代码随想录算法训练营四十三天|图论part01
深度优先搜索(dfs)理论基础
dfs就是可一个方向去搜直到尽头再换方向,换方向的过程就涉及到了回溯。
代码框架
因为dfs搜索可一个方向,并需要回溯,所以用递归的方式来实现是最方便的。
先来回顾一下回溯法的代码框架:
void backtracking(参数) {if (终止条件) {存放结果;return;}for (选择:本层集合中元素(树中节点孩子的数量就是集合的大小)) {处理节点;backtracking(路径,选择列表); // 递归回溯,撤销处理结果}
}据此给出dfs的代码框架:
void dfs(参数) {if (终止条件) {存放结果;return;}for (选择:本节点所连接的其他节点) {处理节点;dfs(图,选择的节点); // 递归回溯,撤销处理结果}
}所有可达路径
题目链接:98. 所有可达路径 (kamacoder.com)
【题目描述】
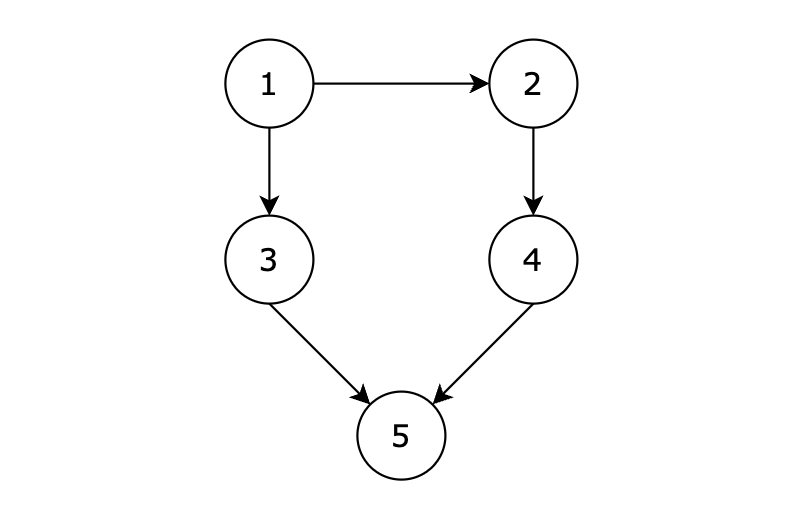
给定一个有 n 个节点的有向无环图,节点编号从 1 到 n。请编写一个程序,找出并返回所有从节点 1 到节点 n 的路径。每条路径应以节点编号的列表形式表示。
【输入描述】
第一行包含两个整数 N,M,表示图中拥有 N 个节点,M 条边
后续 M 行,每行包含两个整数 s 和 t,表示图中的 s 节点与 t 节点中有一条路径
【输出描述】
输出所有的可达路径,路径中所有节点的后面跟一个空格,每条路径独占一行,存在多条路径,路径输出的顺序可任意。
如果不存在任何一条路径,则输出 -1。
注意输出的序列中,最后一个节点后面没有空格! 例如正确的答案是 1 3 5,而不是 1 3 5, 5后面没有空格!
输入示例
5 5
1 3
3 5
1 2
2 4
4 5
输出示例
1 3 5
1 2 4 5
提示信息
用例解释:
有五个节点,其中的从 1 到达 5 的路径有两个,分别是 1 -> 3 -> 5 和 1 -> 2 -> 4 -> 5。
因为拥有多条路径,所以输出结果为:
1 3 5
1 2 4 5或
1 2 4 5
1 3 5
都算正确。数据范围:
图中不存在自环
图中不存在平行边
1 <= N <= 100
1 <= M <= 500
使用邻接矩阵存储
使用二维数组来表示图,因为有n个节点,节点编号从1开始,所以我们申请(n+1)*(n+1)大的二维数组;然后构造m个边:
int[][] graph=new int[n+1][n+1];
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){int a=in.nextInt();int b=in.nextInt();graph[a][b]=1;
}使用邻接矩阵存储dfs的代码:
public static void dfs(List<List<Integer>> graph, int x, int n) { //x表示当前遍历到的节点if (x == n) {res.add(new ArrayList<>(list));return;}for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){if(graph[x][i]==1){list.add(i);dfs(graph,i,n);list.remove(list.size()-1);}}}打印结果:
for(List<Integer> tmp:res){for(int i=0;i<tmp.size()-1;i++){System.out.print(tmp.get(i)+" ");}System.out.println(tmp.get(tmp.size()-1));
}整体代码如下:
import java.util.*;public class Main{static List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();static List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();public static void main(String[] args){Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);int n=in.nextInt();int m=in.nextInt();int[][] graph=new int[n+1][n+1];for(int i=0;i<m;i++){int a=in.nextInt();int b=in.nextInt();graph[a][b]=1;}list.add(1);dfs(graph,1,n);if(res.isEmpty())System.out.println(-1);for(List<Integer> tmp:res){for(int i=0;i<tmp.size()-1;i++){System.out.print(tmp.get(i)+" ");}System.out.println(tmp.get(tmp.size()-1));}}public static void dfs(int[][] graph,int x,int n){//x表示当前遍历到的节点if(x==n){res.add(new ArrayList<>(list));return;}for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){if(graph[x][i]==1){list.add(i);dfs(graph,i,n);list.remove(list.size()-1);}}}
}使用邻接表存储
List<List<Integer>> graph = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>(n + 1);for(int i=0;i<=n;i++){graph.add(new ArrayList<>());}for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {int a = in.nextInt();int b = in.nextInt();graph.get(a).add(b);}使用领接表存储的dfs的写法:
public static void dfs(List<List<Integer>> graph, int x, int n) { //x表示当前遍历到的节点if (x == n) {res.add(new ArrayList<>(list));return;}for (int i : graph.get(x)) {list.add(i);dfs(graph, i, n);list.remove(list.size() - 1);}}打印结果:
if (res.isEmpty()) System.out.println(-1);for (List<Integer> tmp : res) {for (int i = 0; i < tmp.size() - 1; i++) {System.out.print(tmp.get(i) + " ");}System.out.println(tmp.get(tmp.size() - 1));}整体代码如下:
import java.util.*;public class Main {static List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();static List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);int n = in.nextInt();int m = in.nextInt();//邻接表写法List<List<Integer>> graph = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>(n + 1);for(int i=0;i<=n;i++){graph.add(new ArrayList<>());}for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {int a = in.nextInt();int b = in.nextInt();graph.get(a).add(b);}list.add(1);dfs(graph, 1, n);if (res.isEmpty()) System.out.println(-1);for (List<Integer> tmp : res) {for (int i = 0; i < tmp.size() - 1; i++) {System.out.print(tmp.get(i) + " ");}System.out.println(tmp.get(tmp.size() - 1));}}public static void dfs(List<List<Integer>> graph, int x, int n) { //x表示当前遍历到的节点if (x == n) {res.add(new ArrayList<>(list));return;}for (int i : graph.get(x)) {list.add(i);dfs(graph, i, n);list.remove(list.size() - 1);}}
}广度优先搜索(bfs)理论基础
bfs就是先把本节点所连接的所有节点遍历一遍,走到下一个节点的时候,再把连接该节点的所有节点遍历一遍,四面八方的搜索过程。
代码模板
private static final int[][] dir = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}};//表示四个方向
// grid 是地图,也就是一个二维数组
// visited标记访问过的节点,不要重复访问
// x,y 表示开始搜索节点的下标public static void bfs(char[][] grid, boolean[][] visited, int x, int y) {// 定义队列,存储坐标对Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();// 起始节点加入队列queue.offer(new int[]{x, y});// 只要加入队列,立刻标记为访问过的节点visited[x][y] = true;// 开始遍历队列里的元素while (!queue.isEmpty()) {// 从队列取出元素int[] current = queue.poll();int curx = current[0];int cury = current[1];// 向当前节点的四个方向(上下左右)遍历for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {// 获取周边四个方向的坐标int nextx = curx + dir[i][0];int nexty = cury + dir[i][1];// 检查坐标是否越界,如果越界直接跳过if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.length || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].length) {continue;}// 如果节点没被访问过if (!visited[nextx][nexty]) {// 将该节点加入队列,作为下一轮要遍历的节点queue.offer(new int[]{nextx, nexty});// 只要加入队列立刻标记,避免重复访问visited[nextx][nexty] = true;}}}}