语音大模型速览(三)- cosyvoice2
CosyVoice 2: Scalable Streaming Speech Synthesis with Large Language Models
- 论文链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2412.10117
- 代码链接:https://github.com/FunAudioLLM/CosyVoice
一句话总结
CosyVoice 2 是一款改进的流式语音合成模型,其核心创新包括采用有限标量量化(FSQ) 提升语音令牌的码本利用率,简化文本 - 语音语言模型架构以直接使用预训练大语言模型(如 Qwen2.5-0.5B)作为骨干,以及开发块感知因果流匹配模型,实现单一模型支持流式和非流式合成。通过在大规模多语言数据集(中文 130,000 小时、英文 30,000 小时等)上训练,该模型达到人类 parity 自然度,流式模式下响应延迟极低且合成质量几乎无损,在内容一致性(WER 低至 2.45%)、 speaker 相似度(最高 0.812)和语音质量(NMOS 达 3.96)上表现优异,同时支持情感、口音等精细指令控制。
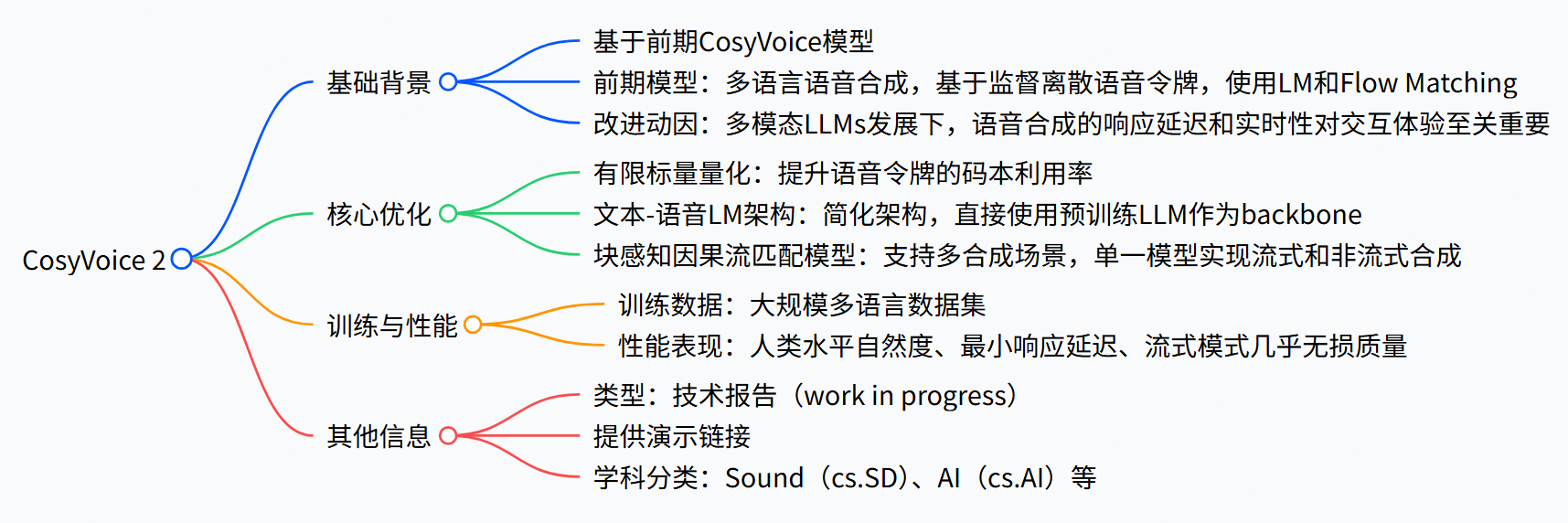
模型结构
核心创新





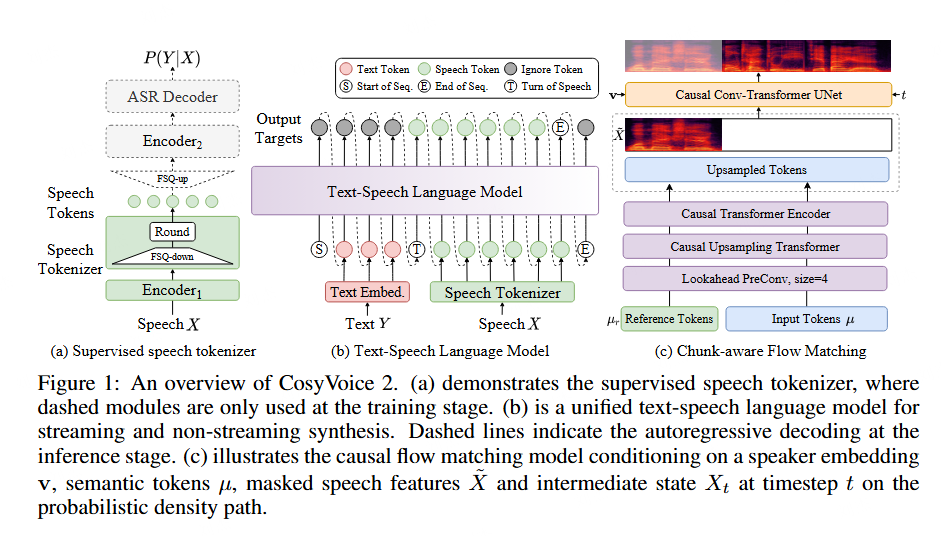
实验数据
核心代码块解读
语音token和文本token是如何兼容输入的
见cosyvoice/llm/llm.py
@torch.inference_mode()def inference(self,text: torch.Tensor,text_len: torch.Tensor,prompt_text: torch.Tensor,prompt_text_len: torch.Tensor,prompt_speech_token: torch.Tensor,prompt_speech_token_len: torch.Tensor,embedding: torch.Tensor,sampling: int = 25,max_token_text_ratio: float = 20,min_token_text_ratio: float = 2,uuid: str = '',) -> Generator[torch.Tensor, None, None]:device = text.devicetext = torch.concat([prompt_text, text], dim=1)print('text: ', text.shape, )text_len += prompt_text_lentext = self.llm.model.model.embed_tokens(text)# 3. concat llm_inputsos_eos_emb = self.llm_embedding.weight[self.sos_eos].reshape(1, 1, -1)task_id_emb = self.llm_embedding.weight[self.task_id].reshape(1, 1, -1)if prompt_speech_token_len != 0:prompt_speech_token_emb = self.speech_embedding(prompt_speech_token)else:prompt_speech_token_emb = torch.zeros(1, 0, self.llm_input_size, dtype=text.dtype).to(device)lm_input = torch.concat([sos_eos_emb, text, task_id_emb, prompt_speech_token_emb], dim=1)# 4. cal min/max_lengthmin_len = int((text_len - prompt_text_len) * min_token_text_ratio)max_len = int((text_len - prompt_text_len) * max_token_text_ratio)# 5. step by step decodefor token in self.inference_wrapper(lm_input, sampling, min_len, max_len, uuid):yield token
主要内容:
- 把prompt文本和输入文本拼接
text = torch.concat([prompt_text, text], dim=1) - 文本embedding映射
text = self.llm.model.model.embed_tokens(text) - speech prompt token 映射:
prompt_speech_token_emb = self.speech_embedding(prompt_speech_token) - token embedding映射后拼接:
lm_input = torch.concat([sos_eos_emb, text, task_id_emb, prompt_speech_token_emb], dim=1) - 输入到模型中,做 Next token prediction
怎么在 text prompt 里面做 instruct 的
见 cosyvoice/cli/frontend.py
def frontend_instruct2(self, tts_text, instruct_text, prompt_speech_16k, resample_rate, zero_shot_spk_id):model_input = self.frontend_zero_shot(tts_text, instruct_text + '<|endofprompt|>', prompt_speech_16k, resample_rate, zero_shot_spk_id)del model_input['llm_prompt_speech_token']del model_input['llm_prompt_speech_token_len']return model_input做法非常朴素,就是直接把 instruct_text + '<|endofprompt|>' 作为 prompt text 输入。值得注意的是,这种情况下,llm_prompt_speech_token 是会被删除的,那么如果音色和semantic token 不解耦的情况下,是否会导致一些音色不相似问题。
如何做文本音频混合流式
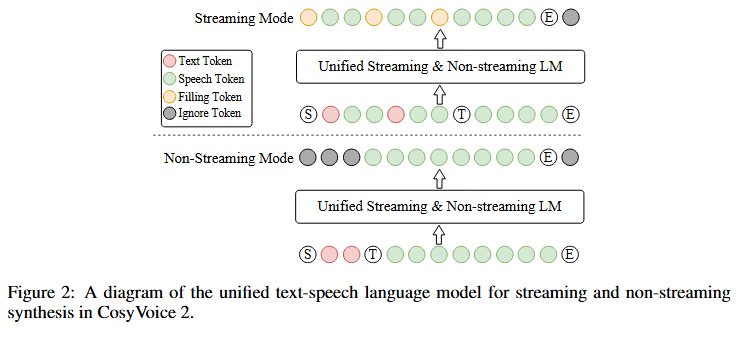
def prepare_lm_input_target(self, text_token, text_token_emb, text_token_len, speech_token, speech_token_emb, speech_token_len):lm_target, lm_input = [], []text_token = unpad_sequence(text_token, text_token_len.cpu(), batch_first=True)speech_token = unpad_sequence(speech_token, speech_token_len.cpu(), batch_first=True)text_token_emb = unpad_sequence(text_token_emb, text_token_len.cpu(), batch_first=True)speech_token_emb = unpad_sequence(speech_token_emb, speech_token_len.cpu(), batch_first=True)for i in range(len(text_token)):# bistream sequenceif random.random() < 0.5 and speech_token_len[i] / text_token_len[i] > self.mix_ratio[1] / self.mix_ratio[0]: # 满足音频大于text的倍数长度关系this_lm_target, this_lm_input = [], []this_lm_target.append(IGNORE_ID)this_lm_input.append(self.llm_embedding.weight[self.sos_eos].reshape(1, -1))for j in range(((text_token_len[i] + 1) / self.mix_ratio[0]).ceil().int().item()):this_text_token = text_token[i][j * self.mix_ratio[0]: (j + 1) * self.mix_ratio[0]].tolist() # 每mix_radio(5)个文本token切成一个块this_speech_token = speech_token[i][j * self.mix_ratio[1]: (j + 1) * self.mix_ratio[1]].tolist() # 每mix_radio(15)个语音token切成一个块if len(this_text_token) == self.mix_ratio[0]:assert len(this_speech_token) == self.mix_ratio[1]this_lm_target += [IGNORE_ID] * (self.mix_ratio[0] - 1)this_lm_target += this_speech_token # target: ignore_id * (5-1) + 15个语音tokenthis_lm_target.append(self.speech_token_size + 2) # target: + eosthis_lm_input.append(text_token_emb[i][j * self.mix_ratio[0]: (j + 1) * self.mix_ratio[0]]) # input: 5个文本token对应的embeddingthis_lm_input.append(speech_token_emb[i][j * self.mix_ratio[1]: (j + 1) * self.mix_ratio[1]]) # input: + 15个语音token对应的embeddingelse:# 处理最后一个文本token不足5个的情况this_lm_target += [-1] * len(this_text_token)this_lm_target += speech_token[i][j * self.mix_ratio[1]:].tolist()this_lm_target.append(self.speech_token_size)this_lm_input.append(text_token_emb[i][j * self.mix_ratio[0]:])this_lm_input.append(self.llm_embedding.weight[self.task_id].reshape(1, -1))this_lm_input.append(speech_token_emb[i][j * self.mix_ratio[1]:])# 整体上target是token, input是embeddingthis_lm_target, this_lm_input = torch.tensor(this_lm_target), torch.concat(this_lm_input, dim=0)# unistream sequenceelse:this_lm_target = torch.tensor([IGNORE_ID] * (1 + text_token_len[i]) + speech_token[i].tolist() + [self.speech_token_size])this_lm_input = torch.concat([self.llm_embedding.weight[self.sos_eos].reshape(1, -1), text_token_emb[i],self.llm_embedding.weight[self.task_id].reshape(1, -1), speech_token_emb[i]], dim=0)lm_target.append(this_lm_target)lm_input.append(this_lm_input)lm_input_len = torch.tensor([i.size(0) for i in lm_input], dtype=torch.int32)lm_input = pad_sequence(lm_input, batch_first=True, padding_value=IGNORE_ID)lm_target = pad_sequence(lm_target, batch_first=True, padding_value=IGNORE_ID)return lm_target, lm_input, lm_input_len
见 cosyvoice/llm/llm.py
chunk aware flow-matching
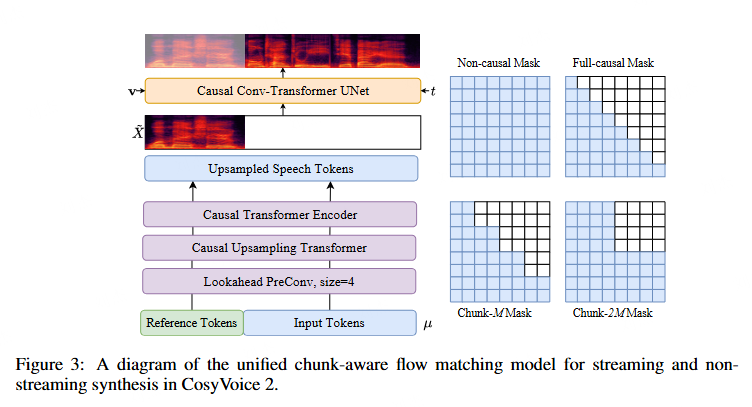
两个核心点:
- 由于 semantic token 到 mel 的映射使用的是因果的 transformer(即只能看到之前的信息,用 mask 实现的),所以可以用过 mask 来控制因果长度,即上图提到的 chunk mask
- 由于 flow-matching 需要多步计算,直接把 unet 做成多次循环,看为多步计算。
遗留问题
- instruct text 和 prompt text 的混用,只用
<|endofprompt|>标识做区分,模型会混淆吗?而且,llm_prompt_speech_token被删除,会导致音色一致性变差吗?(根本的问题是 semantic token 是否能跟音色完全解耦),这种设计是否需要优化,或者在训练模式上是否需要调整。 - 文本和音频按N:M的比例混合训练,这种方式是否是比较合理的方式,因为N:M不能保证音频和文本token一定对应,这是个问题。有没有更好的设计方式?
- chunk flow-matching 的训练设计比较麻烦,整体上有没有更简洁的方案?
