PAT 1086 Tree Traversals Again

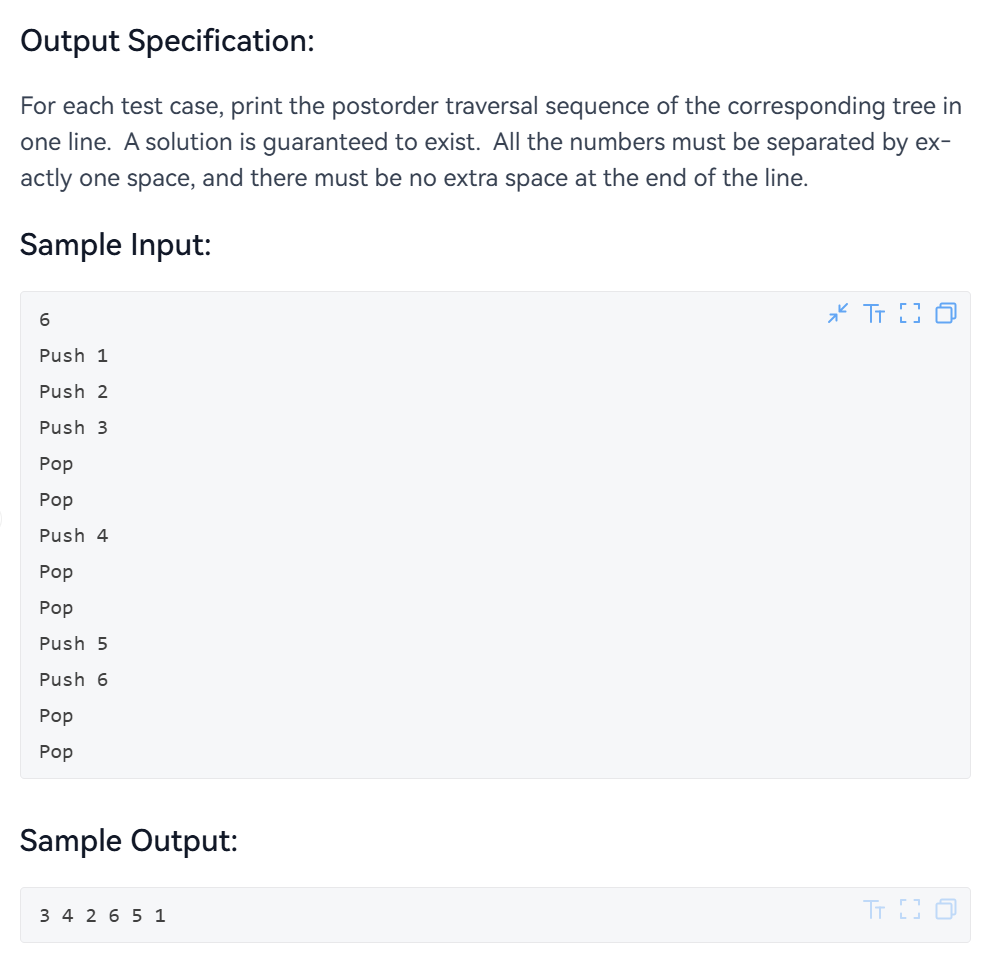
这一题的大意是说给出N个点,然后用栈的方式来建树,通过入栈和出栈的顺序来建立一棵二叉树,建立好树后,输出其后序遍历的序列。
我的思路是,根据题目中的入栈出栈,模拟建树,建好树后输出其后序遍历序列。
我刚开始采用的是用指针来构造树,比较麻烦,容易出错:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <limits.h>
#include <queue>
#include <string.h>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
// 123456789
struct node
{int data;struct node* l;struct node* r;
}tree;
int N;
stack<int> stackk;
node* insert(int id,node* root)
{if(root==nullptr){root=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node));root->data=id;root->l=nullptr;root->r=nullptr;return root;}else{if(root->l!=nullptr){root->l=insert(id,root->l);}else{root->r=insert(id,root->r);}}
}
node* dfsfind(node* root,int topid)
{if(root==nullptr){return nullptr;}if(root->data!=topid){if(root->l!=nullptr){root=dfsfind(root->l,topid);if(root!=nullptr){return root;}}if(root->r!=nullptr){root=dfsfind(root->r,topid);if(root!=nullptr){return root;}}}else{return root;}
}void postorder(node* root)
{if(root==nullptr){return ;}postorder(root->l);postorder(root->r);cout<<root->data<<" ";}
int main()
{//ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(cin>>N;node* root=nullptr;int topid=0;for(int i=0;i<2*N;i++){string s;int id;cin>>s;if(s=="Push"){cin>>id;stackk.push(id);if(topid!=0){node* temp=dfsfind(root,topid);temp=insert(id,temp);cout<<temp->data<<endl;topid=0;}else{root=insert(id,root);}}else{topid=stackk.top();stackk.pop();}}postorder(root);return 0;}
这个代码不能通过。
对于PAT这种算法竞赛,在写树或者链表等数据结构的时候尽可能的用数组来模拟。这样的话比较方便,不容易写错,而且数组模拟可以直接获取下标,很方便。
于是:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <limits.h>
#include <queue>
#include <string.h>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
// 123456789
struct node
{int data;int l;int r;
};
int N;
stack<int> st;
int cnt;
void postorder(vector<node> &tree,int root)
{if(root==-1){return ;}postorder(tree,tree[root].l);postorder(tree,tree[root].r);if(cnt!=0)cout<<" ";cout<<tree[root].data;cnt++;
}
int main()
{//ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(cin>>N;vector<node> tree(N+1);for(int i=0;i<=N;i++){tree[i].l=-1;tree[i].r=-1;tree[i].data=-1;}int topid=0;string s;for(int i=0;i<N*2;i++){string s;int x;cin>>s;if(s=="Push"){cin>>x;st.push(x);tree[x].data=x;if(tree[topid].l==-1){tree[topid].l=x;}else{tree[topid].r=x;}topid=x; }else{topid=st.top();st.pop();}}postorder(tree,1);return 0;
}
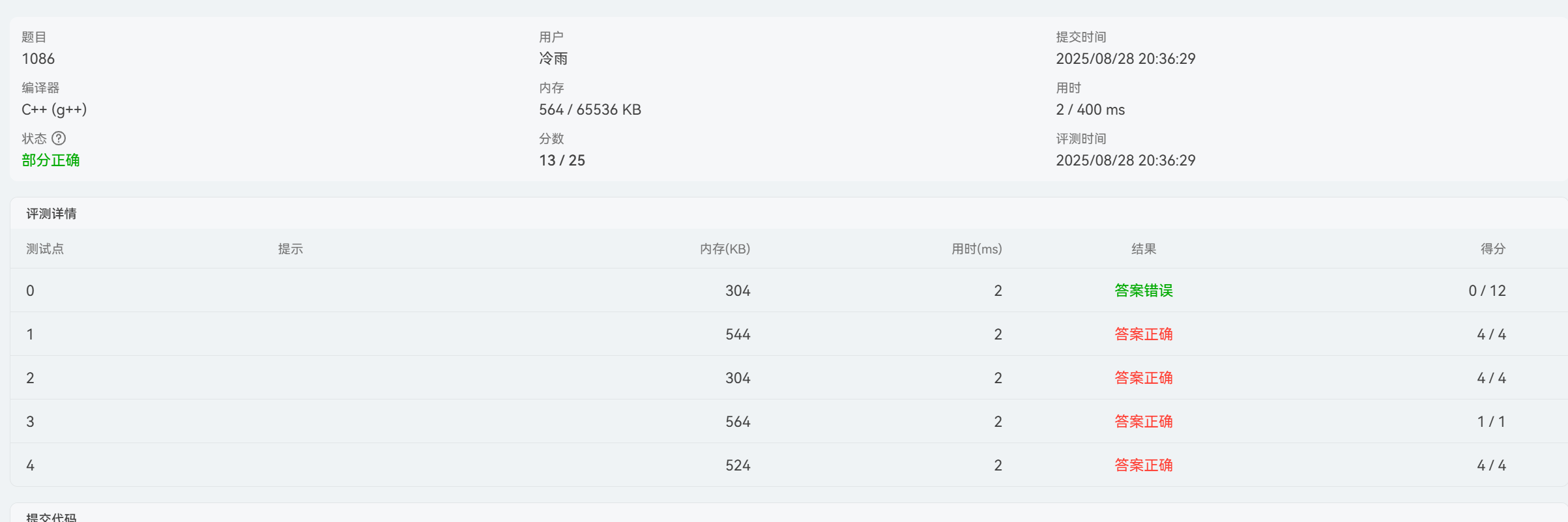
但这有一个测试点不过原因是,我们不能错误的把1这个点当作根节点,因为有可能第一次输入可能不是1.
因此:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <limits.h>
#include <queue>
#include <string.h>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
// 123456789
struct node
{int data;int l;int r;
};
int N;
stack<int> st;
int cnt;
void postorder(vector<node> &tree,int root)
{if(root==-1){return ;}postorder(tree,tree[root].l);postorder(tree,tree[root].r);if(cnt!=0)cout<<" ";cout<<tree[root].data;cnt++;
}
int main()
{//ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(cin>>N;vector<node> tree(N+1);for(int i=0;i<=N;i++){tree[i].l=-1;tree[i].r=-1;tree[i].data=-1;}int topid=0;string s;bool hasroot=false;int root; for(int i=0;i<N*2;i++){string s;int x;cin>>s;if(s=="Push"){cin>>x;//cout<<x<<endl;if(hasroot==false){hasroot=true;root=x;}st.push(x);tree[x].data=x;//cout<<tree[x].data<<endl;if(tree[topid].l==-1){tree[topid].l=x;}else{tree[topid].r=x;}topid=x; }else{topid=st.top();st.pop();}}postorder(tree,root);return 0;
}
成功通过
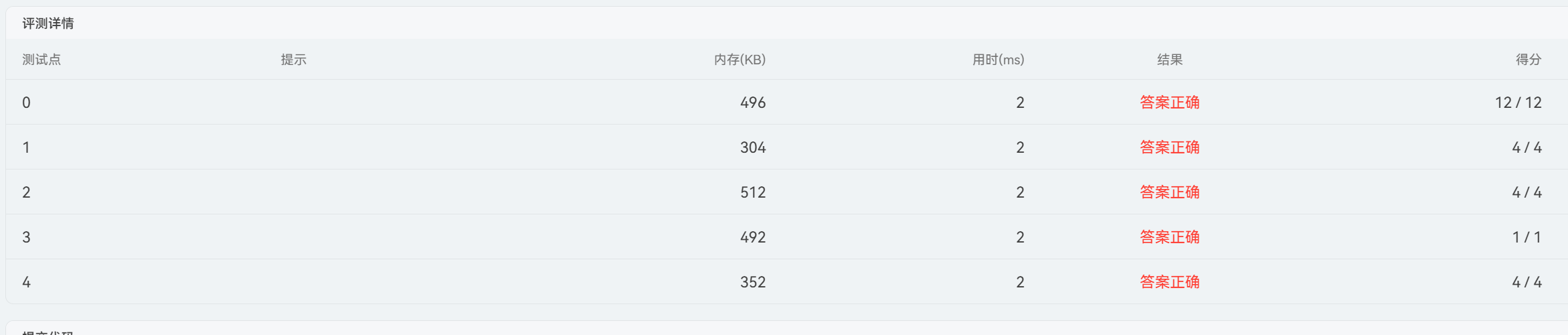
我在网上看到这一题还可以不建树来写
因为入栈顺序push恰好是前序遍历左右根,出栈顺序pop恰好是中序序列左根右,根据前序序列和中序序列是得到后序序列的:
原理
前序序列的第一个元素 = 根节点。
在中序序列中找到该根的位置:
左边部分 → 左子树的中序
右边部分 → 右子树的中序
在前序序列中,根之后的一段对应左子树,另一段对应右子树。
这样就能递归恢复二叉树。
得到树以后,再做一次后序遍历即可。
这里不详细叙述了。
有一道类似的题目:
已知后序遍历和中序遍历,求层次遍历:
PAT 1020 Tree Traversals
