stl--保研机试极限复习
一、stl
1.1 vector
基础操作
#include<vector>
using namespace std;//1.初始化
vector <int> vec1; //创建一个空数组
vector <int> vec2(5,0); //创建一个包含5个元素的数组,初始值为0(如果是vec2(5),默认值int也是0)
vector <int> vec3={1,2,3,4,5}; //列表初始化
vector <int> vec4(vec3); //拷贝构造
vector <int> vec2d(3,vector<int>(4,0)); //三行四列 初始值为0//2.访问+增删改查vector<int> v={1,2,3};v.push_back(4); //末尾插入4
v.pop_back(); //删除尾元素// 在指定位置(迭代器指定)前插入元素
v.insert(v.begin() + 1, 5); // 在第二个元素位置插入5 -> {1, 5, 2, 3}
v.insert(v.end(), 2, 6); // 在末尾插入2个6 -> {1, 5, 2, 3, 6, 6}// 删除指定位置(迭代器指定)或范围的元素
v.erase(v.begin() + 2); // 删除第三个元素 -> {1, 5, 3, 6, 6}
v.erase(v.begin(), v.begin()+2);// 删除前两个元素 -> {3, 6, 6} 范围的话就不包括自己
v.clear(); // 清空vector中的所有元素//3. vector的容量与大小
v = {1, 2, 3}
cout << "元素个数: " << v.size() << endl;
cout << "是否为空: " << v.empty() << endl; // 若空返回true,否则返回falsev.resize(5); // 将元素数量调整为5,新增元素默认初始化为0 -> {1,2,3,0,0}
v.resize(7, 100); // 将元素数量调整为7,新增元素初始化为100 -> {1,2,3,0,0,100,100}
v.resize(2); // 将元素数量调整为2,删除多余元素 -> {1,2}总结:
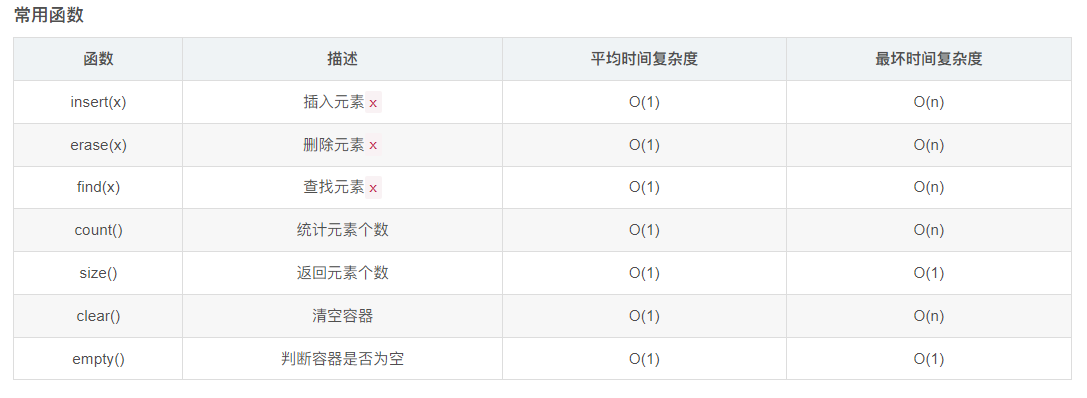
插入 删除用 push_back(),pop_back,或者 固定位置用 insert(),erase();
resize()用于调整数组大小 size()获取数组大小 empty() 判断是否为空
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>vector<int> v = {5, 3, 1, 4, 2};sort(v.begin(), v.end()); // 默认升序
sort(v.rbegin(), v.rend()); // 降序排序
sort(v.begin(), v.end(),greater<int>());//降序// 自定义排序规则(例如按绝对值排序)
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), [](int a, int b) {return abs(a) < abs(b);
});// 二分查找(必须在有序序列上)
bool found = binary_search(v.begin(), v.end(), 3); // 找到返回true,否则falsev.reserve(1000); // 预留1000个元素的空间 ,使用 reserve 预先分配足够空间,可以避免多次扩容带来的性能开销//三步去除重复元素
vector<int> v = {1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 4};
auto last = unique(v.begin(), v.end()); // 去除连续重复元素,unique返回的是一个迭代器
v.erase(last, v.end()); // 真正删除重复元素 -> {1,2,3,4}总结:
排序 用sort(v.begin(),v.end()) 默认是升序 降序可以 sort(v.rbegin(),v.rend())或者sort(v.begin(),v.end(),greater<int>())
二分查找 用 binary_search(v.begin(),v.end(),3)
去除重复元素 unique 返回最后重复元素的迭代器 erase(last,end);删除
1.2 map
| 特性 | map | unordered_map |
|---|---|---|
| 底层数据结构 | 红黑树 (自平衡二叉搜索树) | 哈希表 |
| 元素顺序 | 按键有序排序 (默认升序) | 无序 |
| 查找时间复杂度 | O(log n) | 平均 O(1),最坏 O(n) |
| 插入/删除时间复杂度 | O(log n) | 平均 O(1),最坏 O(n) |
| 需要键的可比性 | 需要定义 < 操作符或提供自定义比较器 | 需要定义 == 操作符和哈希函数 |
| 机试常用场景 | 需要有序遍历、范围查询、数据量不大时 | 需要快速查找、查找频率高、不关心顺序时 |
常考的哈希表就是 unordered_map这个数据结构
基础用法:
#include <map>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <string>
using namespace std;//1.初始化 //空map key为string类型 value为int 类型
map<string,int> mp1;
unordered_mao<string,int>ump1;
// 列表初始化
map<string, int> mp2 = {{"Alice", 90}, {"Bob", 85}};
unordered_map<string, int> ump2 = {{"Apple", 3}, {"Banana", 5}};//2. 访问//使用下标操作符 [] (如果键不存在,会创建新键值对,值为默认值)
int score = mp1["Alice"]; // 存在则返回对应值,不存在则插入默认值0
int count = ump1["Apple"]; // 同上//3.插入/修改// 使用下标操作符 [] (如果键存在则修改值,不存在则插入)
mp1["Charlie"] = 95;
ump1["Orange"] = 7;// 使用 insert 成员函数
mp1.insert({"David", 88});
ump1.insert(make_pair("Grape", 4)); // 也可以使用 make_pair// 使用 emplace (C++11, 效率更高,直接原地构造)
mp1.emplace("Eve", 92);
ump1.emplace("Peach", 6);//4.查找
// 使用 find() 成员函数(推荐方式,返回迭代器,找不到则返回 end())auto it_mp = mp1.find("Bob");
if (it_mp != mp1.end()) {cout << "Found: " << it_mp->first << ", " << it_mp->second << endl; // 输出键值对
} else {cout << "Not found in map." << endl;
}auto it_ump = ump1.find("Banana");
if (it_ump != ump1.end()) {cout << "Found: " << it_ump->first << ", " << it_ump->second << endl;
} else {cout << "Not found in unordered_map." << endl;
}// 使用 count() 成员函数(返回键出现的次数,对于map和unordered_map,只能是0或1)
if (mp1.count("David") > 0) {cout << "Key exists in map." << endl;
}
if (ump1.count("Grape") > 0) {cout << "Key exists in unordered_map." << endl;
}//5.删除auto it_to_erase_mp = mp1.find("David");
if (it_to_erase_mp != mp1.end()) {mp1.erase(it_to_erase_mp);
}auto it_to_erase_ump = ump1.find("Orange");
if (it_to_erase_ump != ump1.end()) {ump1.erase(it_to_erase_ump);
}//6.遍历
//遍历 map 和 unordered_map 的方式是相同的,但 **map 的遍历结果是按键升序排列的,而unordered_map 的遍历结果顺序是不确定的
cout << "Map elements (ordered by key):" << endl;
for (auto it = mp1.begin(); it != mp1.end(); ++it) {cout << it->first << ": " << it->second << endl; // 使用 -> 访问成员
}cout << "Unordered_map elements (unordered):" << endl;
for (auto it = ump1.begin(); it != ump1.end(); ++it) {cout << it->first << ": " << it->second << endl;
}// 2. 使用范围for循环(C++11, 更简洁)[12](@ref)
cout << "Map elements (using range-for):" << endl;
for (const auto& kv : mp1) { // 使用引用避免拷贝,const 表示不修改cout << kv.first << ": " << kv.second << endl;
}cout << "Unordered_map elements (using range-for):" << endl;
for (const auto& kv : ump1) {cout << kv.first << ": " << kv.second << endl;
}
补充用法
// 获取大小[12]
cout << "Map size: " << mp1.size() << endl;
cout << "Unordered_map size: " << ump1.size() << endl;// 判断是否为空[12]
if (mp1.empty()) { cout << "Map is empty." << endl; }
if (ump1.empty()) { cout << "Unordered_map is empty." << endl; }//统计频率:统计字符串、数字等出现的次数(通常使用 unordered_map 以追求速度)
string input="asdsaasca";
unordered_map<string ,int> freq;
for(char c:input)
{
freq[c]++;
}//快速查找:检查某个元素是否存在
unordered_map<string, int> studentScores;
// ... 添加数据
if (studentScores.find("Alice") != studentScores.end()||studentScores.count("Alice")>0) {// Alice 存在
}//映射关系:建立两个数据之间的对应关系
map<string, string> config = {{"version", "1.0"}, {"language", "C++"}};
string lang = config["language"];1.3 queue
队列 先进先出
| 方法/操作 | 功能描述 | 时间复杂度 |
|---|---|---|
push(x) | 将元素 x 插入到队列的尾部 | O(1) |
pop() | 移除队列的头部元素 | O(1) |
front() | 返回队列头部元素的引用(但不移除它) | O(1) |
back() | 返回队列尾部元素的引用(但不移除它) | O(1) |
empty() | 检查队列是否为空,返回 true 或 false | O(1) |
size() | 返回队列中当前元素的个数 | O(1) |
1.4 priority_queue
#include <queue>
using namespace std;// 1. 默认定义(大顶堆):优先级高的先出队,即队首元素最大
priority_queue<int> pq1; // 2. 小顶堆定义:优先级低的先出队,即队首元素最小。常用greater<int>
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> pq2;
priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, greater<pair<int, int>>> pq; // (距离, 节点ID)的小顶堆// 3. 使用自定义比较函数/仿函数
struct MyComparator {bool operator()(const int& a, const int& b) const {return a > b; // 自定义比较规则,例如希望绝对值大的优先级高可改为 abs(a) < abs(b)}
};
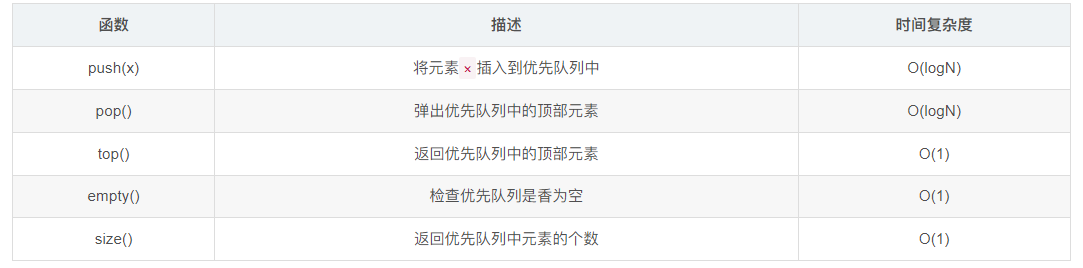
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, MyComparator> pq3;priority_queue<int> pq;// 插入元素
pq.push(3);
pq.push(1);
pq.push(4);
pq.push(1);
pq.push(5); // 队列内元素:{5, 4, 3, 1, 1} (从队首到队尾的逻辑顺序)// 访问元素(获取优先级最高的元素)
cout << pq.top() << endl; // 输出:5// 删除元素(移除优先级最高的元素)
pq.pop(); // 移除5
cout << pq.top() << endl; // 输出:4// 其他操作
cout << "Size: " << pq.size() << endl; // 返回队列中元素个数
cout << "Empty? " << pq.empty() << endl; // 判断队列是否为空1.5 string
| 操作类别 | 常用函数/方法 | 简要说明 | 机试常见度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 🍒 输入输出 | cin >> str | 读取单词,遇空格/换行终止 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
getline(cin, str) | 读取整行(包括空格) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | |
| 📦 初始化 | string s1 | 默认初始化,空字符串 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
string s2("hello") 或 string s2 = "hello" | 使用字符串字面量初始化 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | |
string s3(n, 'c') | 生成由 n 个字符 'c' 组成的字符串 | ⭐⭐ | |
| 📏 属性获取 | s.size() 或 s.length() | 返回字符串长度(无'\0') | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
s.empty() | 判断字符串是否为空 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | |
| 🔍 元素访问 | s[index] | 访问指定索引位置的字符(不检查越界) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
s.at(index) | 访问指定索引位置的字符(检查越界,越界则抛出out_of_range异常) | ⭐⭐⭐ | |
s.front() | 访问第一个字符 | ⭐⭐ | |
s.back() | 访问最后一个字符 | ⭐⭐ | |
| 🔗 字符串拼接 | s1 + s2 | 字符串拼接,返回新字符串 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
s1 += s2 | 将 s2 追加到 s1 的末尾 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | |
s1.append(s2) | 将 s2 追加到 s1 的末尾 | ⭐⭐⭐ | |
| 📋 字符串比较 | s1 == s2, s1 != s2, s1 < s2, s1 <= s2, s1 > s2, s1 >= s2 | 按字典序比较字符串 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| 🔎 查找与替换 | s.find(target) | 查找子串或字符,返回首次出现的索引,未找到返回 string::npos | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
s.replace(pos, len, new_str) | 从位置 pos 开始,将 len 个字符替换为 new_str | ⭐⭐⭐ | |
| **✂️ 子串操作** | s.substr(pos, len) | 返回从 pos 开始、长度为 len 的子串 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| 🧹 修改与清理 | s.insert(pos, str) | 在 pos 位置插入字符串 str | ⭐⭐⭐ |
s.erase(pos, len) | 删除从 pos 开始的 len 个字符 | ⭐⭐⭐ | |
s.push_back(c) | 在末尾添加一个字符 c | ⭐⭐ | |
s.pop_back() | 删除末尾一个字符 | ⭐⭐ | |
s.clear() | 清空字符串 | ⭐⭐⭐ | |
| 🔄 类型转换 | to_string(num) | 将数值(int, double等)转换为字符串 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
stoi(s), stol(s), stoll(s) | 将字符串转换为整数(int, long, long long) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | |
stof(s), stod(s) | 将字符串转换为浮点数(float, double) | ⭐⭐⭐ | |
| 🛠️ 其他常用 | reverse(s.begin(), s.end()) | 反转转字符串(需要 #include <algorithm>) |
#include <iostream>
#include <string> // 必须包含string头文件
#include <cctype> // 用于字符处理函数,如tolower, isdigit
#include <algorithm> // 用于reverse等算法using namespace std;int main() {// 🍒 1. 输入输出 (非常重要!)string s1;cout << "Enter a word (stops at space): ";cin >> s1; // 遇到空格或换行停止,空格或换行会留在输入缓冲区cout << "You entered (cin): " << s1 << endl;// 清除输入缓冲区中的换行符,为后续getline做准备cin.ignore(); string s2;cout << "Enter a line (with getline, includes spaces): ";getline(cin, s2); // 读取整行,包括空格,直到换行符(但换行符不会读入字符串)cout << "You entered (getline): " << s2 << endl;// 📦 2. 初始化string empty_str; // 空字符串string literal_str = "Hello, World!"; // 字符串字面量string repeat_str(5, 'A'); // "AAAAA"string copy_str = literal_str; // "Hello, World!"// 📏 3. 获取字符串属性cout << "Length of '" << literal_str << "': " << literal_str.size() << endl; // 或 length()cout << "Is empty? " << (empty_str.empty() ? "Yes" : "No") << endl; // 判断是否为空// 🔍 4. 访问字符cout << "First char: " << literal_str[0] << endl; // 'H' - 不检查越界,越界行为未定义cout << "Char at index 7: " << literal_str.at(7) << endl; // 'W' - 检查越界,越界抛出std::out_of_range异常// cout << literal_str.at(100); // 这会抛出异常cout << "Front char: " << literal_str.front() << endl; // 'H'cout << "Back char: " << literal_str.back() << endl; // '!'// 🔗 5. 字符串拼接string a = "Hello", b = "World";string c = a + " " + b; // "Hello World"a += " C++"; // a 变为 "Hello C++"a.append("!"); // a 变为 "Hello C++!"cout << "c: " << c << endl;cout << "a: " << a << endl;// 📋 6. 字符串比较 (按字典序)string x = "apple", y = "banana";if (x < y) {cout << x << " comes before " << y << endl;} else if (x > y) {cout << x << " comes after " << y << endl;} else {cout << x << " equals " << y << endl;}// 🔎 7. 查找子串string text = "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog.";size_t pos = text.find("fox"); // 查找子串"fox",返回起始索引(16)if (pos != string::npos) { // npos 是一个表示无效位置的静态常量值,通常是size_t的最大值cout << "'fox' found at position: " << pos << endl;} else {cout << "'fox' not found." << endl;}// 也可以查找字符pos = text.find('q'); // 4// ✂️ 8. 获取子串string sub = text.substr(4, 5); // 从索引4开始,取5个字符 -> "quick"cout << "Substring: " << sub << endl;// 🧹 9. 修改字符串string demo = "HelloJava";demo.replace(5, 4, "C++"); // 从索引5开始,替换4个字符("Java")为"C++" -> "HelloC++"cout << "After replace: " << demo << endl;demo.insert(5, " "); // 在索引5处插入一个空格 -> "Hello C++"cout << "After insert: " << demo << endl;demo.erase(6, 3); // 从索引6开始,删除3个字符 -> "Hello"cout << "After erase: " << demo << endl;demo.push_back('!'); // 在末尾添加字符'!' -> "Hello!"cout << "After push_back: " << demo << endl;demo.pop_back(); // 删除最后一个字符 -> "Hello"cout << "After pop_back: " << demo << endl;// demo.clear(); // 清空字符串 -> ""// 🔄 10. 类型转换// 数字转字符串int num = 42;double pi = 3.14159;string num_str = to_string(num); // "42"string pi_str = to_string(pi); // "3.141590" (注意精度)cout << "num_str: " << num_str << ", pi_str: " << pi_str << endl;// 字符串转数字string int_str = "123";string double_str = "45.67";int int_val = stoi(int_str); // 123double double_val = stod(double_str); // 45.67cout << "int_val: " << int_val << ", double_val: " << double_val << endl;// 注意:如果转换失败(如字符串包含非数字字符),stoi/stod会抛出invalid_argument异常// 🛠️ 11. 其他常用操作// 反转字符串string to_reverse = "abcd";reverse(to_reverse.begin(), to_reverse.end()); // "dcba"cout << "Reversed: " << to_reverse << endl;// 遍历字符串cout << "Traversing by index: ";for (size_t i = 0; i < text.size(); ++i) {cout << text[i]; // 或 text.at(i)}cout << endl;cout << "Traversing by range-based for loop: ";for (char ch : text) { // 只读遍历cout << ch;}cout << endl;// 需要修改字符时使用引用string lower_str = "HELLO";for (char &ch : lower_str) {ch = tolower(ch); // 转为小写 -> "hello"}cout << "To lower: " << lower_str << endl;return 0;
}后续有遇见再补充
