsumer(channel){@Overridepublic void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {String str = new String(body);OrderMsg orderMsg = JSON.parseObject(str,OrderMsg.class);log.info("现在时间是"+ LocalDateTime.now() +"接收到订单超时信息:"+orderMsg);channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag(),false);}});}catch (Exception e){System.out.println(e);}}
}
十、优先级队列
除了第七章的消费者优先级,消息队列也可以有优先级。
我们在创建队列时,可以通过设置参数x-max-priority,设置该逻辑队列有几个优先级。多少个优先级,其实就创建了几个实际的队列。
而在消息推送时,可以用如下代码设置消息的优先级
AMQP.BasicProperties abp = new AMQP.BasicProperties.Builder().priority(2).build();
channel.basicPublish("", queName, abp , jsonMsg.getBytes());
这样的设定,可以把消息推送到指定优先级的队列。在消息分发时,消费者会优先处理优先级高的消息。
十一、代码展示
大家可以移步我的码云
