通过具有一致性嵌入的大语言模型(LMMs)实现端到端乳腺癌放射治疗计划制定|文献速递-医学影像算法文献分享
Title
题目
End-to-end breast cancer radiotherapy planning via LMMs with consistencyembedding
通过具有一致性嵌入的大语言模型(LMMs)实现端到端乳腺癌放射治疗计划制定
01
文献速递介绍
近年来,受大型语言模型(LLM)启发的新一代人工智能模型(即基础模型)的出现,标志着其与以往范式存在显著差异(Moor 等人,2023)。这些模型具有规模庞大、功能多样的特点,这源于它们在多样化数据上进行的自监督训练。目前,这些基础模型已能够在多个领域实现最先进(SOTA)的性能,包括多模态推理、图文生成、图像 captioning 以及文本引导的图像分割等任务(Bubeck 等人,2023;Dai 等人,2024;Driess 等人,2023;Li 等人,2023b;Liu 等人,2024;Lai 等人,2024)。 这些特性意味着人工智能与医疗实践的融合可能迎来范式转变——医疗实践本身就依赖多模态信息来制定全面的临床决策。此外,这也为克服目前 500 多种经 FDA 批准的人工智能模型的局限性提供了契机,这些模型大多仅针对特定任务,且依赖单模态信息(Joshi 等人,2024)。具体而言,与这些单模态人工智能不同,结合基础模型的通用医疗人工智能能够全面理解临床工作流程,可接收多种医疗数据,包括影像模态、电子健康记录、实验室结果、基因组学数据,甚至临床报告(Singhal 等人,2023;Rajpurkar 和 Lungren,2023;Wu 等人,2023b;Moor 等人,2023;Tu 等人,2024)。通过理解各类数据及其相互关系,多模态人工智能能够提供患者数据的全面视图,从而助力更准确的诊断、个性化治疗方案的制定,并减少医疗差错。 本文聚焦的放射肿瘤学领域,多模态整合至关重要,使其成为评估基础模型潜力的最重要临床领域之一。因此,我们在此介绍 RO-LMM——一种专为支持放射肿瘤学临床工作流程设计的原型大型多模态模型(LMM)。具体而言,本研究显著扩展了我们先前的相关工作 LLMSeg(Oh 等人,2024),后者侧重于多模态分割。更具体地说,RO-LMM 通过处理放射肿瘤学中更广泛的临床任务,扩大了 LLMSeg 的应用范围:(1)它能将大量患者病史和检查结果高效总结为简洁且信息丰富的临床笔记;(2)能从临床专家视角提出合适的放射治疗策略;(3)在三维(3D)计算机断层扫描(CT)图像上勾画与所提放射治疗策略一致的放疗靶区。RO-LMM 的这种多方面功能,在支持临床专业人员的专业工作方面展现出显著进步。 在训练 LLM 执行从放疗策略建议到靶区分割的一系列连续任务时,我们发现每个任务都存在误差累积的可能性,这可能导致端到端性能的显著下降。因此,本研究的另一重要贡献是采用并扩展了噪声嵌入微调(NEFTune)技术(Jain 等人,2024),该技术在针对每个目标任务的训练过程中,会向嵌入中注入均匀噪声。更具体地说,为进一步增强模型的适用性,我们开发了一种新颖的一致性嵌入微调(CEFTune)技术,通过添加正则化损失来强制模型在噪声输入和干净输入下的预测保持一致。此外,通过扩展到文本相关任务之外,我们将这些概念应用于 3D 分割任务,提出了新颖的噪声嵌入分割(NESEG)和一致性嵌入分割(CESEG)技术。这些进展防止了后续任务之间的误差传播,共同显著提升了端到端模型在内部和外部验证中的泛化能力。 作为概念验证研究,我们的 RO-LMM 框架被应用于乳腺癌研究——乳腺癌是一种高发癌症,其放射治疗相对标准化,且仅需基于 CT 影像。我们的贡献可总结如下: - 提出了一个全面的框架 RO-LMM,其中 LMM 为乳腺癌放射治疗的广泛工作流程提供支持。据我们所知,该原型是首个支持放射肿瘤学全面工作流程的模型。 - 为防止在临床背景总结、放疗策略建议和基于计划的靶区分割等连续临床任务中可能出现的误差累积,我们探索了噪声增强和一致性方法,并提出了新颖的训练方法(如 CEFTune、NESEG 和 CESEG),显著增强了我们方法的稳健性。 - 通过在乳腺癌患者的真实临床数据上进行多种验证设置的实验,我们证明了 RO-LMM 的性能优于传统方法。
Abatract
摘要
Recent advances in AI foundation models have significant potential for lightening the clinical workload bymimicking the comprehensive and multi-faceted approaches used by medical professionals. In the field ofradiation oncology, the integration of multiple modalities holds great importance, so the opportunity offoundational model is abundant. Inspired by this, here we present RO-LMM, a multi-purpose, comprehensivelarge multimodal model (LMM) tailored for the field of radiation oncology. This model effectively managesa series of tasks within the clinical workflow, including clinical context summarization, radiotherapy strategysuggestion, and plan-guided target volume segmentation by leveraging the capabilities of LMM. In particular, toperform consecutive clinical tasks without error accumulation, we present a novel Consistency Embedding FineTuning (CEFTune) technique, which boosts LMM’s robustness to noisy inputs while preserving the consistencyof handling clean inputs. We further extend this concept to LMM-driven segmentation framework, leading to anovel Consistency Embedding Segmentation (CESEG) techniques. Experimental results including multi-centervalidation confirm that our RO-LMM with CEFTune and CESEG results in promising performance for multipleclinical tasks with generalization capabilities.
人工智能基础模型的最新进展具有巨大潜力,可通过模仿医疗专业人员采用的全面、多层面方法来减轻临床工作负担。在放射肿瘤学领域,多模态整合至关重要,因此基础模型的应用前景十分广阔。受此启发,我们提出了RO-LMM——一种专为放射肿瘤学领域设计的多功能、综合性大型多模态模型(LMM)。该模型借助LMM的能力,有效处理临床工作流程中的一系列任务,包括临床背景总结、放射治疗策略建议以及基于计划的靶区分割。 特别地,为了在执行连续临床任务时避免误差累积,我们提出了一种新颖的一致性嵌入微调(CEFTune)技术,该技术在增强LMM对噪声输入的稳健性的同时,保持了处理干净输入时的一致性。我们进一步将这一概念扩展到LMM驱动的分割框架中,形成了一种新颖的一致性嵌入分割(CESEG)技术。包括多中心验证在内的实验结果证实,结合了CEFTune和CESEG的RO-LMM在多项临床任务中表现出良好性能,并具备泛化能力。
Method
方法
In this section, we provide a detailed description of our proposedapproach designed for sequential text generation tasks, including summarization and suggestions, as well as text-driven image segmentation,whose robustness is improved by consistency embedding finetuning.The overall framework is illustrated in Fig. 2.
在本节中,我们将详细描述所提出的方法,该方法适用于连续的文本生成任务(包括总结和建议)以及文本驱动的图像分割任务,通过一致性嵌入微调增强了这些任务的稳健性。整体框架如图2所示。
Conclusion
结论
In this work, we introduce RO-LMM, a multi-purpose, comprehensive foundation model tailored for radiation oncology. Addressinglimitations in current medical AI models confined to specific tasks, ROLMM demonstrates proficiency in diverse tasks encompassing overallworkflow of radiation oncology: clinical report summarization, radiotherapy strategy suggestion, and plan-guided 3D target volume segmentation. Another key contribution of this work is the introductionof consistency technique into both text and segmentation task. Resultsfrom multi-center cohort datasets confirm RO-LMM’s promising performance and noteworthy generalization capabilities across diverse tasks.These findings mark a significant stride towards developing a versatileAI model, hinting at the potential for a multi-purpose medical AI modelin radiation oncology
在本研究中,我们介绍了RO-LMM——一种专为放射肿瘤学设计的多功能、综合性基础模型。为解决当前医疗人工智能模型局限于特定任务的问题,RO-LMM在放射肿瘤学的整体工作流程中展现出处理多种任务的能力,包括临床报告总结、放射治疗策略建议以及基于计划的三维靶区勾画。本研究的另一核心贡献是将一致性技术引入文本任务和分割任务中。来自多中心队列数据集的结果证实,RO-LMM在各类任务中均表现出良好性能,并具备显著的泛化能力。这些发现标志着在开发多功能人工智能模型方面迈出了重要一步,也为放射肿瘤学领域多功能医疗人工智能模型的发展潜力提供了启示。
Results
结果
5.1. Clinical report summarization
We present the performance of our model on the clinical reportsummarization task, along with confidence intervals for each method,in Table 2. Our fine-tuned model of RO-LMM-S demonstrate significant improvements over the Defaults, providing consistent margins inall metrics and confidence intervals. Notably, RO-LMM-S outperformsChatGPT with few-shot in-context learning.Moreover, we evaluate the generated summaries using expertisebased rubrics by two clinical experts and compare them to Defaults,including ChatGPT and LLaMa-2. As shown in Table 3, our RO-LMM-Smodel significantly outperforms all Defaults in both internal and external validations, thanks to its domain-specific knowledge. Additionally,Pearson correlation (𝑟) analysis reveals strong positive inter-cliniciancorrelations (> 0.85 and > 0.95 for internal and external validation,respectively), confirming the reliability of our rubrics and the clinicalrelevance of RO-LMM-S. Therefore, our RO-LMM-S provides practicaland meaningful summaries that can assist in the field of radiationoncology
5.1 临床报告总结 我们在表2中呈现了模型在临床报告总结任务上的性能,以及每种方法的置信区间。我们经过微调的RO-LMM-S模型相较于基准模型展现出显著提升,在所有指标和置信区间中均保持稳定优势。值得注意的是,RO-LMM-S的性能优于采用少样本上下文学习的ChatGPT。 此外,我们通过两位临床专家基于专业评分标准对生成的总结内容进行评估,并与包括ChatGPT和LLaMa-2在内的基准模型进行对比。如表3所示,得益于其领域特定知识,我们的RO-LMM-S模型在内部和外部验证中均显著优于所有基准模型。此外,皮尔逊相关系数(𝑟)分析显示,临床专家之间存在强正相关(内部验证>0.85,外部验证>0.95),这证实了我们评分标准的可靠性以及RO-LMM-S的临床相关性。因此,我们的RO-LMM-S能够提供实用且有意义的总结内容,可为放射肿瘤学领域提供辅助支持。
Figure
图
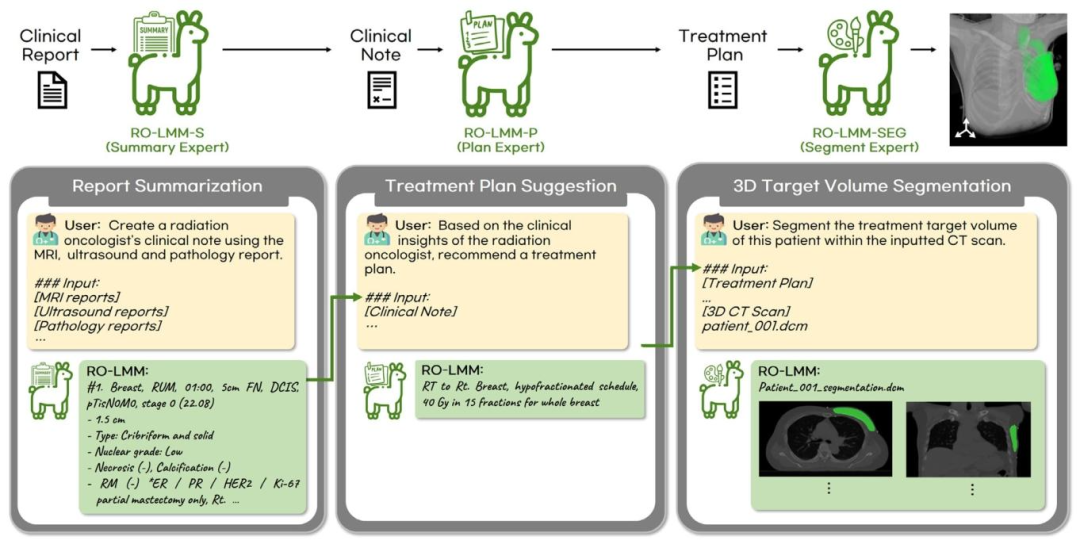
Fig. 1. RO-LMM as an assistant large multimodal model (LMM) in the field of radiation oncology. The model seamlessly covers various tasks such as clinical report summarization,radiation radiotherapy strategy suggestion, and 3D target volume segmentation.
图1. RO-LMM作为放射肿瘤学领域的辅助大型多模态模型(LMM) 该模型可无缝处理多项任务,包括临床报告总结、放射治疗策略建议以及三维靶区勾画。
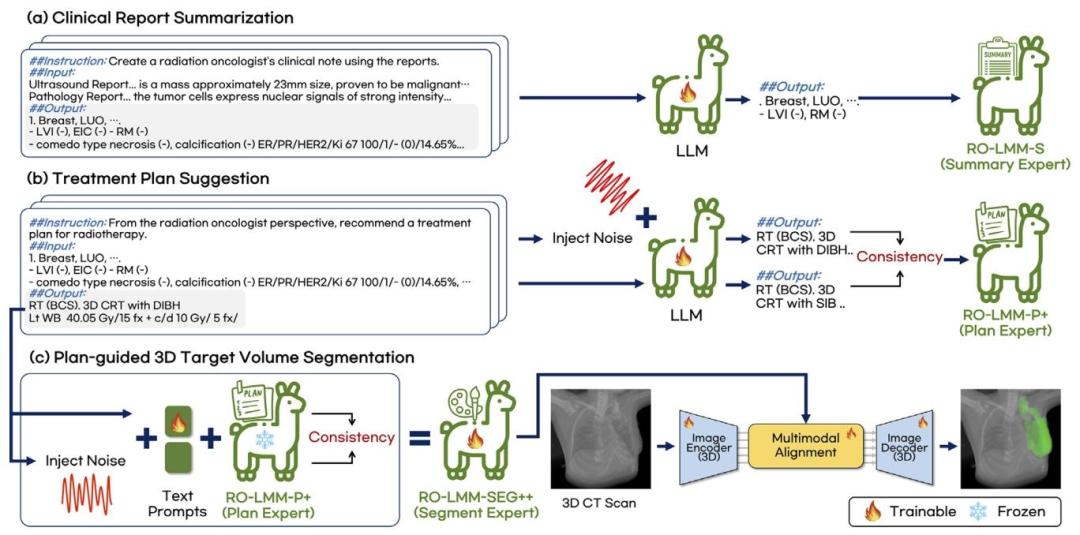
Fig. 2. Schematics of RO-LMM training for three different tasks. (a) RO-LMM-S for clinical note summarization. (b) RO-LMM-P++ for radiotherapy strategy suggestion. (c)RO-LMM-SEG++ for plan-guided target volume segmentation.
图2. RO-LMM针对三项不同任务的训练示意图 (a)用于临床笔记总结的RO-LMM-S; (b)用于放射治疗策略建议的RO-LMM-P++; (c)用于基于计划的靶区勾画的RO-LMM-SEG++。
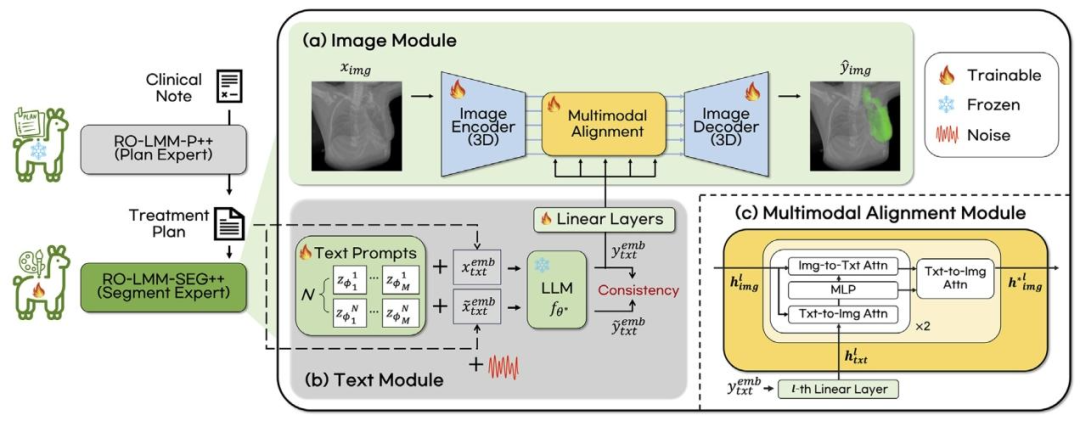
Fig. 3. Schematics of RO-LMM-SEG++ for plan-guided 3D target volume segmentation task, which composed of (a) image module and (b) text module. These module outputs arealigned through (c) multimodal alignment module
图3. 用于基于计划的三维靶区勾画任务的RO-LMM-SEG++示意图 该模型由(a)图像模块和(b)文本模块组成,两个模块的输出通过(c)多模态对齐模块实现对齐。
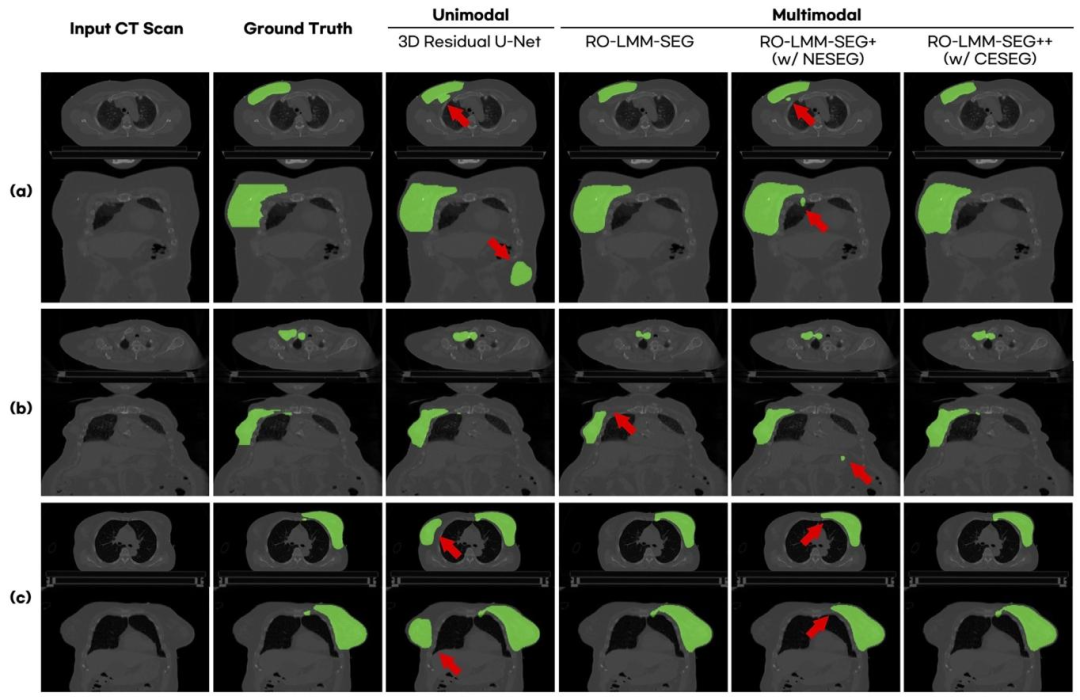
Fig. 4. Qualitative comparison on 3D target volume segmentation task. Red arrows indicate errors.
图4. 三维靶区勾画任务的定性对比 红色箭头指示错误区域。
Table
表
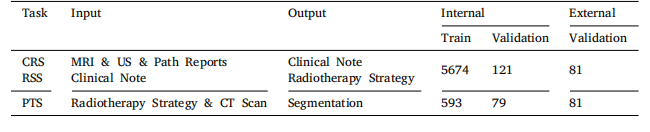
Table 1Training data details. CRS: Clinical Report Summarization. RSS: Radiotherapy StrategySuggestion. PTS: Plan-guided Target Segmentation. US: Ultrasound. Path: Pathology
表1 训练数据详情 CRS:临床报告总结 RSS:放射治疗策略建议 PTS:基于计划的靶区勾画 US:超声 Path:病理学
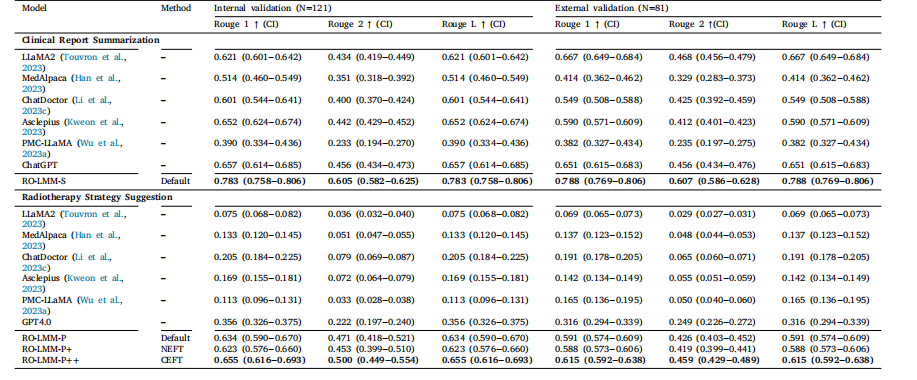
Table 2Quantitative comparison for clinical note summarization. Vanilla: the instruction fine tuning. CI: confidence interval
表2 临床笔记总结的定量对比 Vanilla:指令微调 CI:置信区间
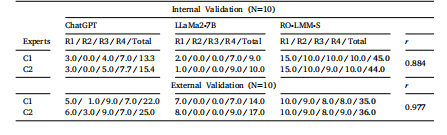
Table 3Clinical expert analysis for report summarization. R#: each rubric, C#:each clinicalexper.
表3 报告总结的临床专家分析 R#:各项评分标准 C#:各位临床专家
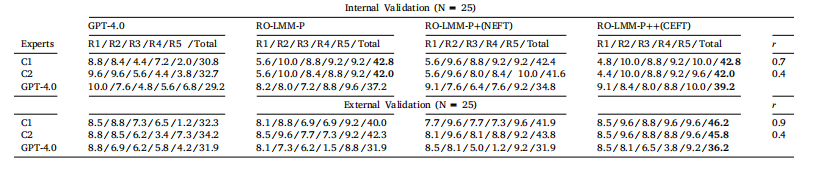
Table 4Clinical expert analysis for radiotherapy strategy suggestion. R#: each rubric, C#: each clinical expert.
表4 放射治疗策略建议的临床专家分析 R#:各项评分标准 C#:各位临床专家
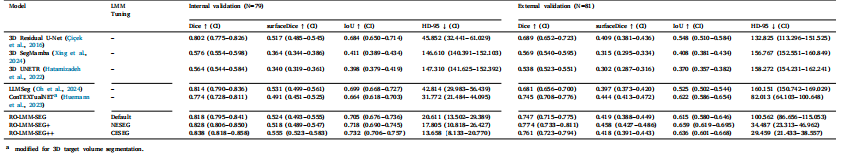
Table 5Comparison of 3D target volume segmentation performance
表5. 三维靶区勾画性能对比
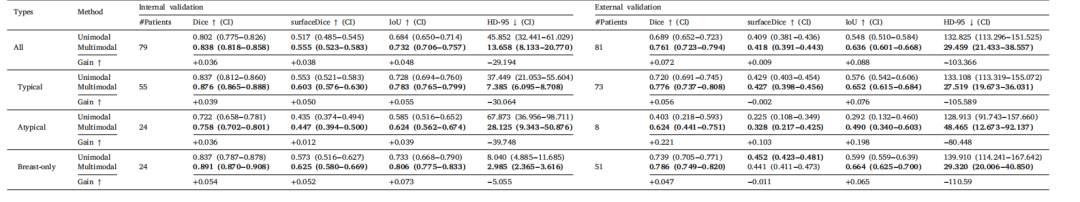
Table 6Comparison of 3D target segmentation performance for overall and specific patient types
表6 整体及特定患者类型的三维靶区勾画性能对比
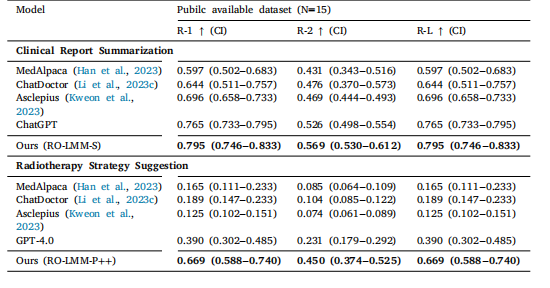
Table 7Quantitative comparison results for our RO-LMM’s clinical report summarization andradiotherapy strategy suggestion performance on the publicly available dataset.
表7 我们的RO-LMM在公开数据集上的临床报告总结和放射治疗策略建议性能的定量对比结果
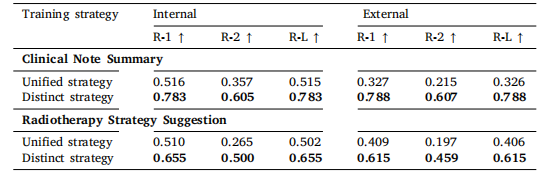
Table 8Ablation study on adopting separate expertise for each textual task against unifiedstrategy.
表8 针对每项文本任务采用独立专业知识与统一策略的消融研究
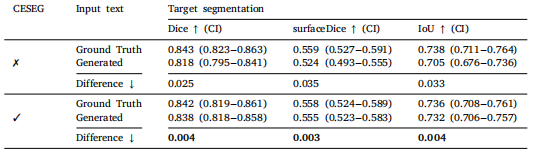
Table 9Ablation study on CESEG for target segmentation performance with input text variation.
表9 输入文本变化情况下,CESEG对靶区勾画性能的消融研究
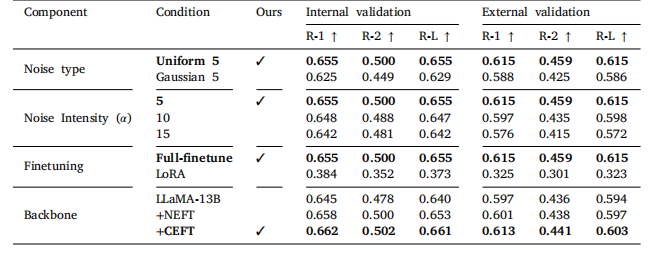
Table 10Component analysis of our proposed method on radiotherapy strategy suggestion..
表10 我们提出的方法在放射治疗策略建议方面的组件分析
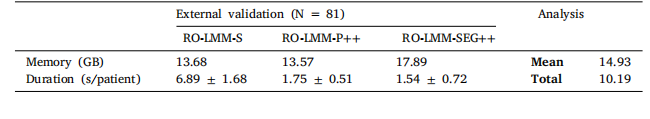
Table 11Inference computational complexity.
表11 推理计算复杂度
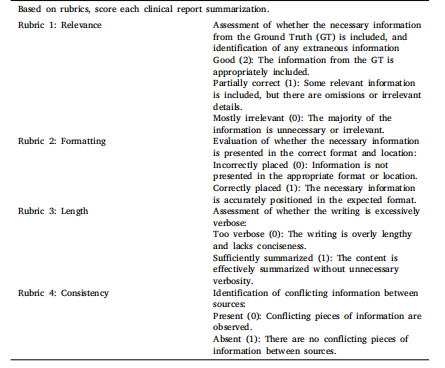
Table A.1The proposed expertise-based rubrics for assessing the performance of clinical reportsummarization.
表A.1 用于评估临床报告总结性能的基于专业知识的评分标准

Table A.2Score rubrics for radiotherapy strategy suggestion.
表A.2 放射治疗策略建议的评分标准
